Java IO流之BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream分析
简介
BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream都是缓冲流,缓冲流实际上里面有一个缓冲区,即字节数组,用流读取存储在硬盘上较大文件的时,频繁从硬盘中读取数据效率比较低,花费时间较长.缓冲流的作用就是将数据先读取到内存里面,然后从内存里面读取数据,读取速度得到很大的提升.
BufferedInputStrem介绍
1.构造方法
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) {this(in, DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);}
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size) {}- 无size参数的构造方法,创建的默认大小8192字节的字节数组.
- 有size的参数构造方法,创建的是指定size大小字节数组的缓冲输入流.
2.内部变量
protected volatile byte buf[];
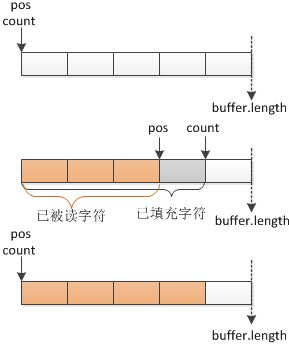
protected int count;
protected int pos;
protected int markpos = -1;
protected int marklimit;- buf---是缓冲输入流中的缓冲区,即字节数组buf.
- count---缓冲输入流里面的有效字节数.
- pos---缓冲区当前的位置.
- markpos---缓冲区标记的位置,当调用mark()方法的时候,会将缓冲区当前位置pos保存到markpos.
- marklimit---表示的是mark()方法标记后再调用reset()方法之前最多读取的字节.
3.内部方法
public synchronized int read() throws IOException {}
public synchronized int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {}
public synchronized long skip(long n) throws IOException {}
public synchronized int available() throws IOException {}
public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) {}
public synchronized void reset() throws IOException {}
public boolean markSupported() {}
public void close() throws IOException {}- read()---从缓冲区读取一个字节.
- read(byte b[],int off,int len)---将缓冲区的数据读取到字节数组b的off位置开始,长度为len.
- skip(long n)---跳过字节的数.
- available()---从输入流中可读取字节总数的估算值.
- mark(int readlimit)---对缓冲区当前位置pos,进行标记.并设置标记后可读取的最大值readlimit.
- markSupported()---是否支持标记.
- close()---关闭输入流.
BufferedOutputStream介绍
1.构造方法
public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out) { this(out, 8192);}
public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out, int size) {}- 无size的构造方法,创建默认大小为8192字节的缓冲输出流.
- 有size的构造方法,创建指定大小size的缓冲输出流.
2.内部变量
protected byte buf[];
protected int count;- buf---缓冲输出流中缓冲区,即为一字节数组buf.
- count----缓冲输出流中有效的字节数.
3.内部方法
public synchronized void write(int b) throws IOException {}
public synchronized void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {}
public synchronized void flush() throws IOException {}- write(int b)---将数据b写到缓冲数组buf中.
- write(byte b[],int off, int len)---将字节数组b中off索引开始,长度为len个字节写到缓冲区中.
- flush()---刷新缓冲区,将缓冲区里面的数据写到输出流中.
案例:
通过BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream复制,效率极大提高.
public class BufferedInputStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File source = new File("D:\\软件.zip");
File dest = new File("D:\\copy\\soft.zip");
copyFile(source, dest);
}
private static void copyFile(File source, File dest) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(source));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest));
byte buffer[] = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
bos.write(buffer);
}
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
}BufferedInputStream源码分析
public class BufferedInputStream extends FilterInputStream {
// 默认缓冲区的大小
private static int DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE = 8192;
// 缓冲字节数组可扩展到最大字节
private static int MAX_BUFFER_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
// 缓冲区为一个字节数组
protected volatile byte buf[];
// 返回的是一个原子更新器,保证字节数组buf操作是原子性的.
private static final AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater bufUpdater =
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater.newUpdater(BufferedInputStream.class, byte[].class, "buf");
// 缓冲区里面有效的字节数
protected int count;
// 缓冲区里面当前的位置索引
protected int pos;
// 缓冲区里面标记的位置,也就是最后一次调用mark()方法时,记录pos的值.调用reset()时会将pos值重置为markpos的值
protected int markpos = -1;
// marklimit是mark()标记后,在调用reset()之前可读取的最大的字节数,限制标记后buffer的最大值
protected int marklimit;
// 获取输入流,将输入流数据读取到缓冲区里面
private InputStream getInIfOpen() throws IOException {
InputStream input = in;
if (input == null)
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
return input;
}
// 获取缓冲字节数组
private byte[] getBufIfOpen() throws IOException {
byte[] buffer = buf;
if (buffer == null)
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
return buffer;
}
// 创建缓冲输入流,里面缓冲区是一字节数组,大小为默认的8192字节
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) {
this(in, DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);
}
// 创建缓冲输入流,并且指定缓冲区的大小
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size) {
super(in);
if (size <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0");
}
buf = new byte[size];
}
// 调用fill()方法将输入流中数据填充到缓冲区里面.
// 1.没标记的情况下,读完缓冲区数据,不再保存已被读取过的数据.
// 2.有标记的情况下,
// 1)标记的位置markpos>0,需要保存标记之后的数据,标签之前的数据可丢弃
// 2)标记的位置为0,而marklimit小于buffer.length,标记失效
// 3)标记的位置为0,而marklimit大于buffer.lenght,可以扩容buffer.
private void fill() throws IOException {
byte[] buffer = getBufIfOpen();
if (markpos < 0)
pos = 0; /* no mark: throw away the buffer */
else if (pos >= buffer.length) /* no room left in buffer */
if (markpos > 0) { /* can throw away early part of the buffer */
int sz = pos - markpos;
System.arraycopy(buffer, markpos, buffer, 0, sz);
pos = sz;
markpos = 0;
} else if (buffer.length >= marklimit) {
markpos = -1; /* buffer got too big, invalidate mark */
pos = 0; /* drop buffer contents */
} else if (buffer.length >= MAX_BUFFER_SIZE) {
throw new OutOfMemoryError("Required array size too large");
} else { /* grow buffer */
int nsz = (pos <= MAX_BUFFER_SIZE - pos) ? pos * 2 : MAX_BUFFER_SIZE;
if (nsz > marklimit)
nsz = marklimit;
byte nbuf[] = new byte[nsz];
System.arraycopy(buffer, 0, nbuf, 0, pos);
if (!bufUpdater.compareAndSet(this, buffer, nbuf)) {
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
}
buffer = nbuf;
}
count = pos;
int n = getInIfOpen().read(buffer, pos, buffer.length - pos);
if (n > 0)
count = n + pos;
}
// 此方法表示的是从缓冲区里面获取一个字节
public synchronized int read() throws IOException {
// 当缓冲区数据全部被读取完,会先填充缓冲区
if (pos >= count) {
fill();
if (pos >= count)
return -1;
}
return getBufIfOpen()[pos++] & 0xff;
}
// 将缓冲区的数据写到字节数组b里面,off是字节数组b的起始位置,长度为len
private int read1(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException {
int avail = count - pos;
// 缓冲区没有可读数据,如果要读取的字节数长度大于缓冲区长度,且没有标记的情况下
// 直接从输入流中读取字节
if (avail <= 0) {
if (len >= getBufIfOpen().length && markpos < 0) {
return getInIfOpen().read(b, off, len);
}
// 否则调用fill()填充缓冲区
fill();
avail = count - pos;
if (avail <= 0)
return -1;
}
// 实际能够读取的长度是avail
int cnt = (avail < len) ? avail : len;
// 缓冲区当前位置pos,复制cnt长度到字节数组b中
System.arraycopy(getBufIfOpen(), pos, b, off, cnt);
pos += cnt;
return cnt;
}
// 将缓冲区的数据写到字节数组b里面,off是字节数组的起始位置,长度为len
public synchronized int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
getBufIfOpen(); // Check for closed stream
if ((off | len | (off + len) | (b.length - (off + len))) < 0) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else if (len == 0) {
return 0;
}
int n = 0;
for (;;) {
int nread = read1(b, off + n, len - n);
//nread<=0,没有可读的字节数
if (nread <= 0)
return (n == 0) ? nread : n;
n += nread;
if (n >= len)
return n;
// if not closed but no bytes available, return
InputStream input = in;
if (input != null && input.available() <= 0)
return n;
}
} 关于缓冲输入流填充方法fill().存在多种情况,分析如下:
- count是从输入流读取数据填充到缓冲区有效字节数.
- pos是从缓冲区读取字节数据的当前位置.
- marklimit是调用mark()后,在调用reset()方法之前从缓冲区可读取的最大的字节数.
1.缓冲区没有标记的情况下,即markpos<0时,缓冲区中已被读取过的字节不需要保存.即pos>=count时,会将pos和count重置为0.然后从输入流读取数据填充缓冲区0到buffer.length之间的位置.
2.缓冲区标记的情况下.即markpos>=0情况下,
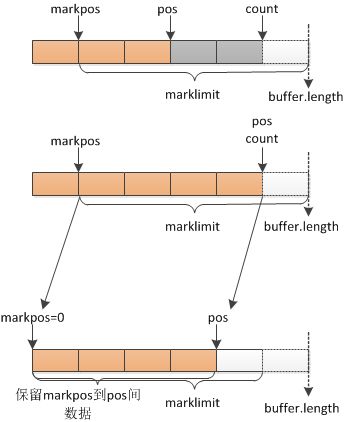
1)当markpos>0的时,下次刷新缓冲的时候,需要将markpos到pos之间数据保留.从输入流中读取数据填充pos到buffer.length之间的位置.如下图,当markpos>0时,并且pos>=buffer.length.下次读取输入流的里面数据的时候,会将markpos到pos之间的数据保存.
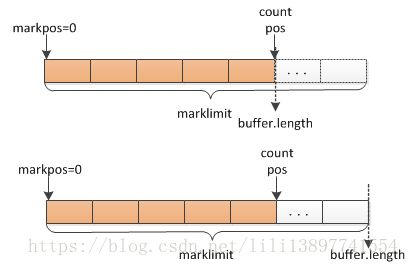
2)当markpos=0的时候,buffer.length>marklimit,并且pos>buffer.length表示的是缓冲区里面没有剩余的位置.如果继续保留markpos到pos之间数据,那么刷新缓冲区之后,缓冲区依旧没有剩余位置,因为pos>=buffer.length.缓冲区没有空出位置,所以marklimit存在意义就是进行一个限定,根据buffer.length与marklimit大小来判断标记是否失效.源码中buffer.length>=marklimit的时候,标记失效.缓冲区里面0到buffer.length之间的位置是空的.可以进行填充.
3)当markpos=0.buffer.length
如下,扩充后容量的是2*pos和marklimit中的最小值.扩容后缓冲区会保留原先0-pos之间的数据.然后从输入流继续读取数据.
BufferedOutputStream源码分析
public class BufferedOutputStream extends FilterOutputStream {
// 缓冲输出流中的缓冲区为字节数组
protected byte buf[];
// 缓冲区有效的数据大小
protected int count;
// 创建默认大小为8192字节的缓冲输出流
public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out) {
this(out, 8192);
}
// 创建指定大小size的缓冲输出流
public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out, int size) {
super(out);
if (size <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0");
}
buf = new byte[size];
}
// 将缓冲区里面有效字节数写到输出流out中
private void flushBuffer() throws IOException {
if (count > 0) {
out.write(buf, 0, count);
count = 0;
}
}
// 将数据b写到缓冲区里面
public synchronized void write(int b) throws IOException {
// 缓冲区已满情况下,会将数据写到输出流中
if (count >= buf.length) {
flushBuffer();
}
// 将字节b写到缓冲区里面
buf[count++] = (byte) b;
}
// 将数据写入到缓冲区里面
public synchronized void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
// 如果写入的长度大于缓冲区长度,先刷新缓冲区,将缓冲区所有的数据写到输出流out去
// 然后将要写入缓冲区的字节数组b,直接写到输出流
if (len >= buf.length) {
/*
* If the request length exceeds the size of the output buffer, flush the output buffer and then write the data
* directly. In this way buffered streams will cascade harmlessly.
*/
flushBuffer();
out.write(b, off, len);
return;
}
// 如果写入缓冲区的数据长度大于缓冲区剩余的长度,将缓冲区里面数据写到输出流
// 然后将字节数组b,起始位置off,长度为len数据写到缓冲区里面
if (len > buf.length - count) {
flushBuffer();
}
System.arraycopy(b, off, buf, count, len);
count += len;
}
// 刷新缓冲区,将缓冲区里面数据写到输出流中
public synchronized void flush() throws IOException {
flushBuffer();
out.flush();
}
}