Raft一致性框架_Copycat基础学习(一)
Copycat is a fault-tolerant state machine replication framework. Built
on the Raft consensus algorithm, it handles replication and
persistence and enforces strict ordering of inputs and outputs,
allowing developers to focus on single-threaded application logic. Its
event-driven model allows for efficient client communication with
replicated state machines, from simple key-value stores to wait-free
locks and leader elections. You supply the state machine and Copycat
takes care of the rest, making it easy to build robust, safe
distributed systems.
上面一段摘录于Copycat官网的介绍(http://atomix.io/copycat/),那么Copycat 是一个基于Raft一致性算法的编程框架,它能够为分布式应用中的状态提供一致性。本文主要基于Copycat官网给的示例进行学习.
1.首先在IDE里面创建一个maven工程,并在pom文件中加入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.atomix.copycatgroupId>
<artifactId>copycat-serverartifactId>
<version>1.1.4version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.atomix.copycatgroupId>
<artifactId>copycat-clientartifactId>
<version>1.1.4version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.atomix.catalystgroupId>
<artifactId>catalyst-nettyartifactId>
<version>1.1.1version>
dependency>2.自定义StateMachine以及Command
//自定了MapstateMachine,它继承框架提供的StateMachine类,MapstateMachine主要处理来自客户端的操作,如示例建的这个类,用于处理两个操作,put和get.put用于向map中写入键值,get用于获取值
public class MapstateMachine extends StateMachine implements Snapshottable {
//此为copycat-server需要维护的一致性数据结构,本例使用的是MAP
private Map map = new HashMap<>();
//定义对map的put操作
public Object put(Commit commit) {
try {
map.put(commit.operation().key(), commit.operation().value());
} finally {
commit.close();
}
return null;
}
//定义对map的get操作
public Object get(Commit commit) {
try {
return map.get(commit.operation().key());
} finally {
commit.close();
}
}
//以下两个方法来自于实现Snapshottable的接口,实现这个接口是用于copycat-server能够对本地状态日志进行压缩,并形成snapshot(快照),当copycat-server重启后,可以从快照恢复状态,如果有其它的server加入进来,可以将快照复制到其它server上.
@Override
public void snapshot(SnapshotWriter writer) {
writer.writeObject(map);
}
@Override
public void install(SnapshotReader reader) {
map = reader.readObject();
}
} GetQuery类
package com.xkx.common;
import io.atomix.copycat.Query;
//定义对MapstateMachine查询的命令
public class GetQuery implements Query<Object> {
private final Object key;
public GetQuery(Object key){
this.key = key;
}
public Object key(){
return key;
}
}PutCommand类
package com.xkx.common;
import io.atomix.copycat.Command;
public class PutCommand implements CommandPutCommand和GetQuery类都实现Command接口.
3.最后定义服务器端和客户端,copycat_server这里我们实现3个,copyCat_server-1,copyCat_server-2,copyCat_server-3。它们共同组成一个cluster.这里我们通过copyCat_server-2,copyCat_server-3 join到copyCat_server-1的方式形成cluseter
copyCat_server-1 实现
package com.xkx.myCopycat;
import com.xkx.common.GetQuery;
import com.xkx.common.MapstateMachine;
import com.xkx.common.PutCommand;
import io.atomix.catalyst.transport.Address;
import io.atomix.catalyst.transport.netty.NettyTransport;
import io.atomix.copycat.server.CopycatServer;
import io.atomix.copycat.server.storage.Storage;
import io.atomix.copycat.server.storage.StorageLevel;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
//设置server_1的地址和端口
Address address = new Address("127.0.0.1", 5000);
//通过chain的方式创建copy_cat server
CopycatServer server = CopycatServer.builder(address)
.withStateMachine(MapstateMachine::new)
.withTransport(NettyTransport.builder()
.withThreads(4)
.build())
.withStorage(Storage.builder()
.withDirectory(new File("logs"))
.withStorageLevel(StorageLevel.DISK)
.build())
.build();
//注册putCommand和GetQuery命令类
server.serializer().register(PutCommand.class);
server.serializer().register(GetQuery.class);
//启动服务器
CompletableFuture future = server.bootstrap();
future.join();
}
} copyCat_server-2 实现
package com.xkx.myCopycat2;
import com.xkx.common.GetQuery;
import com.xkx.common.MapstateMachine;
import com.xkx.common.PutCommand;
import io.atomix.catalyst.transport.Address;
import io.atomix.catalyst.transport.netty.NettyTransport;
import io.atomix.copycat.server.CopycatServer;
import io.atomix.copycat.server.storage.Storage;
import io.atomix.copycat.server.storage.StorageLevel;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
public class Main2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Address address = new Address("127.0.0.1", 5001);
CopycatServer server = CopycatServer.builder(address)
.withStateMachine(MapstateMachine::new)
.withTransport(NettyTransport.builder()
.withThreads(4)
.build())
.withStorage(Storage.builder()
.withDirectory(new File("logs"))
.withStorageLevel(StorageLevel.DISK)
.build())
.build();
server.serializer().register(PutCommand.class);
server.serializer().register(GetQuery.class);
//这里通过join到copyCat-server-1实现cluster
Collection cluster = Collections.singleton(new Address("127.0.0.1", 5000));
server.join(cluster).join();
}
}这里只给出copyCat-server-1和copyCat_server-2 的实现,copyCat-server-3跟copyCat_server-2 实现相同,只是改变了下IP地址和端口.
copycat-client实现
package com.xkx.client;
import com.xkx.common.GetQuery;
import com.xkx.common.PutCommand;
import io.atomix.catalyst.transport.Address;
import io.atomix.catalyst.transport.netty.NettyTransport;
import io.atomix.copycat.client.CopycatClient;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
public class ClientMain {
public static void main(String[] args){
CopycatClient.Builder builder = CopycatClient.builder();
builder.withTransport(NettyTransport.builder()
.withThreads(2)
.build());
CopycatClient client = builder.build();
//客户端注册命令
client.serializer().register(PutCommand.class);
client.serializer().register(GetQuery.class);
//集群的ip以及端口
Collection cluster = Arrays.asList(
new Address("127.0.0.1", 5000),
new Address("127.0.0.1", 5001),
new Address("127.0.0.1", 5002)
);
CompletableFuture future = client.connect(cluster);
future.join();
//使用PutCommand提交三个键值对
CompletableFuture[] futures = new CompletableFuture[3];
futures[0] = client.submit(new PutCommand("foo", "Hello world!"));
futures[1] = client.submit(new PutCommand("bar", "Hello world!"));
futures[2] = client.submit(new PutCommand("baz", "Hello world!"));
//等待集群完成一致性的复制后,打印完成的结果
CompletableFuture.allOf(futures).thenRun(() -> System.out.println("Commands completed!"));
//客户端提交查询
client.submit(new GetQuery("foo")).thenAccept(result -> {
System.out.println("foo is: " + result);
});
}
} 注意copyCat-server 和 copyCat-client都应该使用相同的GetQuery,MapstateMachine,PutCommand类,所以放在了common目录下,也就说他们都需要应用相同的类。
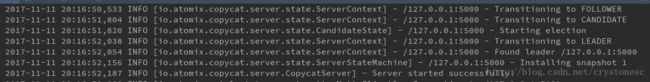
实验结果:
copyCat-server-1 console内容:
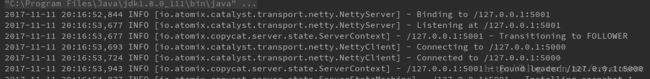
copyCat-server-2 console内容:
copyCat-server-3 console内容:

copyCat-client console内容:

可以看到三台server中copyCat-server-1被选举为Leader,另外两台为Follower,所有请求都会到copyCat-server-1来处理,并通过Raft算法复制到另外两台server。