协议分析之搭建Ubuntu16.04下的Qt开发环境
1.完成虚拟机Ubuntu的搭建
2.完成函数库的安装(libpcap/libnet/libnids/libglib2.0)
3.完成Qt的安装
4.完成开发环境的测试(包括Qt运行的配置)
1.虚拟机的搭建
1.安装设置Ubuntu16.04的虚拟机:

2.安装Ubuntu系统:

3.安装VM Tools:
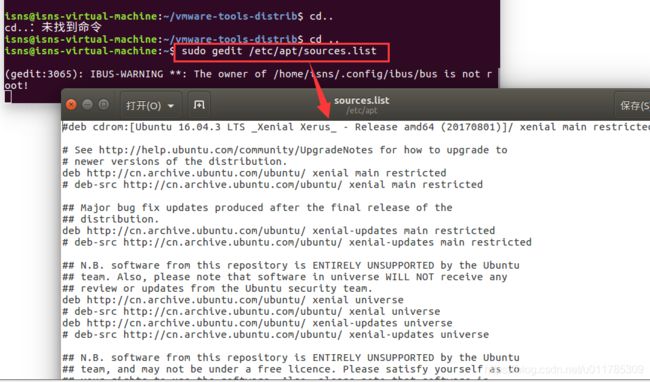
sudo gedit /etc/apt/sources.list
更新源:
sudo apt-get update

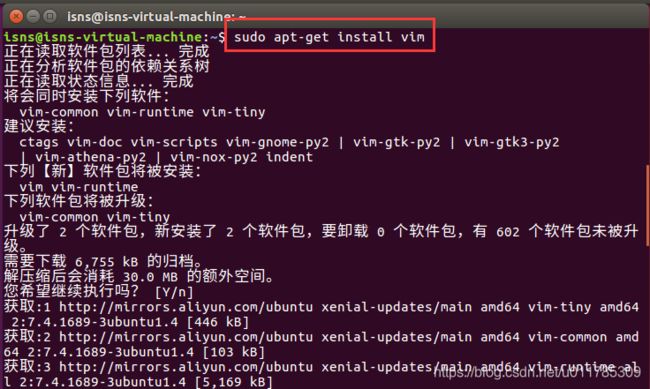
5.后面需要用vim文本编辑器修改配置文件,所以还要安装vim:
sudo apt-get install vim
- 需要提醒一下,我以前安装vim的时候都是失败的,需要安装vim-gtk版的才能成功。如果你安装不了vim的话,可以尝试一下vim-gtk。
sudo apt-get install vim-gtk
2.函数库的安装(libpcap/libnet/libnids/libglib2.0)
2.1 libpcap
2.1.1 libpcap简介
Libpcap是Packet Capture Libray的英文缩写,即数据包捕获函数库。该库提供的C函数接口用于捕捉经过指定网络接口的数据包,该接口应该是被设为混杂模式。这个在原始套接字中有提到。
著名的软件TCPDUMP就是在Libpcap的基础上开发而成的。Libpcap提供的接口函数实现和封装了与数据包截获有关的过程。
Libpcap提供了用户级别的网络数据包捕获接口,并充分考虑到应用程序的可移植性。Libpcap可以在绝大多数Linux平台上运行。在Windows平台上,也有一款与其功能类似的开发库:Wincap。
它的应用范围非常广泛,典型应用包括玩罗协议分析器,网络流量发生器,网络入侵检测系统,网络扫描器和其他安全工具。
它的工作在上层应用程序与网络接口之间。 主要功能:
- 数据包捕获:捕获流经网卡的原始数据包
- 自定义数据包发送:构造任何格式的原始数据包
- 流量采集与统计:采集网络中的流量信息
- 规则过滤:提供自带规则过滤功能,按需要选择过滤规则
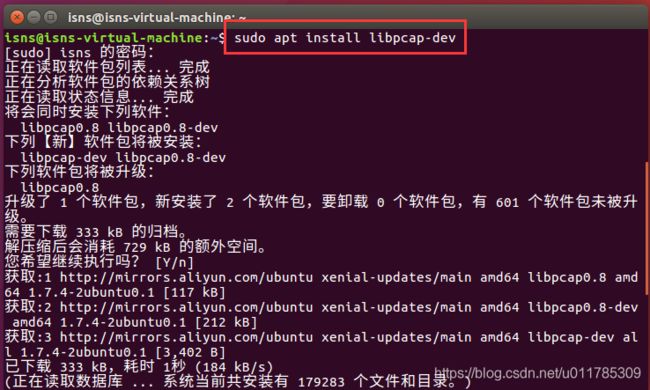
2.1.2 安装过程
sudo apt install libpcap-dev
2.2 libnet
2.2.1 libnet简介
libnet是一个小型的接口函数库,主要用C语言写成,提供了低层网络数据包的构造、处理和发送功能。
常用的接口函数和功能:
1.内存管理函数
单数据包内存初始化:
int libnet_init_packet(u_short packet_size, u_char **buf);
单数据包内存释放:
void libnet_destroy_packet(u_char **buf);
多数据包内存初始化:
int libnet_init_packet_arena(struct libnet_arena **arena,
u_short packet_num, u_short packet_size);
访问多数据包内存中的下一个数据包:
u_char *libnet_next_packet_from_arena(struct libnet_arena **arena,
u_short packet_size);
多数据包内存释放:
void libnet_destroy_packet_arena(struct libnet_arena **arena);
2.地址解析函数
解析主机名:
u_char *libnet_host_lookup(u_long ip, u_short use_name);
解析主机名(可重入函数):
void libnet_host_lookup_r(u_long ip, u_short use_name, u_char *buf);
域名解析:
u_long libnet_name_resolve(u_char *ip, u_short use_name);
获取接口设备IP地址:
u_long libnet_get_ipaddr(struct libnet_link_int *l,
const u_char *device, const u_char *ebuf);
获取接口设备硬件地址:
struct ether_addr *libnet_get_hwaddr(struct libnet_link_int *l,
const u_char *device,
const u_char *ebuf);
3.数据包构造函数
ARP协议数据包:
int libnet_build_arp(u_short hrdw, u_short prot, u_short h_len,
u_short p_len, u_short op, u_char *s_ha,
u_char *s_pa, u_char *t_ha, u_char *t_pa,
const u_char *payload, int payload_len,
u_char *packet_buf);
DNS协议数据包:
int libnet_build_dns(u_short id, u_short flags, u_short num_q,
u_short num_answ_rr, u_short num_auth_rr,
u_short num_add_rr, const u_char * payload,
int payload_len, u_char *packet_buf);
以太网协议数据包:
int libnet_build_ethernet(u_char *daddr, u_char *saddr, u_short id,
const u_char *payload, int payload_len,
u_char *packet_buf);
ICMP协议数据包(ICMP_ECHO / ICMP_ECHOREPLY):
int libnet_build_icmp_echo(u_char type, u_char code, u_short id,
u_short seq, const u_char *payload,
int payload_len, u_char *packet_buf);
ICMP协议数据包(ICMP_MASKREQ / ICMP_MASKREPLY):
int libnet_build_icmp_mask(u_char type, u_char code, u_short id,
u_short seq, u_long mask,
const u_char *payload, int payload_len,
u_char *packet_buf);
ICMP协议数据包(ICMP_UNREACH):
int libnet_build_icmp_unreach(u_char type, u_char code,
u_short orig_len, u_char orig_tos,
u_short orig_id, u_short orig_frag,
u_char orig_ttl, u_char orig_prot,
u_long orig_saddr, u_long orig_daddr,
const u_char *payload, int payload_len,
u_char *packet_buf);
ICMP协议数据包(ICMP_TIMEXCEED):
int libnet_build_icmp_timeexceed(u_char type, u_char code,
u_short orig_len, u_char orig_tos,
u_short orig_id, u_short orig_frag,
u_char orig_ttl, u_char orig_prot,
u_long orig_saddr, u_long orig_daddr,
const u_char *payload, int payload_len,
u_char *packet_buf);
ICMP协议数据包(ICMP_REDIRECT):
int libnet_build_icmp_redirect(u_char type, u_char code, u_long gateway,
u_short orig_len, u_char orig_tos,
u_short orig_id, u_short orig_frag,
u_char orig_ttl, u_char orig_prot,
u_long orig_saddr, u_long orig_daddr,
const u_char *payload, int payload_len,
u_char *packet_buf);
ICMP协议数据包(ICMP_TSTAMP / ICMP_TSTAMPREPLY):
int libnet_build_icmp_timestamp(u_char type, u_char code, u_short id,
u_short seq, n_time otime, n_time rtime,
n_time ttime, const u_char *payload,
int payload_len, u_char *packet_buf);
IGMP协议数据包:
int libnet_build_igmp(u_char type, u_char code, u_long ip,
const u_char *payload, int payload_len,
u_char *packet_buf);
IP协议数据包:
int libnet_build_ip(u_short len, u_char tos, u_short ip_id, u_short frag,
u_char ttl, u_char protocol, u_long saddr,
u_long daddr, const u_char *payload, int payload_len,
u_char *packet_buf);
OSPF路由协议数据包:
int libnet_build_ospf(u_short len, u_char type, u_long router_id,
u_long area_id, u_short auth_type,
const char *payload, int payload_s, u_char *buf);
OSPF路由协议数据包(Hello):
int libnet_build_ospf_hello(u_long netmask, u_short interval,
u_char options, u_char priority,
u_int dead_interval, u_long des_router,
u_long backup, u_long neighbor,
const char *payload, int payload_s,
u_char *buf);
OSPF路由协议数据包(DataBase Description (DBD)):
int libnet_build_ospf_dbd(u_short len, u_char options, u_char type,
u_int sequence_num, const char *payload,
int payload_s, u_char *buf);
OSPF路由协议数据包(Link State Request (LSR)):
int libnet_build_ospf_lsr(u_int type, u_int ls_id, u_long adv_router,
const char *payload, int payload_s,
u_char *buf);
OSPF路由协议数据包(Link State Update (LSU)):
int libnet_build_ospf_lsu(u_int num, const char *payload,
int payload_s, u_char *buf);
OSPF路由协议数据包(Link State Acknowledgement (LSA)):
int libnet_build_ospf_lsa(u_short age, u_char options, u_char type,
u_int ls_id, u_long adv_router,
u_int sequence_num, u_short len,
const char *payload, int payload_s,
u_char *buf);
OSPF路由协议数据包(OSPF Link Sate NetworkLink State Router):
int libnet_build_ospf_lsa_net(u_long netmask, u_int router_id,
const char *payload, int payload_s,
u_char *buf);
OSPF路由协议数据包(Link State Router):
int libnet_build_ospf_lsa_rtr(u_short flags, u_short num, u_int id,
u_int data, u_char type, u_char tos,
u_short metric, const char *payload,
int payload_s, u_char *buf);
OSPF路由协议数据包(Link State Summary):
int libnet_build_ospf_lsa_sum(u_long netmask, u_int metric, u_int tos,
const char *payload, int payload_s,
u_char *buf);
OSPF路由协议数据包(Link State AS External):
int libnet_build_ospf_lsa_as(u_long netmask, u_int metric,
u_long fwd_addr, u_int tag,
const char *payload, int payload_s,
u_char *buf);
RIP路由协议数据包:
int libnet_build_rip(u_char cmd, u_char ver, u_short domain,
u_short addr_fam, u_short route_tag, u_long ip,
u_long mask, u_long next_hop, u_long metric,
const u_char *payload, int payload_len,
u_char *packet_buf);
TCP协议数据包:
int libnet_build_tcp(u_short th_sport, u_short th_dport, u_long th_seq,
u_long th_ack, u_char th_flags, u_short th_win,
u_short th_urg, const u_char *payload,
int payload_len, u_char *packet_buf);
UDP协议数据包:
int libnet_build_udp(u_short sport, u_short dport, const u_char *payload,
int payload_len, u_char *packet_buf);
IP协议数据包选项:
int libnet_insert_ipo(struct ipoption *opt, u_char opt_len,
u_char *packet_buf);
TCP协议数据包选项:
int libnet_insert_tcpo(struct tcpoption *opt, u_char opt_len,
u_char *packet_buf);
4.数据包发送函数
打开raw socket:
int libnet_open_raw_sock(int protocol);
关闭raw socket:
int libnet_close_raw_sock(int socket);
选择接口设备:
int libnet_select_device(struct sockaddr_in *sin,
u_char **device, u_char *ebuf);
打开链路层接口设备:
struct libnet_link_int *libnet_open_link_interface(char *device,
char *ebuf);
关闭链路层接口设备:
int libnet_close_link_interface(struct libnet_link_int *l);
发送IP数据包:
int libnet_write_ip(int socket, u_char *packet, int packet_size);
发送链路层数据包:
int libnet_write_link_layer(struct libnet_link_int *l,
const u_char *device, u_char *packet,
int packet_size);
检验和计算:
int libnet_do_checksum(u_char *packet, int protocol, int packet_size);
5.相关的支持函数
随机数种子生成器:
int libnet_seed_prand();
获取随机数:
u_long libnet_get_prand(int modulus);
16进制数据输出:
void libnet_hex_dump(u_char * buf, int len, int swap, FILE *stream);
端口列表链初始化:
int libnet_plist_chain_new(struct libnet_plist_chain **plist,
char *token_list);
获取端口列表链的下一项(端口范围):
int libnet_plist_chain_next_pair(struct libnet_plist_chain *plist,
u_short *bport, u_short *eport);
端口列表链输出显示:
int libnet_plist_chain_dump(struct libnet_plist_chain *plist);
获取端口列表链:
u_char *libnet_plist_chain_dump_string(struct libnet_plist_chain *plist);
端口列表链内存释放:
void libnet_plist_chain_free(struct libnet_plist_chain *plist);
2.2.2 安装过程
sudo apt install libpnet-dev
2.3 libnids
2.3.1 libnids简介
Libnids 是一个用于网络入侵检测开发的专业编程接口,它使用了Libpcap所以它具有捕获数据包的功能。同时,Libnids提供了TCP数据流重组功能,所以对于分析基于TCP协议的各种协议Libnids都能胜任。Libnids还提供了对IP分片进行重组的功能,以及端口扫描检测和异常数据包检测功能。
一、基本常量
1.报警类型
enum
{
NIDS_WARN_IP =1, //IP数据包异常
NIDS_WARN_TCP,//TCP数据包异常
NIDS_WARN_UDP,//UDP数据包异常
NIDS_WARN_SCAN//表示有扫描攻击发生
}
enum
{
NIDS_WARN_UNDEFINED=0, //表示未定义
NIDS_WARN_IP_OVERSIZED.//表示IP数据包超长
NIDS_WARN_IP_INVLIST,//表示无效的碎片队列
NIDS_WARN_IP_OVERLAP,//表示发生重叠
NIDS_WARN_IP_HDR,//表示无效IP首部,IP数据包发生异常
NIDS_WARN_IP_SRR,//表示源路由IP数据包
NIDS_WARN_TCP_TOOMUCH,//表示tcp数据个数太多,因为在libnids中在同一时刻捕获的tcp个数最大值为tcp连接参数的哈希表长度3/4
NIDS_WARN_TCP_HDR,//表示无效TCP首部,TCP数据包发生异常
NIDS_WARN_TCP_BIGAQUEUE,//表示TCP接收的队列数据过多
NIDS_WARN_TCP_BADFLAGS//表示错误标记
}
2.Libnids状态
在对TCP数据流进行重组时,必须考虑到TCP的连接状态,在Libnids中为了方便开发而定义了6种Libnids状态(描述的是连接的逻辑状态)
#define NIDS_JUST_EST 1//表示tcp连接建立
#define NIDS_DATA 2 //表示接受数据的状态
#define NIDS_CLOSE 3 //表示tcp连接正常关闭
#define NIDS_RESET 4 //表示tcp连接被重置关闭
#define NIDS_TIMED_OUT 5 //表示由于超时tcp连接被关闭
#define NIDS_EXITING 6 //表示libnids正在退出
真正的TCP连接状态有11种
enum
{
TCP_ESTABLISHED=1, //表示ESTABLISH状态,TCP连接建立,开始传输数据
TCP_SYN_SENT,//表示syn_sent状态,主动打开
TCP_SYN_RECV,//表示syn_recv状态,接收SYN
TCP_FIN_WAIT1,//表示FIN_WAIT_1状态
TCP_FIN_WAIT2,//表示FIN_WAIT2状态
TCP_TIME_WAIT//表示TIME_WAIT状态
TCP_ClOSE,//表示Closed状态
TCP_CLOSE_WAIT,//表示CLose_WAIT状态
TCP_LAST_ACK,//表示LAST_ACK状态
TCP_LISTEN,//表示LISTEN状态
TCP_CLOSING//表示CLOSING 状态
}
3.校验和,与此相关的常量定义如下:
#define NIDS_DO_CHKSUM 0 //表示告诉Libnids要计算校验和
#define NIDS_DONT_CHKSUM 1//表示告诉LIbnids不需要计算校验和
二、数据结构
1.tuple4:
此数据结构是Libnids中最基本的一种数据结构struct tuple4
{
u_short source;//源端口
u_short dest;//目标端口
u_int saddr; //源IP
u_int daddr;//目的IP
};//用于描述一个地址端口对,它表示发送方IP和端口以及接收方IP和端口
2.half_stream:
此数据结构用来描述在tcp连接中一端的所有信息,可以使客户端也可以是服务端。struct half_stream
{
char state;//表示套接字的状态,也就是tcp连接状态
char collect;//表示是否存储数据到data中,如果大于0就存储,否则忽略
char collect_urg;//是否存储紧急数据到urgdata中,如果大于0就存储,否则忽略
char *data;//存储正常接收的数据
int offset;//存储在data中数据的第一个字节的偏移量
int count;//表示从tcp连接开始已经存储到data中的数据的字节数
int count_new;//表示有多少新数据寸到data 中
int bufsize;//
int rmem_alloc;
int urg_count;
u_int acked;
u_int seq;
u_int ack_seq;
u_int first_data_seg;
u_char urgdata;//用来存储紧急数据
u_char count_new_urg;//表示是否有新的紧急数据到达
u_char urg_seen;
u_int urg_ptr;
u_short window;
u_char ts_on;
u_int curr_ts;
struct skbuff *list;
struct skbuff *listtail;
}
3.tcp_stream:
描述的是一个TCP连接的所有信息struct tcp_stream
{
struct tuple4 addr;//是一个tuple4类型的成员,它表示一个tcp连接的四个重要信息
char nids_state;//表示逻辑连接状态
struct lurker_node *listeners;
struct half_stream client;
struct half_stream server;
struct tcp_stream *next_node;
struct tcp_stream *prev_node;
int hash_index;
struct tcp_stream *next_time;
struct tcp_stream *prev_time;
int read;
struct tcp_stream *next_free;
};//描述了一个TCP连接的完整信息
4.nids_prm:
描述libnids的一些全局参数信息struct nids_prm
{
int n_tcp_streams;//表示哈西表大小,此哈西表用来存放tcp_stream数据结构,
int n_hosts;//表示存放ip碎片信息的哈西表的大小
char *device;
char *filename;//用来存储网络数据捕获文件.如果设置了文件,与此同时就应该设置成员device为null,默认值为NULL
int
sk_buff_size;//表示数据结构sk_buff的大小.数据结构sk_buff是linux内核中一个重要的数据结构,是用来进行数据包队列操作的int
dev_addon;//表示在数据结构sk_buff中用于网络接口上信息的字节数,如果是-1(默认值),那么libnids会根据不同的网络接口进行修正void (*syslog)();//函数指针,默认值为nids_syslog()函数.在syslog中可以检测入侵攻击,如:网络扫描攻击
函数定义类型为nids_syslog(int type,int errnum,struct ip_header * iph,void
*data)int syslog_level;//表示日志等级,默认值为LOG_ALERT.
int scan_num_hosts;//表示存储端口扫描信息的哈西表的大小
int scan_delay;//表示在扫描检测中,两端口扫描的间隔时间
int scan_num_ports;//表示相同源地址必须扫描的tcp端口数目
void (*no_mem)(char *);//当libnids发生内存溢出时被调用
int
(*ip_filter)();//函数指针,此函数可以用来分析ip数据包,当有ip数据包到达时,此函数被调用.默认值为nids_ip_filter,该函数的定义如下:static int nids_ip_filter(struct ip * x,int len)
char *pcap_filter;//表示过滤规则
int promisc;//表示网卡模式,非0为混杂模式,否则为非混杂模式,默认值为1
int one_loop_less;//表示捕获数据返回的时间,以豪秒计算.默认值为1024
int pcap_timeout;
};
在Libnids中用nids_prm数据结构定义了一个全局变量nids_params,其定义和初始值如下:
struct nids_prm nids_params={
1040,//n_tcp_streams
256,//n_hosts
NULL,//device
NULL,//filename
168,//sk_buff_size
-1,//dev_addon
nids_syslog,//syslog()
LOG_ALERT,//syslog_level
256,//scan_num_hosts
3000,//scan_delay
10,//scan_num_prots
nids_no_mem,//no_mem()
nids_ip_filter,//ip_filter
NULL,//pcap_filter
1,//promisc
0,//one_loop_less
1024//pcap_timeout
}在使用Libnids开发程序时,可以首先对nids_params全局变量的值进行修改,这样对整个Libnids就全部有效
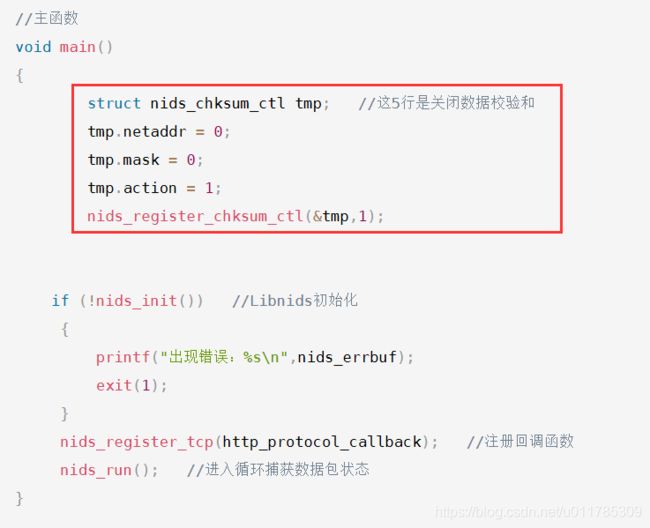
5.nids_chksum_ctl:
描述的是计算校验和struct nids_chksum_ctl
{
u_int netaddr;
u_int mask;
u_int
action;//表示动作,如果是NIDS_DO_CHKSUM,表示要计算校验和;如果是NIDS_DONT_CHKSUM表示不计算校验和u_int reserved;
}
三、Libnids函数
1.基本函数
(1)int nids_init(void);//对libnids进行初始化
(2)void nids_run(void);//运行Libnids,进入循环捕获数据包状态.
(3)int nids_getfd(void);//获得文件描述号
(4)int nids_dispatch(int cnt)//功能是调用Libpcap中的捕获数据包函数pcap_dispatch().
(5)int nids_next(void)//调用Libpcap中的捕获数据包函数pcap_next()
(6)void nids_register_chksum_ctl(struct nids_chksum_ctl *ptr,int
nr)//决定是否计算校验和,它是根据数据结构nids_chksum_ctl中的action进行决定的2.IP碎片函数
(1)void
nids_register_ip_frag(void(*))//此函数的功能是注册一个能够检测所有IP数据包的回调函数,包括IP碎片eg:nids_register_ip_frag(ip_frag_function);
这样就定义了一个回调函数ip_frag_function的定义类型如下:
void ip_frag_function(struct ip *a_packet,int len)
(2)void nids_register_ip(void(*))//此函数定义一个回调函数,此回调函数可以接受正常的IP数据包,eg:
nids_register_ip(ip_function);
此回调函数的定义类型如下:
void ip_function(struct ip * a_packet)
3.TCP数据流重组函数
(1)void nids_register_tcp(void(*))
回调函数的功能是注册一个TCP连接的回调函数,回调函数的类型定义如下:
void tcp_callback(struct tcp_stream *ns,void **param);
其中参数ns表示一个tcp连接的所有信息,它的类型是tcp_stream数据结构;参数param表示要传递的连接参数信息,可以指向一个TCP连接的私有数据
(2)void nids_killtcp(struct tcp_stream * a_tcp)//此函数功能是终止TCP连接
(3)void nids_discard(struct tcp_stream *a_tcp,int
num)//丢弃num字节TCP数据,用于存储更多的数据4.UDP注册函数
(1)void nids_register_udp(void(*));
此函数的功能注册一个分析UDP协议的回调函数,回调函数的类型定义如下:
void udp_callback(struct tuple4 *addr,char *buf,int len,struct ip *
iph);其中参数addr表示的是端口的信息,参数buf表示UDP协议负载数据内容,参数len
表示UDP负载数据的长度;参数iph表示一个IP数据包,包括IP首部,UDP首部以及UDP负载内容
四、利用Libnids开发的流程
用函数nids_init()进行初始化。
然后注册相应的回调函数。不同的回调函数实现不同的功能
最后利用函数nids_run()进入循环捕获数据包的状态。
2.3.2 安装过程
sudo apt install libnids-dev
2.4 libglib2.0
2.4.1 glib简介
glib库是Linux平台下最常用的C语言函数库,它具有很好的可移植性和实用性。
glib是Gtk +库和Gnome的基础。glib可以在多个平台下使用,比如Linux、Unix、Windows等。glib为许多标准的、常用的C语言结构提供了相应的替代物。
2.4.2 安装过程
sudo apt install libglib2.0-dev
3.Qt安装
3.1 Qt简介
Qt(官方发音 [kju:t],音同 cute)是一个跨平台C++图形用户界面应用程序开发框架。
Qt是用于台式机,嵌入式和移动设备的跨平台应用程序开发框架。支持的平台包括Linux,OS X,Windows,VxWorks,QNX,Android,iOS,BlackBerry,Sailfish OS等。
Qt本身并不是一种编程语言。它是用C ++编写的框架。预处理程序MOC(元对象编译器)用于扩展C ++语言,使其具有信号和插槽等功能。在编译步骤之前,MOC将解析使用Qt扩展C ++编写的源文件,并从中生成符合标准的C ++源。因此,框架本身和使用它的应用程序/库可以由任何符合标准的C ++编译器(如Clang,GCC,ICC,MinGW和MSVC)进行编译。
Qt带有自己的名为Qt Creator的集成开发环境(IDE)。它运行在Linux,OS X和Windows上,并提供智能代码完成,语法突出显示,集成的帮助系统,调试器和分析器集成,以及所有主要版本控制系统(例如git,Bazaar)的集成。除了Qt Creator,Windows上的开发人员还可以使用Qt的Visual Studio加载项。其他IDE(如KDevelop的关于KDE)也可以使用。但是,当然根本不强制使用任何IDE。
3.2 安装过程
sudo apt install qtcreator
sudo apt-get install build-essential
sudo apt-get install cmake qt5-default qtcreator

下好以后桌面上并没有出现Qt的图标,于是从启动器去查找程序。
方法是:点击桌面,按【Windows】键,搜索Qt:

为了下次方便,我们右键,将它锁定到启动器:
4.完成开发环境的测试(包括Qt运行的配置)
1.新建项目:

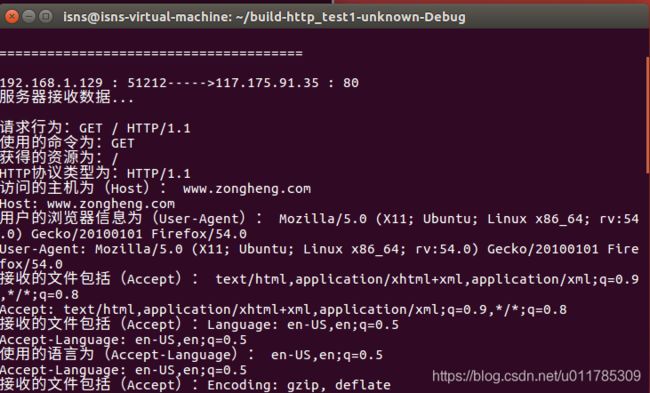
2.这里用之前写的HTTP协议抓包程序进行测试:
#include"nids.h" //Libnids的头文件,必须包含
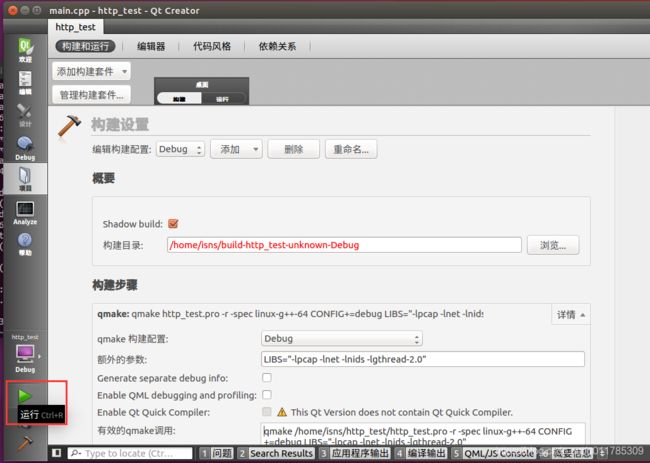
#include3.配置Qt运行额外的参数:
LIBS="-lpcap -lnet -lnids -lgthread-2.0"

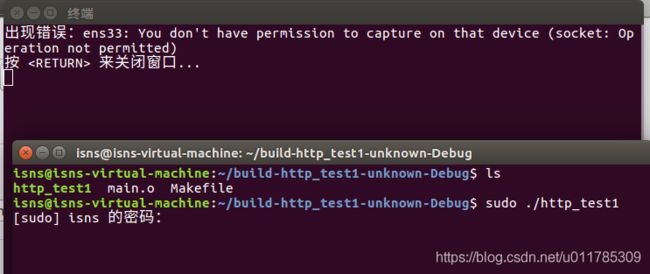
4.然后运行程序:
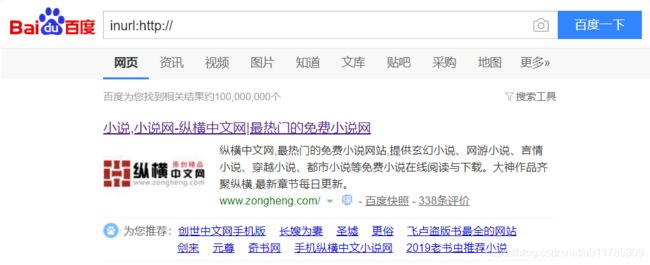
5.用虚拟机自带的浏览器去访问一个使用HTTP协议的URL。
用Google语法搜一下,找一个http的网站:
6.抓包成功: