计算机视觉——python3的SIFT与harris特征匹配及sift原理描述
python实现图像sift特征检测
sift特征包括兴趣点检测器和描述子,是过去十年中最成功的图像局部描述子之一。sift描述算子具有非常强的稳健性,而且sift特征对于尺度、旋转和亮度都具有不变性,十分突出的点不会因光照、尺度、旋转等因素的改变而消失。因此,它可用于三维视角和噪声的可靠匹配。总结前人的结论sift算子可解决的问题有:
• 目标的旋转、缩放、平移(RST)
• 图像仿射/投影变换(视点viewpoint)
• 弱光照影响(illumination)
• 部分目标遮挡(occlusion)
• 杂物场景(clutter)
• 噪声
*参考资料
(1)python计算机视觉编程
(2)相关sift算子博客讲解
*运行环境
(1)使用python3.7版本,用IDLE编写py文件
(2)下载安装vlfeat包,版本0.9.20 官方下载连接:http://www.vlfeat.org/download/(注意要下载20版本,不然会出现找不到.sift文件)
(3)下载完成过后,把vlfeat里win64里的vl.dll和sift.exe和vl.lib复制粘贴到项目目录下:这样子环境配置基本上已完成。
(一)SIFT算法原理(尺度不变特征变换)
1.兴趣点检测
关键点即是特征点,这些点是一些十分突出的点不会因光照、尺度、旋转等因素的改变而消失,比如角点、边缘点、暗区域的亮点以及亮区域的暗点。既然两幅图像中有相同的景物,那么使用某种方法分别提取各自的稳定点,这些点之间会有相互对应的匹配点。以下是怎么取图像关键点的思路:
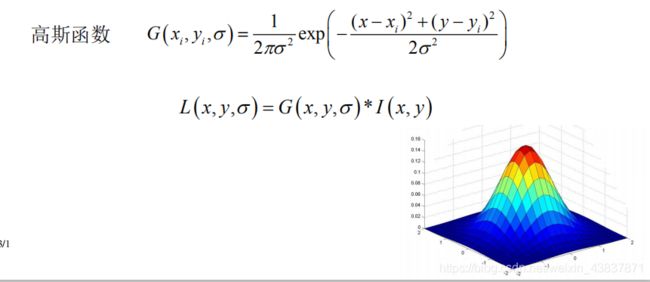
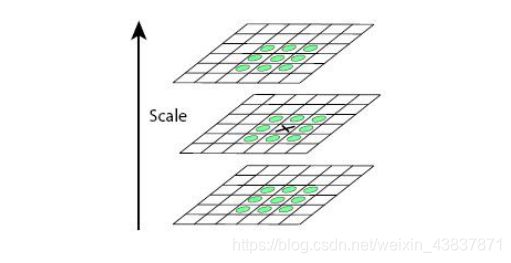
- 建立尺度空间:其主要思想是通过对原始图像进行尺度变换,获得图像多尺度下的空间表示。从而实现边缘、角点检测和不同分辨率上的特征提取,以满足特征点的尺度不变性。而高斯核唯一可以产生 多尺度空间的核,一个图像的尺度空间,L(x, y, σ) ,定义为原始图像 I(x, y)与一个可变尺度的2维高斯函数G(x, y, σ) 卷积运算。
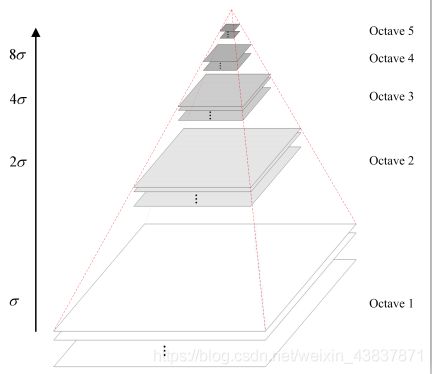
2.高斯金字塔:高斯金子塔的构建过程可分为两步:
(1)对图像做高斯平滑;
(2)对图像做降采样。
为了让尺度体现其连续性,在简单下采样的基础上加上了高斯滤波。一幅图像可以产生几组(octave)图像,一组图像包括几层
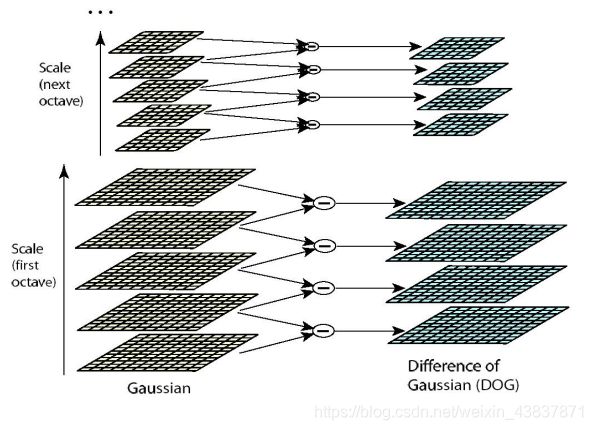
(interval)图像。sift特征是使用高斯差分函数来定位兴趣点,其中有用到高斯卷积滤波对图像进行噪声处理以及降低细节层次。标准差越大即尺度越大图像越模糊图像轮廓就越明显。在DoG高斯差分金字塔对应DOG算子,需构建DOG金字塔可以通过高斯差分图像看出图像上的像素值变化情况。(如果没有变化,也就没有特征。特征必须是变化尽可能多的点。)DOG图像描绘的是目标的轮廓。
例如:对一张图片进行高斯滤波处理和没有进行高斯滤波处理比较,没有进行高斯处图片细节虽然很清晰,但是轮廓不明显,而经过高斯处理过后松鼠的轮廓就比较突出明显,这样有利于特征提取。
Dog算子在检测关键点的时候需要检测出局部极值点,极值点的搜索是在DoG 金字塔内进行的,这些极值点就是候选的特征点。在搜索之前,我们需要在DoG 金字塔内剔除那些像素值过小的点,因为这些像素具有较低的对比度,它们肯定不是稳定的特征点。极值点的搜索不仅需要在它所在尺度空间图像的邻域内进行,还需要在它的相邻尺度空间图像内进行,是通过每一个像素点要和它所有的相邻点比较,看其是否比它的图像域和尺度域的相邻点大或者小。搜索的过程是这样的:从每组的第1 层开始,以第1 层为当前层,对第1 层的DoG 图像中的每个点取一个3×3×3 的立方体,立方体上下层分别为第0 层和第2 层。这样,搜索得到的极值点既有位置坐标(该点所在图像的空间坐标),又有尺度空间坐标(该点所在层的尺度)。当第1 层搜索完成后,再以第2 层为当前层,其过程与第1 层的搜索类似,以此类推。中间的检测点和它同尺度的8个相邻点和上下相邻尺度对应的9×2个点共26个点比较,以确保在尺度空间和二维图像空间都检测到极值点。但是由于Dog算子对图像边缘具有较强的边缘响应,所以要进行排除边缘响应,可以通过计算在该点位置尺度的2×2的Hessian矩阵得到,导数由采样点相邻差来估计。
最后通过下面方式得到关键点:
2.描述算子
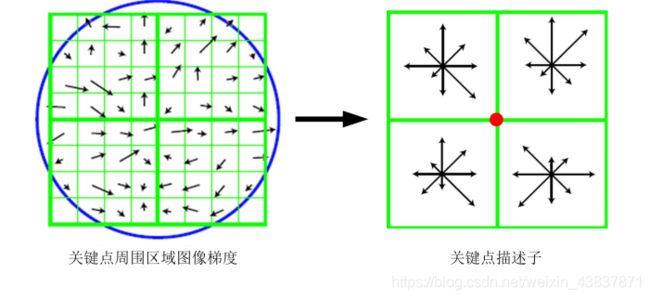
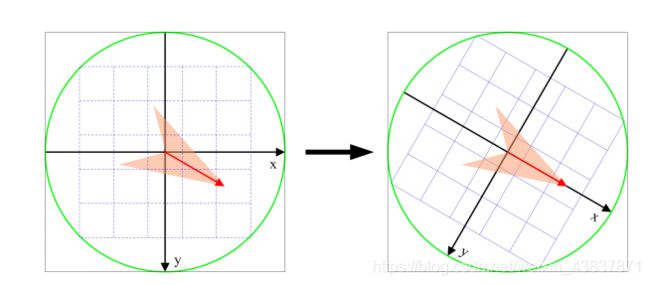
上面所述的兴趣点(关键点)位置描述子给出兴趣点的位置 和尺度信息,为了实现旋转不变性,基于每个点周围图像梯度的方向和大小,sift描述算子使用主方向描述参考方向,主方向使用直方图来衡量。sift描述算子在每个像素点附近选取子区域网格,在每个子区域计算图像梯度方向直方图,拼接起来组成描述算子向量。sift描述算子是由4*4个子区域,每个子区域有8个方向,会产生128个小区间直方图(4*4*8=128)也就是一张图像的每一个像素点都有128维的特征向量来唯一标识,即使方向有变换,也可以通过主方向来同步变换达到旋转不变性。
3.关键点匹配
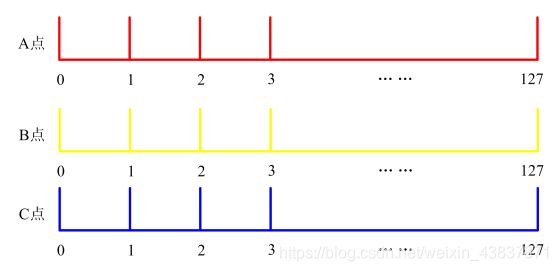
分别对模板图(参考图)和实时图(观测图)建立关键点描述子集合。目标的识别是通过两点集内关键点描述子的比对来完成具有128维的关键点描述子的相似性度量采用欧式距离。
关键点的匹配可以采用穷举法来完成,但是这样耗费的时间太多,一般都采用kd树(Kd树是一个平衡二叉树)的数据结构来完成搜索。搜索的内容是以目标图像的关键点为基准,搜索与目标图像的特征点最邻近的原图像特征点和次邻近的原图像特征点。
SIFT原理详解链接:https://blog.csdn.net/shouhuxianjian/article/details/46663699
(二)对两张图像进行简单的SIFT及Harris特征匹配
1.sift特征匹配
首先创建一个sift.py文件,把相应的函数写在里面。用IDLE写代码可能会出现找不到一些工具包,所以一定要导入vlfeat开源工具包提供的二进制文件计算图像的sift特征。
写sift.py文件的时候要记得导入另外一些包,以方便读取其他函数。
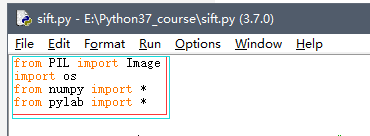
sift.py
from PIL import Image
import os
from numpy import *
from pylab import *
def process_image(imagename, resultname, params="--edge-thresh 10 --peak-thresh 5"):
""" 处理一幅图像,然后将结果保存在文件中"""
if imagename[-3:] != 'pgm':
#创建一个pgm文件
im = Image.open(imagename).convert('L')
im.save('tmp.pgm')
imagename ='tmp.pgm'
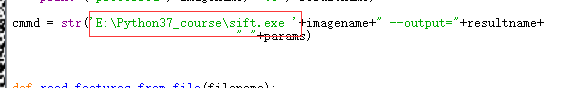
cmmd = str("sift "+imagename+" --output="+resultname+" "+params)
os.system(cmmd)
print ('processed', imagename, 'to', resultname)
def read_features_from_file(filename):
"""读取特征属性值,然后将其以矩阵的形式返回"""
f = loadtxt(filename)
return f[:,:4], f[:,4:] #特征位置,描述子
def write_featrues_to_file(filename, locs, desc):
"""将特征位置和描述子保存到文件中"""
savetxt(filename, hstack((locs,desc)))
def plot_features(im, locs, circle=False):
"""显示带有特征的图像
输入:im(数组图像),locs(每个特征的行、列、尺度和朝向)"""
def draw_circle(c,r):
t = arange(0,1.01,.01)*2*pi
x = r*cos(t) + c[0]
y = r*sin(t) + c[1]
plot(x, y, 'b', linewidth=2)
imshow(im)
if circle:
for p in locs:
draw_circle(p[:2], p[2])
else:
plot(locs[:,0], locs[:,1], 'ob')
axis('off')
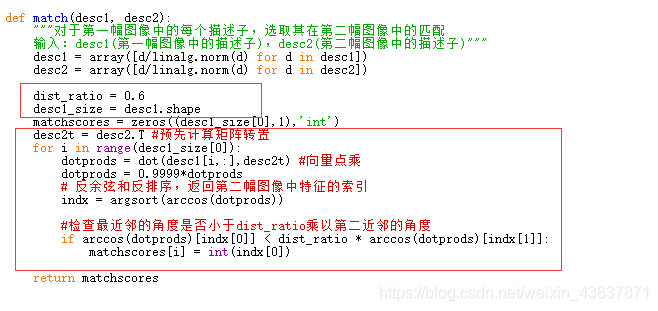
def match(desc1, desc2):
"""对于第一幅图像中的每个描述子,选取其在第二幅图像中的匹配
输入:desc1(第一幅图像中的描述子),desc2(第二幅图像中的描述子)"""
desc1 = array([d/linalg.norm(d) for d in desc1])
desc2 = array([d/linalg.norm(d) for d in desc2])
dist_ratio = 0.6
desc1_size = desc1.shape
matchscores = zeros((desc1_size[0],1),'int')
desc2t = desc2.T #预先计算矩阵转置
for i in range(desc1_size[0]):
dotprods = dot(desc1[i,:],desc2t) #向量点乘
dotprods = 0.9999*dotprods
# 反余弦和反排序,返回第二幅图像中特征的索引
indx = argsort(arccos(dotprods))
#检查最近邻的角度是否小于dist_ratio乘以第二近邻的角度
if arccos(dotprods)[indx[0]] < dist_ratio * arccos(dotprods)[indx[1]]:
matchscores[i] = int(indx[0])
return matchscores
def match_twosided(desc1, desc2):
"""双向对称版本的match()"""
matches_12 = match(desc1, desc2)
matches_21 = match(desc2, desc1)
ndx_12 = matches_12.nonzero()[0]
# 去除不对称的匹配
for n in ndx_12:
if matches_21[int(matches_12[n])] != n:
matches_12[n] = 0
return matches_12
def appendimages(im1, im2):
"""返回将两幅图像并排拼接成的一幅新图像"""
#选取具有最少行数的图像,然后填充足够的空行
rows1 = im1.shape[0]
rows2 = im2.shape[0]
if rows1 < rows2:
im1 = concatenate((im1, zeros((rows2-rows1,im1.shape[1]))),axis=0)
elif rows1 >rows2:
im2 = concatenate((im2, zeros((rows1-rows2,im2.shape[1]))),axis=0)
return concatenate((im1,im2), axis=1)
def plot_matches(im1,im2,locs1,locs2,matchscores,show_below=True):
""" 显示一幅带有连接匹配之间连线的图片
输入:im1, im2(数组图像), locs1,locs2(特征位置),matchscores(match()的输出),
show_below(如果图像应该显示在匹配的下方)
"""
im3=appendimages(im1,im2)
if show_below:
im3=vstack((im3,im3))
imshow(im3),title('SIFT特征匹配')
cols1 = im1.shape[1]
for i in range(len(matchscores)):
if matchscores[i]>0:
plot([locs1[i,0],locs2[matchscores[i,0],0]+cols1], [locs1[i,1],locs2[matchscores[i,0],1]],'c')
axis('off')
调用代码:
from PIL import Image
from pylab import *
import sys
import sift
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
if len(sys.argv) >= 3:
im1f, im2f = sys.argv[1], sys.argv[2]
else:
im1f = '01.jpg'
im2f = '04.jpg'
im1 = array(Image.open(im1f))
im2 = array(Image.open(im2f))
sift.process_image(im1f, 'out_sift_1.txt')
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('out_sift_1.txt')
figure()
gray()
subplot(121)
sift.plot_features(im1, l1, circle=False)
sift.process_image(im2f, 'out_sift_2.txt')
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file('out_sift_2.txt')
subplot(122)
sift.plot_features(im2, l2, circle=False)
#matches = sift.match(d1, d2)
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
print( '{} matches'.format(len(matches.nonzero()[0])))
figure()
gray()
sift.plot_matches(im1, im2, l1, l2, matches, show_below=True)
show()2.harris特征匹配
harris特征匹配基本思路与sift是一样的,只是sift是在harris之上进行的改进。harris对于旋转不变性匹配识别效果很差基本上会出现很多错误点匹配。而sift通过主方向梯度改变会达到很好的旋转不变性效果。
harris.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from scipy.ndimage import filters
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from numpy import *
def compute_harris_response(im,sigma=3):
""" Compute the Harris corner detector response function
for each pixel in a graylevel image. """
# derivatives
imx = zeros(im.shape)
filters.gaussian_filter(im, (sigma,sigma), (0,1), imx)
imy = zeros(im.shape)
filters.gaussian_filter(im, (sigma,sigma), (1,0), imy)
# compute components of the Harris matrix
Wxx = filters.gaussian_filter(imx*imx,sigma)
Wxy = filters.gaussian_filter(imx*imy,sigma)
Wyy = filters.gaussian_filter(imy*imy,sigma)
# determinant and trace
Wdet = Wxx*Wyy - Wxy**2
Wtr = Wxx + Wyy
return Wdet / Wtr
def get_harris_points(harrisim,min_dist=10,threshold=0.1):
""" Return corners from a Harris response image
min_dist is the minimum number of pixels separating
corners and image boundary. """
# find top corner candidates above a threshold
corner_threshold = harrisim.max() * threshold
harrisim_t = (harrisim > corner_threshold) * 1
# get coordinates of candidates
coords = array(harrisim_t.nonzero()).T
# ...and their values
candidate_values = [harrisim[c[0],c[1]] for c in coords]
# sort candidates (reverse to get descending order)
index = argsort(candidate_values)[::-1]
# store allowed point locations in array
allowed_locations = zeros(harrisim.shape)
allowed_locations[min_dist:-min_dist,min_dist:-min_dist] = 1
# select the best points taking min_distance into account
filtered_coords = []
for i in index:
if allowed_locations[coords[i,0],coords[i,1]] == 1:
filtered_coords.append(coords[i])
allowed_locations[(coords[i,0]-min_dist):(coords[i,0]+min_dist),
(coords[i,1]-min_dist):(coords[i,1]+min_dist)] = 0
return filtered_coords
def plot_harris_points(image,filtered_coords):
""" Plots corners found in image. """
figure()
gray()
imshow(image)
plot([p[1] for p in filtered_coords],
[p[0] for p in filtered_coords],'*')
axis('off')
show()
def get_descriptors(image,filtered_coords,wid=5):
""" For each point return pixel values around the point
using a neighbourhood of width 2*wid+1. (Assume points are
extracted with min_distance > wid). """
desc = []
for coords in filtered_coords:
patch = image[coords[0]-wid:coords[0]+wid+1,
coords[1]-wid:coords[1]+wid+1].flatten()
desc.append(patch)
return desc
def match(desc1,desc2,threshold=0.5):
""" For each corner point descriptor in the first image,
select its match to second image using
normalized cross correlation. """
n = len(desc1[0])
# pair-wise distances
d = -ones((len(desc1),len(desc2)))
for i in range(len(desc1)):
for j in range(len(desc2)):
d1 = (desc1[i] - mean(desc1[i])) / std(desc1[i])
d2 = (desc2[j] - mean(desc2[j])) / std(desc2[j])
ncc_value = sum(d1 * d2) / (n-1)
if ncc_value > threshold:
d[i,j] = ncc_value
ndx = argsort(-d)
matchscores = ndx[:,0]
return matchscores
def match_twosided(desc1,desc2,threshold=0.5):
""" Two-sided symmetric version of match(). """
matches_12 = match(desc1,desc2,threshold)
matches_21 = match(desc2,desc1,threshold)
ndx_12 = where(matches_12 >= 0)[0]
# remove matches that are not symmetric
for n in ndx_12:
if matches_21[matches_12[n]] != n:
matches_12[n] = -1
return matches_12
def appendimages(im1,im2):
""" Return a new image that appends the two images side-by-side. """
# select the image with the fewest rows and fill in enough empty rows
rows1 = im1.shape[0]
rows2 = im2.shape[0]
if rows1 < rows2:
im1 = concatenate((im1,zeros((rows2-rows1,im1.shape[1]))),axis=0)
elif rows1 > rows2:
im2 = concatenate((im2,zeros((rows1-rows2,im2.shape[1]))),axis=0)
# if none of these cases they are equal, no filling needed.
return concatenate((im1,im2), axis=1)
def plot_matches(im1,im2,locs1,locs2,matchscores,show_below=True):
""" Show a figure with lines joining the accepted matches
input: im1,im2 (images as arrays), locs1,locs2 (feature locations),
matchscores (as output from 'match()'),
show_below (if images should be shown below matches). """
im3 = appendimages(im1,im2)
if show_below:
im3 = vstack((im3,im3))
imshow(im3)
cols1 = im1.shape[1]
for i,m in enumerate(matchscores):
if m>0:
plot([locs1[i][1],locs2[m][1]+cols1],[locs1[i][0],locs2[m][0]],'c')
axis('off')
def imresize(im,sz):
""" Resize an image array using PIL. """
pil_im = Image.fromarray(uint8(im))
return array(pil_im.resize(sz))
调用代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from scipy.ndimage import filters
from harris import *
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
im1 = array(Image.open("6.jpg").convert("L"))
im2 = array(Image.open("12.jpg").convert("L"))
# resize to make matching faster
#im1 = imresize(im1, (im1.shape[1]/2, im1.shape[0]/2))
#im2 = imresize(im2, (im2.shape[1]/2, im2.shape[0]/2))
wid = 5
harrisim = compute_harris_response(im1, 5)
filtered_coords1 = get_harris_points(harrisim, wid+1)
d1 = get_descriptors(im1, filtered_coords1, wid)
harrisim = compute_harris_response(im2, 5)
filtered_coords2 = get_harris_points(harrisim, wid+1)
d2 = get_descriptors(im2, filtered_coords2, wid)
matches = match_twosided(d1, d2)
figure()
gray()
plot_matches(im1, im2, filtered_coords1, filtered_coords2, matches)
show()
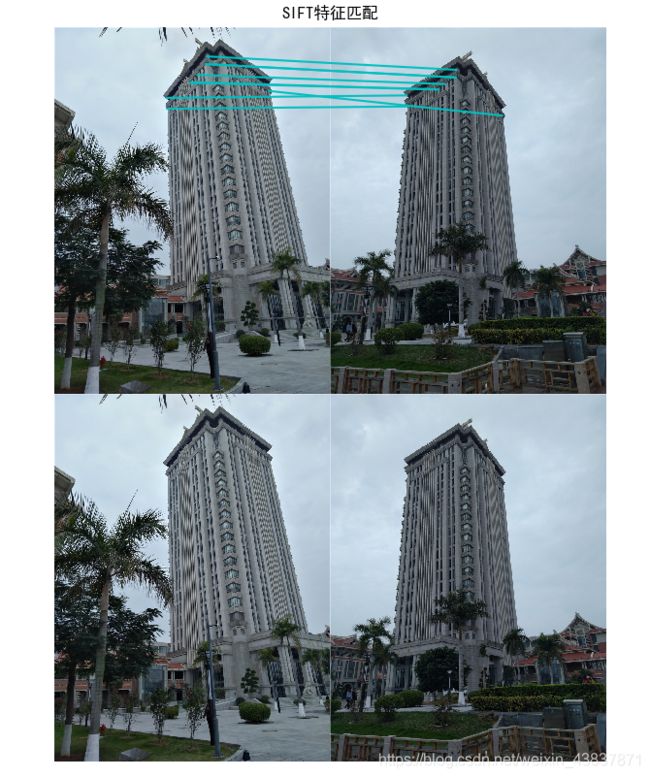
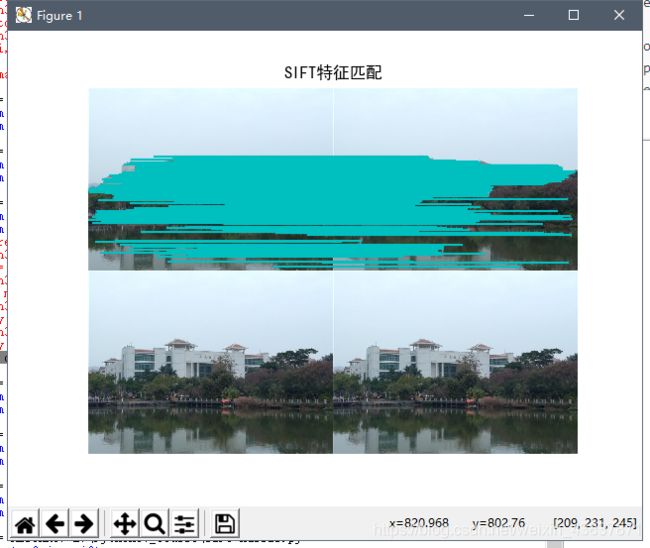
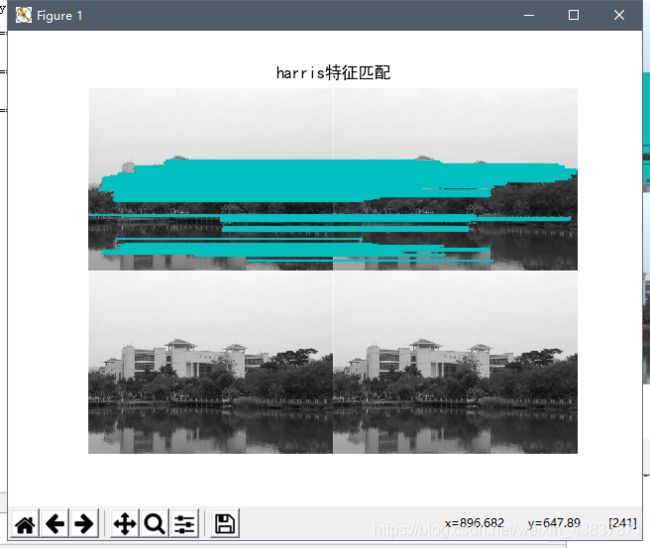
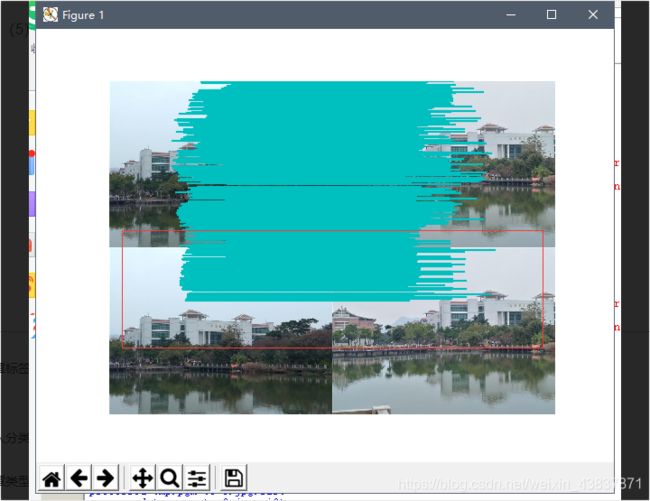
1.两张相同图像运行代码结果
对于同一张照片匹配效果来说,sift匹配出的特征点更多,而harris算法相对于会少一点,不过效果差不多。
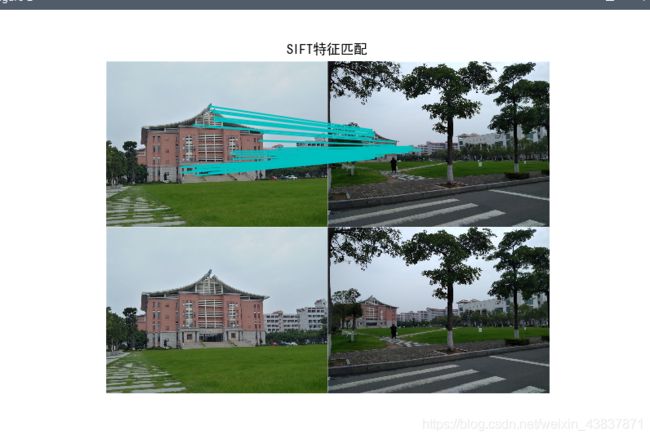
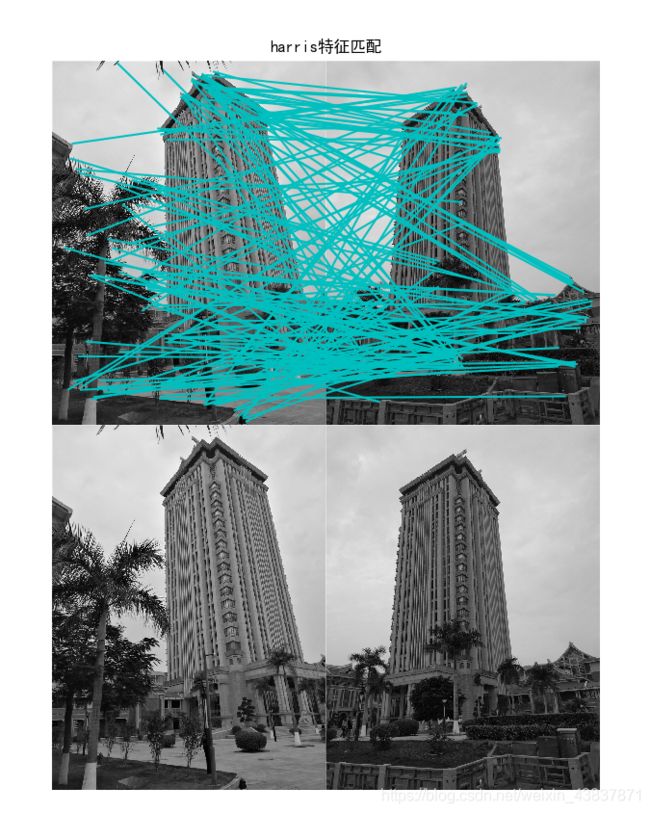
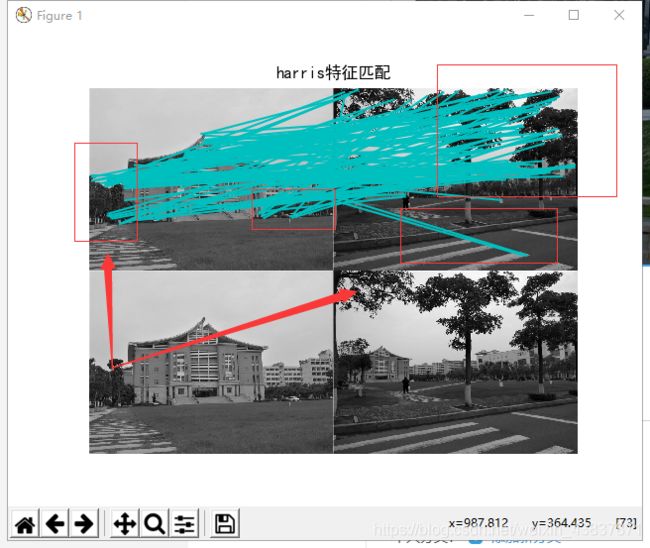
2.光照强度,角度不一样对比:
从以下结果可以说明harris对旋转角度识别性不大,基本上出现匹配点错误,虽然sift也有匹配错误点,但是相对来说不会随意匹配,从harris匹配线可看出,匹配线杂乱无章,不想sift算子位置一一平行对应。所以对于旋转角度过后sift算法会更适合图像匹配,不过对于像素点多而又没有旋转角度拍摄可以用harris来匹配,视觉效果可能会比较清晰,如果想匹配效果达到很高,建议还是使用sift算法匹配。
运行代码出现的问题情况:
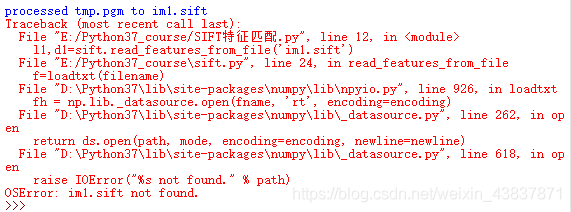
(1)会出现.sift文件找不到或出现sift文件为空和数组索引越界问题
解决方法:可能vlfeat下载了0.9.21版本,21版本里的win64里的文件可能会有改动或存在不兼容性,(1)重新下载0.9.20版本,把win64里的vl.dii,vl.lib,sift.exe放在项目目录下;一般这样操作后就能运行,(2)如果还是同样错误,就把sift.exe所在路径的目录复制到 process_image()函数里(注意不要出现中文字符,sift.exe后有一个空格);
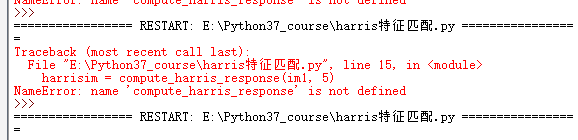
(2)如果有运行harris调用代码出现找不到harris.py文件里的函数
解决方法:可能你的头文件导入harris.py文件方法有错。不能直接向sift那样直接import harris
(3)输入的数组尺寸应该一样大
解决方法:把两张匹配图片的大小及像素设置成一样的(或者是一同一宽度比列转换高度)。如果大小改了还有错就是你的代码哪里多写了东西,一般都是主函数调用文件出错,导致运行出错。
(4)sift匹配链接出错
解决方法:这个可能是版本之间不兼容的问题,可能是你用了python2的代码用在python3里,去sift.py文件有关match函数的代码看一遍,有没有语法错误。如果你用的是《计算机视觉编程》这本书的代码,一般不会出错。
(5)sift匹配线超出图像范围
解决方法:出现这种问题,可能是match函数或者是plot_match函数与你配置出现不兼容问题。一般来说,没有改进的函数也是能运行的,但运行结果很慢。可能我的电脑有点问题导致出错,我尝试了很多种方法,发现都没用,在另外一篇博文发现一种match函数的改进方法可以解决错误:并且加快sift运行结果的速度,建议用改善的match函数来提取特征点。
原来的代码:
def match(desc1,desc2,threshold=0.5):
""" For each corner point descriptor in the first image,
select its match to second image using
normalized cross correlation. """
n = len(desc1[0])
# pair-wise distances
d = -ones((len(desc1),len(desc2)))
for i in range(len(desc1)):
for j in range(len(desc2)):
d1 = (desc1[i] - mean(desc1[i])) / std(desc1[i])
d2 = (desc2[j] - mean(desc2[j])) / std(desc2[j])
ncc_value = sum(d1 * d2) / (n-1)
if ncc_value > threshold:
d[i,j] = ncc_value
ndx = argsort(-d)
matchscores = ndx[:,0]
return matchscores改进的代码:
总的来说:(1)sift更适用于图像特征检测,旋转不变性较强、可以解决一些光线和亮度问题,且比harris灵活、匹配准确些。
(2)可以用改善过后的match函数运行sift会提高运行速度
(3)虽然sift算法能够解决旋转角度、光线亮度问题,但是也不是十分准确,对于旋转角度过大和光线亮度反差很大时,也会出现错误点匹配(甚至会出现找不到特征点),且sift算法对光线亮度方面没有旋转方面效果好。
参考博文:https://blog.csdn.net/zhuxiaoyang2000/article/details/53930610