LeetCode C++ 109. Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree【DFS/Linked List】中等
Given the head of a singly linked list where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height balanced BST.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1 .
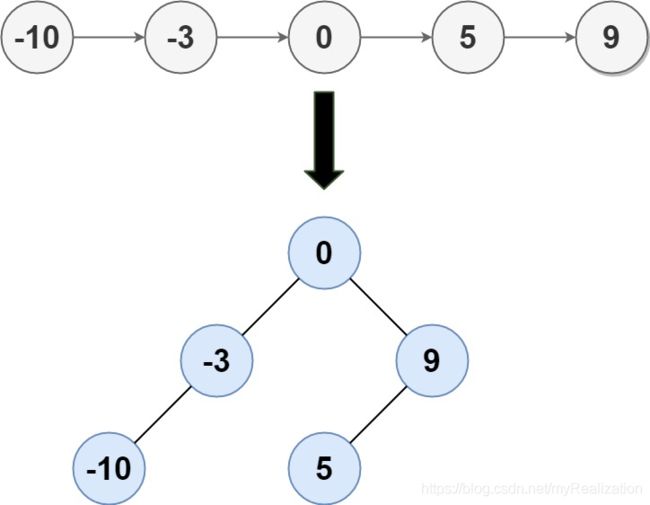
Input: head = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
Explanation: One possible answer is [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the shown height balanced BST.
Example 2:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [0]
Output: [0]
Example 4:
Input: head = [1,3]
Output: [3,1]
Constraints:
- The numner of nodes in
headis in the range[0, 2 * 10^4]. -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
题意:给出一个升序有序的单链表,将其转换成高度平衡的二叉搜索树。
思路:双指针+递归。两个指针,一快一慢,快的每次走两步,慢的每次走一步,当快指针遍历结束时,慢指针指向的也就是链表的中间位置,将其作为二叉搜索树当前结点的值。然后递归左右链表形成左右子树。注意:需要断开左右链表!
代码:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* sortedListToBST(ListNode* head) {
if(!head) return nullptr;
if(!head->next) return new TreeNode(head->val);
//找到链表的中点slow
ListNode *slow = head, fast = head, prev = head;
while(fast && fast->next){
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
//prev指向中间位置的前一个结点
while(prev->next != slow)
prev = prev->next;
//将中点左边的链表分开
prev->next = nullptr;
//递归建立子树
root = new TreeNode(slow->val);
root->left = sortedListToBST(head);
root->right = sortedListToBST(slow->next);
return root;
}
};
如果将寻找中点和前一个结点的过程结合起来,代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* sortedListToBST(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr) return nullptr;
if (head->next == nullptr) return new TreeNode(head->val);
//leftEnd指向mid的前一个结点, mid指向第二个结点
//按照快指针的走法, midNext此时应到第三个结点
ListNode *leftEnd = head, *mid = head->next, *midNext = mid->next;
while (midNext && midNext->next) {
leftEnd = leftEnd->next;
mid = mid->next;
midNext = midNext->next->next;
}
leftEnd->next = nullptr;
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(mid->val);
root->left = sortedListToBST(head);
root->right = sortedListToBST(mid->next);
return root;
}
};
效率:
执行用时:28 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了99.82% 的用户
内存消耗:24.1 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00% 的用户