【代码整理】微软官方Python进阶教程
视频地址:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1WT4y137cD?p=1
官方Github:https://github.com/microsoft/c9-python-getting-started
一、格式化和Linting
Linting
Pylint for Python
#windows
pip install pylint
Type hints
def get_greeting(name):
return 'Hello, ' + name
def get_greeting(name: str) -> str:
return 'Hello, ' + name
VScode中启用Linting(Ctrl+Shift+P)

写入不符合规范的代码后,会给出提示
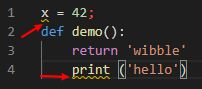
良好的格式和规范,有助于代码的可读性
二、Lambdas
示例(sort按照指定关键字排序):
def sorter(item):
return item['name']
presenters = [
{'name':'Susan','age':50},
{'name':'Christopher','age':47}
]
presenters.sort(key=sorter)
print(presenters)
使用Lambda
presenters = [
{'name':'Susan','age':50},
{'name':'Christopher','age':47}
]
presenters.sort(key=lambda item: item['name'])
print(presenters)
#self.name -- field
class Presenter():
def __init__(self,name):
#Constructor
self.name = name
def say_hello(self):
#method
print('Hello, ' + self.name)
presenter = Presenter('Chris')
presenter.name = 'Christopher'
presenter.say_hello()
改进,可以在输入后对其进行验证
#self.name -- field
class Presenter():
def __init__(self,name):
#Constructor
self.name = name
@property
def name(self):
print('In the getter')
return self.__name
@name.setter
def name(self,value):
print('In setter')
#在此处设置验证等
#cool validation here
self.__name = value
presenter = Presenter('Chris')
presenter.name = 'Christopher'
print(presenter.name)
四、Inheritance
示例1:
class Person:
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
def say_hello(self):
print('Hello, ' + self.name
class Student(Person):
def __init__(self,name,school):
#rules
super().__init__(name)
self.school = school
def sing_school_song(self):
print('Ode to ' + self.school)
student = Student('Christopher', 'UMD')
student.say_hello()
student.sing_school_song()
print(isinstance(student,Student))
print(f'Is this a student? {isinstance(student,Student)}')
print(isinstance(student,Person))
print(issubclass(Student,Person))
示例2(修改子类中继承的函数):
class Person:
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
def say_hello(self):
print('Hello, ' + self.name
class Student(Person):
def __init__(self,name,school):
#rules
super().__init__(name)
self.school = school
def sing_school_song(self):
print('Ode to ' + self.school)
def say_hello(self):
#Let the parent do some work
super().say_hello()
#Add on custom code
print('I am rather tired')
student = Student('Christopher', 'UMD')
student.say_hello()
示例3(__str__):
class Person:
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
def say_hello(self):
print('Hello, ' + self.name
class Student(Person):
def __init__(self,name,school):
#rules
super().__init__(name)
self.school = school
def sing_school_song(self):
print('Ode to ' + self.school)
def say_hello(self):
#Let the parent do some work
super().say_hello()
#Add on custom code
print('I am rather tired')
def __str__(self):
return f'{self.name} attends {self.school}'
student = Student('Christopher', 'UMD')
print student
五、Mixins(multiple inheritance)
示例:
class Loggable:
def __init__(self):
self.title = ''
def log(self):
print('Log message from ' + self.title)
class Connection:
def __init__(self):
self.server = ''
def connect(self):
print('Connecting to database on ' + self.server)
#framework
def framework(item):
#Perform the connection
if isinstance(item, Connection):
item.connect()
#Log the operation
if isinstance(item,Loggable):
item.log()
class SqlDatabase(Connection, Loggable):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.title = 'Sql Connection Demo'
self.server = 'Some Server'
class JustLog(Loggable):
def __init__(self):
self.title = 'Just logging'
#Create an instance of our class
sql_connection = SqlDatabase()
#Use our framework
framework(sql_connection)# connects and logs
#Just Log
just_log = JustLog()
framework(just_log)
六、Managing the file system
python3.6 – pathlib
# Grab the library
from pathlib import Path
#Where am i
cwd = Path.cwd()
print(cwd)
#Combine parts to create full path and file name
new_file = Path.joinpath(cwd,'new_file.txt')
print(new_file)
#Dose this exist?
print(new_file.exists())
Working with directories
from pathlib import Path
cwd = Path.cwd()
#Get the parent dir
parent = cwd.parent
#Is this a dir
print(parent.is_dir())
#Is this a file
print(parent.is_file())
#List child dirs
for child in parent.iterdir():
if child.is_dir():
print(child)
Working with files
from pathlib import Path
cwd = Path.cwd()
demo_file = Path(Path.joinpath(cwd, 'demo.txt'))
#Get the file name
print(demo_file.name)
#Get the extension
print(demo_file.suffix)
#Get the folder
print(demo_file.parent.name)
#Get the size
print(demo_file.stat().st_size)
七、Working with files
stream = open(file_name,mode,buffer_size)
#can we read?
print(stream.readable())
#read the first character
print(stream.read(1))
#read a line
print(stream.readline())
stream.close()
Writing to a file
stream = open('output.txt','wt')#write text
#write a single string
stream.write('H')
#write multiple strings---(list)
stream.writelines(['ello',' ','world'])
stream.write('\n')
stream.close()
Managing the stream
stream = open('output.txt','wt')
stream.write('demo!')
#Put the cursor back at the start
stream.seek(0)
stream.write('cool')#overwrite the file --> 'cool!'
#Write the data to file|刷新缓冲区,即使打开文件也可以看到内容变动
stream.flush()
#save file
stream.close()
八、cleanup with with
Re-writing with a try/finally
try:
stream = open('output.txt','wt')
stream.write('Lorem ipsum dolar')
finally:
stream.close()
Simplifying with with
with open('output.txt','wt') as stream:
stream.write('Lorem ipsum dolar')
九、Asynchronous operations
Python3.4
asyncio module 3.7 or higher
async def main():
start_time = default_timer()
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
two_task = asyncio.create_task(load_data(session,2))
three_task = asyncio.create_task(load_data(session,3))
#执行以上两个task,同时可以执行print
print('Doing other work')
#异步等待await,直到有一个返回值result再继续执行
two_result = await two_task
three_result = await three_task
elapsed_time = default_timer() - start_time
print(f'The operation took {elapsed_time:.2} seconds')
