Java 8 - 14 新特性和API ---持续更新ing
Java8:
默认接口实现:
在JDK1.7之前,只要是 interface 声明的,就是一个接口,里面的方法是public 并且不能有方法体的
但JDK1.8加入默认的实现,也就是 default
优点就是在不改变现有规则的情况下,加入扩展
JDK1.9:
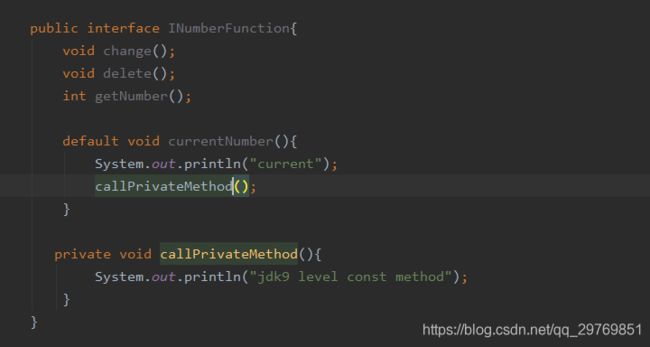
允许接口定义private的普通方法,可以在接口的default方法里调用,但可用性不大
Code:
public interface INumberFunction{
void change();
void delete();
int getNumber();
default void currentNumber(){
System.out.println("current");
callPrivateMethod();
}
private void callPrivateMethod(){
System.out.println("jdk9 level const method");
}
}
Predicate:
源码:
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package java.util.function;
import java.util.Objects;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Predicate {
boolean test(T var1);
default Predicate and(Predicate other) {
Objects.requireNonNull(other);
return (t) -> {
return this.test(t) && other.test(t);
};
}
default Predicate negate() {
return (t) -> {
return !this.test(t);
};
}
default Predicate or(Predicate other) {
Objects.requireNonNull(other);
return (t) -> {
return this.test(t) || other.test(t);
};
}
static Predicate isEqual(Object targetRef) {
return null == targetRef ? Objects::isNull : (object) -> {
return targetRef.equals(object);
};
}
static Predicate not(Predicate target) {
Objects.requireNonNull(target);
return target.negate();
}
}
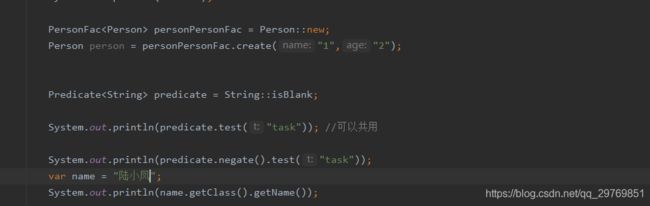
可以理解为一个比较器 常用方法 test() 返回一个boolean 值
negate() 取反比较(相比于test) 返回当前实例 可以链式调用
执行结果:
false
true
Function :
源码:
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package java.util.function;
import java.util.Objects;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Function {
R apply(T var1);
default Function compose(Function before) {
Objects.requireNonNull(before);
return (v) -> {
return this.apply(before.apply(v));
};
}
default Function andThen(Function after) {
Objects.requireNonNull(after);
return (t) -> {
return after.apply(this.apply(t));
};
}
static Function identity() {
return (t) -> {
return t;
};
}
}
函数式操作,学习这个需要对泛型(java1.5)有一定的了解,比如:
CallBack
List
List
List
Map
apply() :
Function function1 = integer -> integer*=3;
System.out.println(function1.apply(6));
输出结果:
18
compose:
private static void functionMethod() {
Function function1 = integer -> integer *= 3;
System.out.println(function1.apply(6));
Function function4 = integer -> integer *= 3;
System.out.println(function1.compose(function4).apply(6));
Function function2 = (user) -> user.substring(0, user.length() - 1);
System.out.println(function2.apply("那一年 风吹半夏"));
Function function3 = (person) -> person.getName().isBlank();
}
输出:
18
54
那一年 风吹半
supplier:
源码:
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package java.util.function;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Supplier {
T get();
}
可以看出只有一个get方法,可以理解为是一个抽象工厂模式,下面我们进行测试一下.
private static void supplier(){
Supplier sp = String::new;
System.out.println(sp.get());
Supplier personSupplier = Person::new;
Person person = personSupplier.get();
person.setName("陆小凤");
System.out.println(person.getName());
}
执行结果:
陆小凤
Consumer:源码:
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package java.util.function;
import java.util.Objects;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Consumer {
void accept(T var1);
default Consumer andThen(Consumer after) {
Objects.requireNonNull(after);
return (t) -> {
this.accept(t);
after.accept(t);
};
}
}
说明:主要是对入参做一些列的操作,在stream里,主要是用于forEach;内部迭代的时候,对传入的参数,做一系列的业务操作,没有返回值;
示例代码:
Consumer consumer = value ->{
value += 2;
System.out.println(value);
System.out.println(value % 2);
};
consumer.accept(10);
运行结果:
12
0
Optional : (接口)