【图像处理】libtiff读写三维TIFF图像(附详细代码)
【fishing-pan:https://blog.csdn.net/u013921430转载请注明出处】
前言
做图像处理的第一步是读图,在C++中读图的方式很多,常用的是采用OpenCV读图,但是OpenCV只能读取二维的图像,无法读取三维的图像。除此之外,还可以采用ITK、VTK读取图像,但是这两种工具封装的太好,使用起来并不灵活。这两种工具底层都是调用libtiff库读取图像,所以我们也可以直接利用libtiff读取图像。
今天就讲讲如何利用libtiff读取图像,并且用OpenCV显示其中的一帧。
如果您觉得这篇博文对您有用,请轻轻点赞,谢谢
软件工具:VS2013+libtiff+Win7(X64)
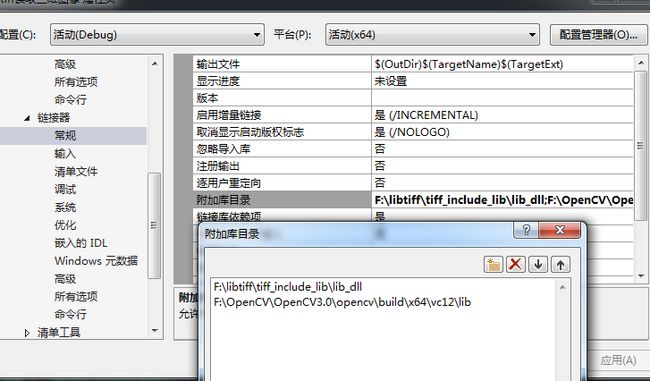
工程配置
由于我的libtiff库是64位的,所以创建的是X64的项目。然后将libtiff和OpenCV的包含目录添加到常规项。
然后将库目录输入到链接器的常规项中
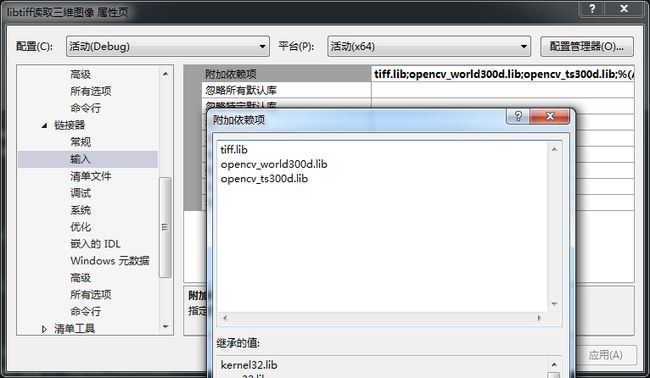
最后,将静态库名添加到链接器的输入项
工程配置就ok了。
代码
为了讲解方便,在此直接给出图像读入和写出的代码;
读入方式1
void open_Fun1(const char* file,vector &buffer,int *size)
{
TIFF *tif = TIFFOpen(file, "r"); //使用TIFFOpen函数以只读形式打开图像。
if (tif == nullptr)
{
cout << "读入图像路径错误,请重新确认";
return;
}
int width, height;
//-------------获取单帧图像的长高
TIFFGetField(tif, TIFFTAG_IMAGEWIDTH, &width);
TIFFGetField(tif, TIFFTAG_IMAGELENGTH, &height);
//TIFFGetField(tif, TIFFTAG_BITSPERSAMPLE, &channel); //------获取通道数
//------------ 获取图片帧数
int nTotalFrame = TIFFNumberOfDirectories(tif);
printf("width: %d\n", width);
printf("Slice: %d\n", nTotalFrame);
printf("height: %d\n", height);
//---------------获取每一帧的像素点数目
int stripSize = TIFFStripSize(tif);
//---------------------申请单帧图像所需的内存空间;
uint32* count = new uint32[height*width];
//uint32* count = new uint32[stripSize];
for (int s = 0; s < nTotalFrame; s++)
{
//---------------------建立单张画布;
Mat MatImage(height, width, CV_8UC1, Scalar::all(0));
TIFFSetDirectory(tif, s); //-------选中第s帧
TIFFReadRGBAImage(tif, width, height, count, 0); //将第s帧的内容传递到count中;默认参数选择是0,所以是逆序读入的。可以使用ORIENTATION_TOPLEFT作为参数,从左上角开始
uint32* rowPoint2Src = count + (height - 1)*width; //构建一个指向最后一行的第一个元素。注意这里,是从最后一行开始读入的
for (int i = 0; i (i, j) = (uchar)TIFFGetG(*colPoint2Src); //按照像素点读取
colPoint2Src++;
}
rowPoint2Src -= width;
}
buffer.push_back(MatImage);
MatImage.release();
}
TIFFClose(tif);
delete[] count;
size[0] = width;
size[1] = height;
size[2] = nTotalFrame;
} 代码分析
1. 打开图像
TIFF* TIFFOpen(const char*, const char*);TIFFOpen( )函数有两个参数,第一个是图像的目录以及文件名,第二个是打开方式。这与一般的文件打开函数是一样的,就不多说了。
2. 获取图像参数
int width, height;
//-------------获取单帧图像的长高
TIFFGetField(tif, TIFFTAG_IMAGEWIDTH, &width);
TIFFGetField(tif, TIFFTAG_IMAGELENGTH, &height);
//TIFFGetField(tif, TIFFTAG_BITSPERSAMPLE, &channel); //------获取通道数
//------------ 获取图片帧数
int nTotalFrame = TIFFNumberOfDirectories(tif);
printf("width: %d\n", width);
printf("Slice: %d\n", nTotalFrame);
printf("height: %d\n", height);
//---------------获取每一帧的像素点数目
int stripSize = TIFFStripSize(tif);如注释中所写,使用TIFFGetField()函数可以获得图像的许多参数,包括单帧图像的长、宽、图像位深、通道数、方向等。
使用TIFFNumberOfDirectories()可以获得图像的帧数,TIFFStripSize()可以获得每一帧的像素点数目。
3. 获取一层图像所以像素点的值
TIFFSetDirectory(tif, s); //-------选中第s帧
TIFFReadRGBAImage(tif, width, height, count, 0); //将第s帧的内容传递到count中;默认参数选择是0,所以是逆序读入的。可以使用ORIENTATION_TOPLEFT作为参数,从左上角开始读取文件时TIFFSetDirectory()寒素可以用从0开始的序号选择任意一帧图像,TIFFReadDirectory()和TIFFWriteDirectory()可以用于顺序读写每一帧,只需要一个while循环即可 。这里的代码先选中图像的第s帧。然后按RGBA图像的方式读入,注意这种方式只能读入8bit的图像,无法读入16bit图像。因为RGBA图像的所有参数都是在0~255之间的,这样构成了一个32bit的RGBA像素的图像。
4. 获取每个像素点的值
uint32* rowPoint2Src = count + (height - 1)*width; //构建一个指向最后一行的第一个元素。注意这里,是从最后一行开始读入的
for (int i = 0; i (i, j) = (uchar)TIFFGetG(*colPoint2Src); //按照像素点读取
colPoint2Src++;
}
rowPoint2Src -= width;
} 因为前面获取每一帧采用的是TIFFReadRGBAImage()的方法,所以这里采用TIFFGetG()获得像素点的值。
转到TIFFGetG() 的定义可以看到如下内容。这里除了不能使用TIFFGetA()之外,其他三种宏获得的像素值是一样的。
#define TIFFGetR(abgr) ((abgr) & 0xff)
#define TIFFGetG(abgr) (((abgr) >> 8) & 0xff)
#define TIFFGetB(abgr) (((abgr) >> 16) & 0xff)
#define TIFFGetA(abgr) (((abgr) >> 24) & 0xff)这样遍历所有的像素点,就能获得所有的像素值。
5. 关闭图像
TIFFClose();这里也不必多说,在所有操作都执行完毕后,关闭图像。
读入方式2
很显然,刚刚的读入方式,只能读入8bit的图像,那么16位的图像如何读入呢?话不多说,shangdaim
代码
void open_Fun2(const char* file, uint16 **buffer,int *size)
{
TIFF *tif = TIFFOpen(file, "r"); //使用TIFFOpen函数以只读形式打开图像。
if (tif == nullptr)
{
cout << "读入图像路径错误,请重新确认";
return;
}
int width, height;
//-------------获取单帧图像的长高
TIFFGetField(tif, TIFFTAG_IMAGEWIDTH, &width);
TIFFGetField(tif, TIFFTAG_IMAGELENGTH, &height);
//TIFFGetField(tif, TIFFTAG_BITSPERSAMPLE, &channel);
//------------ 获取图片帧数
int nTotalFrame = TIFFNumberOfDirectories(tif);
printf("width: %d\n", width);
printf("Slice: %d\n", nTotalFrame);
printf("height: %d\n", height);
//---------------获取每一帧的像素点数目
int stripSize = TIFFStripSize(tif);
*buffer = new uint16[nTotalFrame*stripSize];
int N_size = 0;
for (int s = 0; s < nTotalFrame; s++)
{
for (int row = 0; row < height; row++)
{
TIFFReadScanline(tif, (&(*buffer)[N_size] + row*int(width)), row); //---按行读取
}
N_size += width*height;
TIFFReadDirectory(tif);
}
TIFFClose(tif);
size[0] = width;
size[1] = height;
size[2] = nTotalFrame;
}代码分析
前面参数获取的过程与读入方式1中完全一样,就不作分析了。
获取每个点像素值
int N_size = 0;
for (int s = 0; s < nTotalFrame; s++)
{
for (int row = 0; row < height; row++)
{
TIFFReadScanline(tif, (&(*buffer)[N_size] + row*int(width)), row); //---按行读取
}
N_size += width*height;
TIFFReadDirectory(tif);
}这里的图像读入方式是使用TIFFReadScanline()读入图像,libtiff提供的最简单的接口是scanline方式的接口,用于读取条状或块状的图像,这种方式只能用于读写非压缩格式图像。函数为TIFFReadScanline()和TIFFWriteScanline()。
读入方式3
这里的读入方式3与读入方式1方法其实是一样的。
代码
void open_Fun3(const char* file, vector &buffer,int *size)
{
TIFF *tif = TIFFOpen(file, "r"); //使用TIFFOpen函数以只读形式打开图像。
if (tif == nullptr)
{
cout << "读入图像路径错误,请重新确认";
return;
}
int width, height;
//-------------获取单帧图像的长高
TIFFGetField(tif, TIFFTAG_IMAGEWIDTH, &width);
TIFFGetField(tif, TIFFTAG_IMAGELENGTH, &height);
//TIFFGetField(tif, TIFFTAG_BITSPERSAMPLE, &channel);
//------------ 获取图片帧数
int nTotalFrame = TIFFNumberOfDirectories(tif);
printf("width: %d\n", width);
printf("Slice: %d\n", nTotalFrame);
printf("height: %d\n", height);
//---------------获取每一帧的像素点数目
int stripSize = TIFFStripSize(tif);
//---------------------申请单帧图像所需的内存空间;
uint32* slice = new uint32[height*width];
//uint32* count = new uint32[stripSize];
//---------------------建立单张画布;
for (int z = 0; z(i, j) = TIFFGetR(slice[ss]); //从一帧中的每个点获取像素值
ss++;
}
}
TIFFReadDirectory(tif);
buffer.push_back(MatImage);
MatImage.release();
}
TIFFClose(tif);
delete[] slice;
size[0] = width;
size[1] = height;
size[2] = nTotalFrame;
} 代码分析
与方法一中唯一的不同就是获取每一帧图像的代码不一样,原理是一样的,就不多加赘述。
除了上面的三种方法之外,libtiff 还有提供了一种读取可以处理压缩或非压缩图像的方法,Strip-oriented。这里也不多讲了,有兴趣的朋友可以自己去调研。
图像写出
有读就有写,这是自然,由于篇幅原因,只提供一种图像写出的方法,应该够用了,毕竟了解了原理,过程只是调用API而已。
代码
void saveTiff(const char *path,uint16 *buffer,int *size)
{
int width = size[0];
int height = size[1];
int slice = size[2];
TIFF* out = TIFFOpen(path, "w");
if (out)
{
int N_size = 0;
size_t nCur = 0;
//UChar den = (sizeof(T) == 1) ? 1 : 4;
do{
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_SUBFILETYPE, FILETYPE_PAGE);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_PAGENUMBER, slice);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_IMAGEWIDTH, (uint32)width);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_IMAGELENGTH, (uint32)height);
//TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_RESOLUTIONUNIT, 2);
/*TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_YRESOLUTION, 196.0f);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_XRESOLUTION, 204.0f);*/
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_ORIENTATION, ORIENTATION_TOPLEFT);
//
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_BITSPERSAMPLE, 16); //根据图像位深填不同的值
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_SAMPLESPERPIXEL, 1);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_COMPRESSION, COMPRESSION_NONE);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_PHOTOMETRIC, PHOTOMETRIC_MINISBLACK);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_PLANARCONFIG, PLANARCONFIG_CONTIG);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_ROWSPERSTRIP, height);
for (int m = 0; m < height; m++)
{
TIFFWriteScanline(out, &buffer[N_size + width*m], m, 0);
}
//TIFFWriteEncodedStrip(out, 0, &buffer[N_size], width * height); //另一种写入方法
++nCur;
N_size = N_size + width*height;
} while (TIFFWriteDirectory(out) && nCur < slice);
TIFFClose(out);
cout << "save over";
}
}代码分析
1. TIFFOpen()
使用TIFFOpen()打开写出的文件,此时第二个参数为”w“;
2. 对图像标签赋值
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_SUBFILETYPE, FILETYPE_PAGE);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_PAGENUMBER, slice);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_IMAGEWIDTH, (uint32)width);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_IMAGELENGTH, (uint32)height);
//TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_RESOLUTIONUNIT, 2);
/*TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_YRESOLUTION, 196.0f);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_XRESOLUTION, 204.0f);*/
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_ORIENTATION, ORIENTATION_TOPLEFT);
//
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_BITSPERSAMPLE, 16); //根据图像位深填不同的值
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_SAMPLESPERPIXEL, 1);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_COMPRESSION, COMPRESSION_NONE);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_PHOTOMETRIC, PHOTOMETRIC_MINISBLACK);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_PLANARCONFIG, PLANARCONFIG_CONTIG);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_ROWSPERSTRIP, height);保存TIFF图像时,设置标签是必不可少的过程,其中主要包括压缩方式、图像位深、单帧大小、帧数等信息。
3. 图像赋值
for (int m = 0; m < height; m++)
{
TIFFWriteScanline(out, &buffer[N_size + width*m], m, 0);
}图像写出的方法使用的是之前提到过的TIFFWriteScanline()按行写出函数,函数第一个参数是输出图像的指针,第二个是存放了图像像素值的数组,后面的就是第多少行,以及显出顺序。
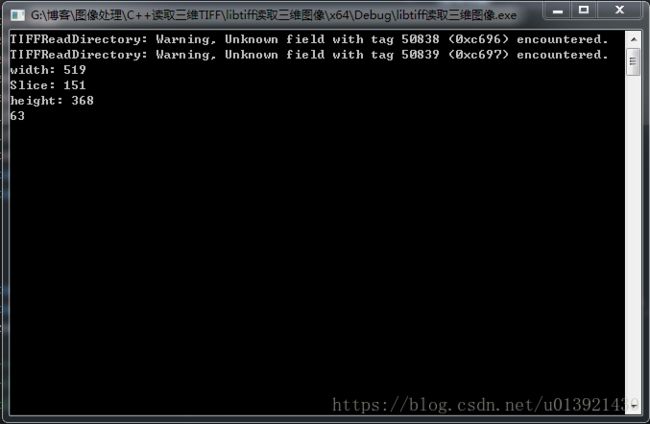
运行结果
结果中输出了图像大小信息,以及三位图像的某一帧。
全部代码
事先说明,这里使用vector或者使用数组存放图像跟图像本身没有关系,只是我自己的编写程序的习惯问题。
//-------opentiff.h
#ifndef OPENTIFF_H
#define OPENTIFF_H
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
void open_Fun1(const char*, vector &buffer,int *size);
void open_Fun2(const char*, uint16 **buffer,int *size);
void open_Fun3(const char*, vector &buffer,int *size);
void saveTiff(const char *path, uint16 *buffer, int *size);
#endif
//-------------test.cpp
//-----------读写三维Tiff
//----------不用先生,2018.03.30
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "tiff.h"
#include "tiffio.h"
#include "opentiff.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
void main()
{
const char* filename8bit = "C:\\Users\\most_pan\\Desktop\\testpic\\test.tif";
const char* filename16bit = "C:\\Users\\most_pan\\Desktop\\testpic\\test16bit.tif";
int *sizes = new int[3];
//------------------调用Fun1()读图
/*vector Three_tiff;
open_Fun1(filename8bit, Three_tiff,sizes);
Mat OutImage;
normalize(Three_tiff[99], OutImage, 1, 0.00, NORM_MINMAX);
imshow("test", OutImage);
cout << (float)Three_tiff[99].at(50, 20);
imwrite("C:/Users/most_pan/Desktop/testss.jpg", Three_tiff[99]);
waitKey(0);
OutImage.release();*/
//------------------调用Fun2()读图
//uint16 *Three_tiff_buffer;
//open_Fun2(filename16bit, &Three_tiff_buffer,sizes);
//const char* filename16bitsave = "C:\\Users\\most_pan\\Desktop\\testpic\\test16bitsave.tif";
//saveTiff(filename16bitsave, Three_tiff_buffer, sizes);
展示一层
//int width = sizes[0];
//int height = sizes[1];
//Mat MatImage(height, width, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(0));
//int s = 0;
//for (int i = 0; i < height; i++)
//{
// for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
// {
// MatImage.at(i, j) = Three_tiff_buffer[s];
// s++;
// }
//}
//Mat OutImage;
//normalize(MatImage, OutImage, 1, 0.00, NORM_MINMAX);
//imshow("test", OutImage);
//waitKey(0);
//MatImage.release();
//OutImage.release();
//delete []Three_tiff_buffer;
//delete[] sizes;
//------------------调用Fun3()读图
vector Three_tiff;
open_Fun3(filename8bit, Three_tiff,sizes);
Mat OutImage;
normalize(Three_tiff[99], OutImage, 1, 0.00, NORM_MINMAX);
imshow("test", OutImage);
waitKey(0);
cout << (float)Three_tiff[99].at(50, 20);
imwrite("C:/Users/most_pan/Desktop/testss.jpg", Three_tiff[99]);
OutImage.release();
system("pause");
return;
}
void open_Fun1(const char* file,vector &buffer,int *size)
{
TIFF *tif = TIFFOpen(file, "r"); //使用TIFFOpen函数以只读形式打开图像。
if (tif == nullptr)
{
cout << "读入图像路径错误,请重新确认";
return;
}
int width, height;
//-------------获取单帧图像的长高
TIFFGetField(tif, TIFFTAG_IMAGEWIDTH, &width);
TIFFGetField(tif, TIFFTAG_IMAGELENGTH, &height);
//TIFFGetField(tif, TIFFTAG_BITSPERSAMPLE, &channel); //------获取通道数
//------------ 获取图片帧数
int nTotalFrame = TIFFNumberOfDirectories(tif);
printf("width: %d\n", width);
printf("Slice: %d\n", nTotalFrame);
printf("height: %d\n", height);
//---------------获取每一帧的像素点数目
int stripSize = TIFFStripSize(tif);
//---------------------申请单帧图像所需的内存空间;
uint32* count = new uint32[height*width];
//uint32* count = new uint32[stripSize];
for (int s = 0; s < nTotalFrame; s++)
{
//---------------------建立单张画布;
Mat MatImage(height, width, CV_8UC1, Scalar::all(0));
TIFFSetDirectory(tif, s); //-------选中第s帧
TIFFReadRGBAImage(tif, width, height, count, 0); //将第s帧的内容传递到count中;默认参数选择是0,所以是逆序读入的。可以使用ORIENTATION_TOPLEFT作为参数,从左上角开始
uint32* rowPoint2Src = count + (height - 1)*width; //构建一个指向最后一行的第一个元素。注意这里,是从最后一行开始读入的
for (int i = 0; i (i, j) = (uchar)TIFFGetG(*colPoint2Src); //按照像素点读取
colPoint2Src++;
}
rowPoint2Src -= width;
}
buffer.push_back(MatImage);
MatImage.release();
}
TIFFClose(tif);
delete[] count;
size[0] = width;
size[1] = height;
size[2] = nTotalFrame;
}
//--------------------------读取16位图像
void open_Fun2(const char* file, uint16 **buffer,int *size)
{
TIFF *tif = TIFFOpen(file, "r"); //使用TIFFOpen函数以只读形式打开图像。
if (tif == nullptr)
{
cout << "读入图像路径错误,请重新确认";
return;
}
int width, height;
//-------------获取单帧图像的长高
TIFFGetField(tif, TIFFTAG_IMAGEWIDTH, &width);
TIFFGetField(tif, TIFFTAG_IMAGELENGTH, &height);
//TIFFGetField(tif, TIFFTAG_BITSPERSAMPLE, &channel);
//------------ 获取图片帧数
int nTotalFrame = TIFFNumberOfDirectories(tif);
printf("width: %d\n", width);
printf("Slice: %d\n", nTotalFrame);
printf("height: %d\n", height);
//---------------获取每一帧的像素点数目
int stripSize = TIFFStripSize(tif);
*buffer = new uint16[nTotalFrame*stripSize];
int N_size = 0;
for (int s = 0; s < nTotalFrame; s++)
{
for (int row = 0; row < height; row++)
{
TIFFReadScanline(tif, (&(*buffer)[N_size] + row*int(width)), row); //---按行读取
}
N_size += width*height; TIFFReadDirectory(tif);
}
TIFFClose(tif);
size[0] = width;
size[1] = height;
size[2] = nTotalFrame;
}
//-------------------读取8位图像
void open_Fun3(const char* file, vector &buffer,int *size)
{
TIFF *tif = TIFFOpen(file, "r"); //使用TIFFOpen函数以只读形式打开图像。
if (tif == nullptr)
{
cout << "读入图像路径错误,请重新确认";
return;
}
int width, height;
//-------------获取单帧图像的长高
TIFFGetField(tif, TIFFTAG_IMAGEWIDTH, &width);
TIFFGetField(tif, TIFFTAG_IMAGELENGTH, &height);
//TIFFGetField(tif, TIFFTAG_BITSPERSAMPLE, &channel);
//------------ 获取图片帧数
int nTotalFrame = TIFFNumberOfDirectories(tif);
printf("width: %d\n", width);
printf("Slice: %d\n", nTotalFrame);
printf("height: %d\n", height);
//---------------获取每一帧的像素点数目
int stripSize = TIFFStripSize(tif);
//---------------------申请单帧图像所需的内存空间;
uint32* slice = new uint32[height*width];
//uint32* count = new uint32[stripSize];
//---------------------建立单张画布;
for (int z = 0; z(i, j) = TIFFGetR(slice[ss]); //从一帧中的每个点获取像素值
ss++;
}
}
TIFFReadDirectory(tif);
buffer.push_back(MatImage);
MatImage.release();
}
TIFFClose(tif);
delete[] slice;
size[0] = width;
size[1] = height;
size[2] = nTotalFrame;
}
void saveTiff(const char *path,uint16 *buffer,int *size)
{
int width = size[0];
int height = size[1];
int slice = size[2];
TIFF* out = TIFFOpen(path, "w");
if (out)
{
int N_size = 0;
size_t nCur = 0;
do{
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_SUBFILETYPE, FILETYPE_PAGE);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_PAGENUMBER, slice);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_IMAGEWIDTH, (uint32)width);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_IMAGELENGTH, (uint32)height);
//TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_RESOLUTIONUNIT, 2);
/*TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_YRESOLUTION, 196.0f);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_XRESOLUTION, 204.0f);*/
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_ORIENTATION, ORIENTATION_TOPLEFT);
//
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_BITSPERSAMPLE, 16); //根据图像位深填不同的值
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_SAMPLESPERPIXEL, 1);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_COMPRESSION, COMPRESSION_NONE);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_PHOTOMETRIC, PHOTOMETRIC_MINISBLACK);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_PLANARCONFIG, PLANARCONFIG_CONTIG);
TIFFSetField(out, TIFFTAG_ROWSPERSTRIP, height);
for (int m = 0; m < height; m++)
{
TIFFWriteScanline(out, &buffer[N_size + width*m], m, 0);
}
//TIFFWriteEncodedStrip(out, 0, &buffer[N_size], width * height); //另一种写入方法
++nCur;
N_size = N_size + width*height;
} while (TIFFWriteDirectory(out) && nCur < slice);
TIFFClose(out);
cout << "save over";
}
} 最后
自己当初编译libtiff的时候花费了不少时间,这里给大家提供我所使用的64位程序的库函数,libtiff(X64),我象征性的收取2个积分,如果确实没积分,可以评论找我,我也会给你提供库文件的。