OpenCL性能对比测试案例,合理使用clfinish()函数,充分发挥指令队列(commandqueue)特性。
用的公司的电脑,配置如下:
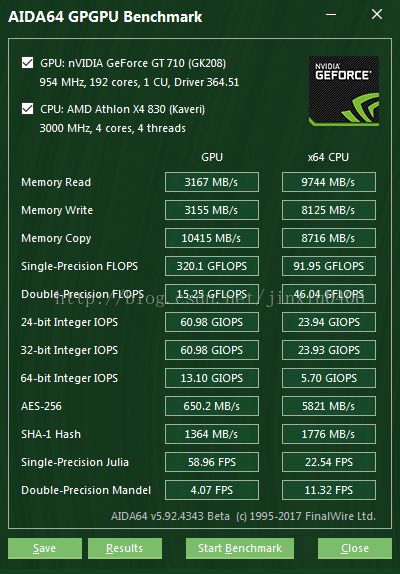
CPU: AMD Athlon X4 830 (3.0GHz 四核)
内存: 8GB
GPU: nVIDIA GT710 (0.954GHz 192cores 1CU)
显存: 1GB
上图,浮点性能测试。
CPU的 float 浮点性能 91.95GFlops。GPU为 320.1GFlops。浮点数计算 GPU领先 3倍多。
然而 这是面对简单计算任务的情况。算是理想性能,不是项目的实际情况。
----------------------------
下面上案例分析:这是一个矩阵加法的测试项目。水平有限,性能一般般。两个矩阵相加,重复1000次。评估单次计算的耗时。
///
/// func opencl特性测试,host to gpu 传输特性。
///
[TestMethod]
public void NC07_gpu()
{
string code = OpenCLMode.OCL.oclModel.LoadCode(filename);
oclm = new OpenCLMode.OCL.oclModel(code);
int i = 100, j = 100;
float[,] A = new float[i, j];
float[,] B = new float[i, j];
float[,] C = new float[i, j];
RandomData(A);//产生随机数据
RandomData(B);
Console.WriteLine("GPU Start:" + DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss:fff"));
Buffer A_Buffer = oclm.AddBufferWrite(A, "A");
Buffer B_Buffer = oclm.AddBufferWrite(B, "B");
NumpyCsharp_ocl nc = new NumpyCsharp_ocl(oclm);
oclBuffer re1 = null;
int loopcount = 1000;//重复一千次
var oA = new oclBuffer() { buffer = A_Buffer, x = i, y = j };
var oB = new oclBuffer() { buffer = B_Buffer, x = i, y = j };
TimeToolConsole ttc = new TimeToolConsole();
ttc.Begin();
for (int loop = 0; loop < loopcount; loop++)
{
re1 = nc.addTables("1", oA, oB);//调用GPU计算
}
TimeSpan tsend = ttc.End2();
string info = "单次用时(毫秒):" + ((double)tsend.Milliseconds / loopcount).ToString("F3");
Console.WriteLine(info);
C = oclm.ReadBuffer(re1);
Console.WriteLine("CPU Start:" + DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss:fff"));
ttc.Begin();
float[,] c2 = new float[i, j];
for (int loop = 0; loop < loopcount; loop++)
{
c2 = nc.addTables(A, B);//CPU计算,未使用多线程,未编译器优化
}
TimeSpan tsend2 = ttc.End2();
string info2 = "单次用时(毫秒):" + ((double)tsend2.Milliseconds / loopcount).ToString("F3");
Console.WriteLine(info2);
//------任务addTables [2*2]矩阵 1000次 -----------------------
//GPU Start:09:56:05:639
//Begin: 09:56:05.648 End: 09:56:05.876 length: 00:00:00.2271448
//单次用时(毫秒):0.227
//CPU Start:09:56:05:878
//Begin: 09:56:05.878 End: 09:56:05.878 length: 00:00:00.0007208
//单次用时(毫秒):0.000
//data err:09:56:05:878
//countError=0
//------任务addTables [100*100]矩阵 1000次 -----------------------
//GPU Start:09:54:08:347
//Begin: 09:54:08.440 End: 09:54:08.674 length: 00:00:00.2315641
//单次用时(毫秒):0.231
//CPU Start:09:54:08:674
//Begin: 09:54:08.674 End: 09:54:09.080 length: 00:00:00.4146318
//单次用时(毫秒):0.414
//data err:09:54:09:095
//countError=0
//GPU Start:09:58:20:588
//Begin: 09:58:20.600 End: 09:58:20.826 length: 00:00:00.2264199
//单次用时(毫秒):0.226
//CPU Start:09:58:20:828
//Begin: 09:58:20.828 End: 09:58:21.197 length: 00:00:00.3693399
//单次用时(毫秒):0.369
//data err:09:58:21:198
//countError=0
//------任务addTables [100*200] 1000次 -----------------------
//GPU Start:09:48:47:821
//Begin: 09:48:47.831 End: 09:48:48.065 length: 00:00:00.2338799
//单次用时(毫秒):0.233
//CPU
//Begin: 09:48:48.066 End: 09:48:48.808 length: 00:00:00.7424350
//单次约 0.742
//GPU取消了 clfinish(),性能提升
//------任务addTables [100*100] 1000次 -----------------------
//GPU Start:10:01:49:840
//Begin: 10:01:49.849 End: 10:01:49.896 length: 00:00:00.0461043
//单次用时(毫秒):0.046
//CPU Start:10:01:49:932
//Begin: 10:01:49.932 End: 10:01:50.311 length: 00:00:00.3787772
//单次用时(毫秒):0.378
//data err:10:01:50:312
//countError=0
int countError = 0;
for (int m = 0; m < c2.GetLength(0); m++)
{
for (int n = 0; n < c2.GetLength(1); n++)
{
if (Math.Abs(c2[m, n] - C[m, n]) > Math.Min(c2[m, n], C[m, n]) * 0.01)
{
countError++;
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("data err:" + DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss:fff"));
Console.WriteLine("countError=" + countError);
Assert.AreEqual(0, countError);
}
CPU部分代码
public float[,] addTables(float[,] t1, float[,] t2)
{
if (t1.GetLength(0) == t2.GetLength(0) && t1.GetLength(1) == t2.GetLength(1))
{
float[,] result = new float[t1.GetLength(0), t1.GetLength(1)];
for (int i = 0; i < t1.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < t1.GetLength(1); j++)
{
result[i, j] = t1[i, j] + t2[i, j];//简单的加法运算
}
}
return result;
}
else { return null; }
}
GPU部分代码
__kernel void AddTables_2D(__global float* output, __global float* t1, __global float* t2, int w, int h)
{
int i = get_global_id(0);
int j = get_global_id(1);
if (i >= w)
{
return;
}
output[i*h + j] = t1[i*h + j] + t2[i*h + j];
}可以看到 计算量小的时候 GPU用时 基本不变。[100*100]以下 用时均 0.2毫秒每次。
CPU随着任务量增加,耗时增加明显。
最后一个 [100*100]的矩阵计算,调整了 opencl模块 取消调用 clfinish()函数,使得GPU部分性能改善。
用时从 0.226 变为 0.046 毫秒每次,性能提升明显。
为何会有这种变化?opencl编程,需要从 CPU端将数据和计算指令放到GPU端,clfinish() 则是等待 GPU端完成后返回一个信号到 CPU,告诉cpu可以发送下一个任务指令。
这个交互过程中存在等待时机,有点浪费。取消等待后,CPU一次性将多个计算指令发送给GPU。例如:1000条矩阵加法的指令。opencl合理配置后,会逐条执行指令。不需要与cpu重复交互。
总结:在复杂计算任务时,应合理使用clfinish()函数,充分发挥opencl指令队列(commandqueue)的特性。
PS:在另一个机器学习的项目中,本人将 LSTM代码,改为了 opencl 执行。clfinish()函数 优化之前,是 9秒100次计算,优化后为 3.6秒100次计算,性能翻倍啊。
可见正确的编程,才能充分发挥计算机的性能。