YouTube网红小哥Siraj Raval系列视频又和大家见面啦!今天要讲的是加密货币价格预测,包含大量代码,还用一个视频详解具体步骤,不信你看了还学不会!
点击观看详解视频
时长22分钟
有中文字幕
▼
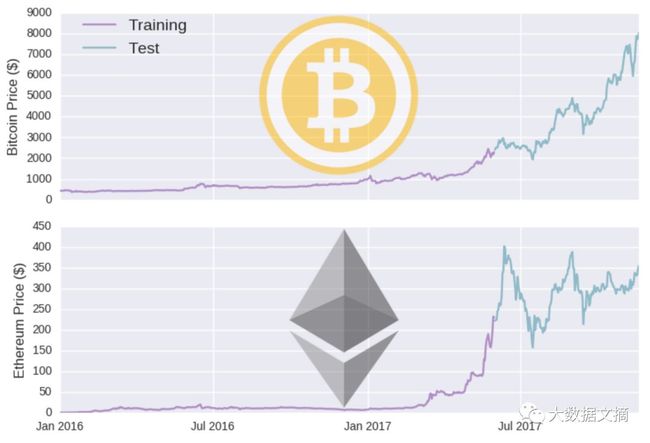
预测加密货币价格其实很简单,用Python+Keras,再来一个循环神经网络(确切说是双向LSTM),只需要9步就可以了!比特币以太坊价格预测都不在话下。
这9个步骤是:
数据处理
建模
训练模型
测试模型
分析价格变化
分析价格百分比变化
比较预测值和实际数据
计算模型评估指标
结合在一起:可视化
数据处理
导入Keras、Scikit learn的metrics、numpy、pandas、matplotlib这些我们需要的库。
## Keras for deep learningfrom keras.layers.core import Dense, Activation, Dropoutfrom keras.layers.recurrent import LSTMfrom keras.layers import Bidirectionalfrom keras.models import Sequential## Scikit learn for mapping metricsfrom sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error#for loggingimport time##matrix mathimport numpy as npimport math##plottingimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt##data processingimport pandas as pd
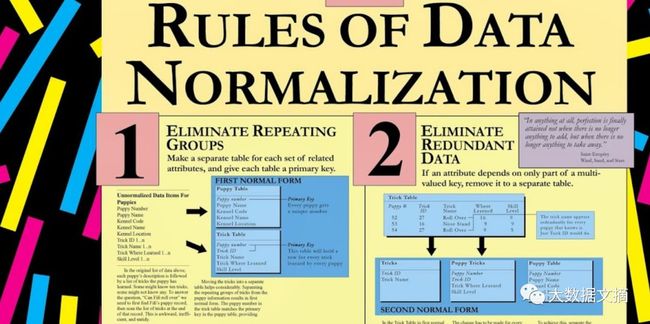
首先,要对数据进行归一化处理。关于数据处理的原则,有张大图,大家可以在大数据文摘公众号后台对话框内回复“加密货币”查看高清图。
def load_data(filename, sequence_length): """ Loads the bitcoin data Arguments: filename -- A string that represents where the .csv file can be located sequence_length -- An integer of how many days should be looked at in a row Returns: X_train -- A tensor of shape (2400, 49, 35) that will be inputed into the model to train it Y_train -- A tensor of shape (2400,) that will be inputed into the model to train it X_test -- A tensor of shape (267, 49, 35) that will be used to test the model's proficiency Y_test -- A tensor of shape (267,) that will be used to check the model's predictions Y_daybefore -- A tensor of shape (267,) that represents the price of bitcoin the day before each Y_test value unnormalized_bases -- A tensor of shape (267,) that will be used to get the true prices from the normalized ones window_size -- An integer that represents how many days of X values the model can look at at once """ #Read the data file raw_data = pd.read_csv(filename, dtype = float).values #Change all zeros to the number before the zero occurs for x in range(0, raw_data.shape[0]): for y in range(0, raw_data.shape[1]): if(raw_data[x][y] == 0): raw_data[x][y] = raw_data[x-1][y] #Convert the file to a list data = raw_data.tolist() #Convert the data to a 3D array (a x b x c) #Where a is the number of days, b is the window size, and c is the number of features in the data file result = [] for index in range(len(data) - sequence_length): result.append(data[index: index + sequence_length]) #Normalizing data by going through each window #Every value in the window is divided by the first value in the window, and then 1 is subtracted d0 = np.array(result) dr = np.zeros_like(d0) dr[:,1:,:] = d0[:,1:,:] / d0[:,0:1,:] - 1 #Keeping the unnormalized prices for Y_test #Useful when graphing bitcoin price over time later start = 2400 end = int(dr.shape[0] + 1) unnormalized_bases = d0[start:end,0:1,20] #Splitting data set into training (First 90% of data points) and testing data (last 10% of data points) split_line = round(0.9 * dr.shape[0]) training_data = dr[:int(split_line), :] #Shuffle the data np.random.shuffle(training_data) #Training Data X_train = training_data[:, :-1] Y_train = training_data[:, -1] Y_train = Y_train[:, 20] #Testing data X_test = dr[int(split_line):, :-1] Y_test = dr[int(split_line):, 49, :] Y_test = Y_test[:, 20] #Get the day before Y_test's price Y_daybefore = dr[int(split_line):, 48, :] Y_daybefore = Y_daybefore[:, 20] #Get window size and sequence length sequence_length = sequence_length window_size = sequence_length - 1 #because the last value is reserved as the y value return X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test, Y_daybefore, unnormalized_bases, window_size
建模
我们用到的是一个3层RNN,dropout率20%。
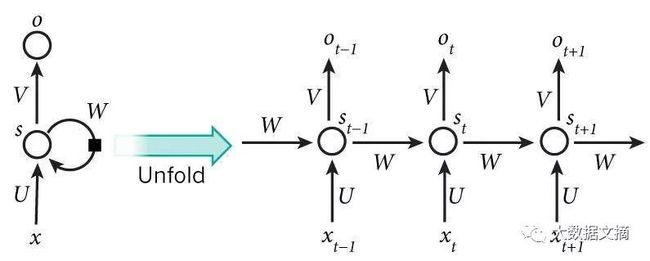
双向RNN基于这样的想法:时间t的输出不仅依赖于序列中的前一个元素,而且还可以取决于未来的元素。比如,要预测一个序列中缺失的单词,需要查看左侧和右侧的上下文。双向RNN是两个堆叠在一起的RNN,根据两个RNN的隐藏状态计算输出。
举个例子,这句话里缺失的单词gym要查看上下文才能知道(文摘菌:everyday?):
I go to the ( ) everyday to get fit.
def initialize_model(window_size, dropout_value, activation_function, loss_function, optimizer): """ Initializes and creates the model to be used Arguments: window_size -- An integer that represents how many days of X_values the model can look at at once dropout_value -- A decimal representing how much dropout should be incorporated at each level, in this case 0.2 activation_function -- A string to define the activation_function, in this case it is linear loss_function -- A string to define the loss function to be used, in the case it is mean squared error optimizer -- A string to define the optimizer to be used, in the case it is adam Returns: model -- A 3 layer RNN with 100*dropout_value dropout in each layer that uses activation_function as its activation function, loss_function as its loss function, and optimizer as its optimizer """ #Create a Sequential model using Keras model = Sequential() #First recurrent layer with dropout model.add(Bidirectional(LSTM(window_size, return_sequences=True), input_shape=(window_size, X_train.shape[-1]),)) model.add(Dropout(dropout_value)) #Second recurrent layer with dropout model.add(Bidirectional(LSTM((window_size*2), return_sequences=True))) model.add(Dropout(dropout_value)) #Third recurrent layer model.add(Bidirectional(LSTM(window_size, return_sequences=False))) #Output layer (returns the predicted value) model.add(Dense(units=1)) #Set activation function model.add(Activation(activation_function)) #Set loss function and optimizer model.compile(loss=loss_function, optimizer=optimizer) return model
训练模型
这里取batch size = 1024,epoch times = 100。我们需要最小化均方误差MSE。
def fit_model(model, X_train, Y_train, batch_num, num_epoch, val_split): """ Fits the model to the training data Arguments: model -- The previously initalized 3 layer Recurrent Neural Network X_train -- A tensor of shape (2400, 49, 35) that represents the x values of the training data Y_train -- A tensor of shape (2400,) that represents the y values of the training data batch_num -- An integer representing the batch size to be used, in this case 1024 num_epoch -- An integer defining the number of epochs to be run, in this case 100 val_split -- A decimal representing the proportion of training data to be used as validation data Returns: model -- The 3 layer Recurrent Neural Network that has been fitted to the training data training_time -- An integer representing the amount of time (in seconds) that the model was training """ #Record the time the model starts training start = time.time() #Train the model on X_train and Y_train model.fit(X_train, Y_train, batch_size= batch_num, nb_epoch=num_epoch, validation_split= val_split) #Get the time it took to train the model (in seconds) training_time = int(math.floor(time.time() - start)) return model, training_time
测试模型
def test_model(model, X_test, Y_test, unnormalized_bases): """ Test the model on the testing data Arguments: model -- The previously fitted 3 layer Recurrent Neural Network X_test -- A tensor of shape (267, 49, 35) that represents the x values of the testing data Y_test -- A tensor of shape (267,) that represents the y values of the testing data unnormalized_bases -- A tensor of shape (267,) that can be used to get unnormalized data points Returns: y_predict -- A tensor of shape (267,) that represnts the normalized values that the model predicts based on X_test real_y_test -- A tensor of shape (267,) that represents the actual prices of bitcoin throughout the testing period real_y_predict -- A tensor of shape (267,) that represents the model's predicted prices of bitcoin fig -- A branch of the graph of the real predicted prices of bitcoin versus the real prices of bitcoin """ #Test the model on X_Test y_predict = model.predict(X_test) #Create empty 2D arrays to store unnormalized values real_y_test = np.zeros_like(Y_test) real_y_predict = np.zeros_like(y_predict) #Fill the 2D arrays with the real value and the predicted value by reversing the normalization process for i in range(Y_test.shape[0]): y = Y_test[i] predict = y_predict[i] real_y_test[i] = (y+1)*unnormalized_bases[i] real_y_predict[i] = (predict+1)*unnormalized_bases[i] #Plot of the predicted prices versus the real prices fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,5)) ax = fig.add_subplot(111) ax.set_title("Bitcoin Price Over Time") plt.plot(real_y_predict, color = 'green', label = 'Predicted Price') plt.plot(real_y_test, color = 'red', label = 'Real Price') ax.set_ylabel("Price (USD)") ax.set_xlabel("Time (Days)") ax.legend() return y_predict, real_y_test, real_y_predict, fig
分析价格变化
def price_change(Y_daybefore, Y_test, y_predict): """ Calculate the percent change between each value and the day before Arguments: Y_daybefore -- A tensor of shape (267,) that represents the prices of each day before each price in Y_test Y_test -- A tensor of shape (267,) that represents the normalized y values of the testing data y_predict -- A tensor of shape (267,) that represents the normalized y values of the model's predictions Returns: Y_daybefore -- A tensor of shape (267, 1) that represents the prices of each day before each price in Y_test Y_test -- A tensor of shape (267, 1) that represents the normalized y values of the testing data delta_predict -- A tensor of shape (267, 1) that represents the difference between predicted and day before values delta_real -- A tensor of shape (267, 1) that represents the difference between real and day before values fig -- A plot representing percent change in bitcoin price per day, """ #Reshaping Y_daybefore and Y_test Y_daybefore = np.reshape(Y_daybefore, (-1, 1)) Y_test = np.reshape(Y_test, (-1, 1)) #The difference between each predicted value and the value from the day before delta_predict = (y_predict - Y_daybefore) / (1+Y_daybefore) #The difference between each true value and the value from the day before delta_real = (Y_test - Y_daybefore) / (1+Y_daybefore) #Plotting the predicted percent change versus the real percent change fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6)) ax = fig.add_subplot(111) ax.set_title("Percent Change in Bitcoin Price Per Day") plt.plot(delta_predict, color='green', label = 'Predicted Percent Change') plt.plot(delta_real, color='red', label = 'Real Percent Change') plt.ylabel("Percent Change") plt.xlabel("Time (Days)") ax.legend() plt.show() return Y_daybefore, Y_test, delta_predict, delta_real, fig
分析价格百分比变化
def binary_price(delta_predict, delta_real): """ Converts percent change to a binary 1 or 0, where 1 is an increase and 0 is a decrease/no change Arguments: delta_predict -- A tensor of shape (267, 1) that represents the predicted percent change in price delta_real -- A tensor of shape (267, 1) that represents the real percent change in price Returns: delta_predict_1_0 -- A tensor of shape (267, 1) that represents the binary version of delta_predict delta_real_1_0 -- A tensor of shape (267, 1) that represents the binary version of delta_real """ #Empty arrays where a 1 represents an increase in price and a 0 represents a decrease in price delta_predict_1_0 = np.empty(delta_predict.shape) delta_real_1_0 = np.empty(delta_real.shape) #If the change in price is greater than zero, store it as a 1 #If the change in price is less than zero, store it as a 0 for i in range(delta_predict.shape[0]): if delta_predict[i][0] > 0: delta_predict_1_0[i][0] = 1 else: delta_predict_1_0[i][0] = 0 for i in range(delta_real.shape[0]): if delta_real[i][0] > 0: delta_real_1_0[i][0] = 1 else: delta_real_1_0[i][0] = 0 return delta_predict_1_0, delta_real_1_0
比较预测值和实际数据
def find_positives_negatives(delta_predict_1_0, delta_real_1_0): """ Finding the number of false positives, false negatives, true positives, true negatives Arguments: delta_predict_1_0 -- A tensor of shape (267, 1) that represents the binary version of delta_predict delta_real_1_0 -- A tensor of shape (267, 1) that represents the binary version of delta_real Returns: true_pos -- An integer that represents the number of true positives achieved by the model false_pos -- An integer that represents the number of false positives achieved by the model true_neg -- An integer that represents the number of true negatives achieved by the model false_neg -- An integer that represents the number of false negatives achieved by the model """ #Finding the number of false positive/negatives and true positives/negatives true_pos = 0 false_pos = 0 true_neg = 0 false_neg = 0 for i in range(delta_real_1_0.shape[0]): real = delta_real_1_0[i][0] predicted = delta_predict_1_0[i][0] if real == 1: if predicted == 1: true_pos += 1 else: false_neg += 1 elif real == 0: if predicted == 0: true_neg += 1 else: false_pos += 1 return true_pos, false_pos, true_neg, false_neg
计算模型评估指标
def calculate_statistics(true_pos, false_pos, true_neg, false_neg, y_predict, Y_test): """ Calculate various statistics to assess performance Arguments: true_pos -- An integer that represents the number of true positives achieved by the model false_pos -- An integer that represents the number of false positives achieved by the model true_neg -- An integer that represents the number of true negatives achieved by the model false_neg -- An integer that represents the number of false negatives achieved by the model Y_test -- A tensor of shape (267, 1) that represents the normalized y values of the testing data y_predict -- A tensor of shape (267, 1) that represents the normalized y values of the model's predictions Returns: precision -- How often the model gets a true positive compared to how often it returns a positive recall -- How often the model gets a true positive compared to how often is hould have gotten a positive F1 -- The weighted average of recall and precision Mean Squared Error -- The average of the squares of the differences between predicted and real values """ precision = float(true_pos) / (true_pos + false_pos) recall = float(true_pos) / (true_pos + false_neg) F1 = float(2 * precision * recall) / (precision + recall) #Get Mean Squared Error MSE = mean_squared_error(y_predict.flatten(), Y_test.flatten()) return precision, recall, F1, MSE
结合在一起:可视化
终于可以看看我们的成果啦!
首先是预测价格vs实际价格:
y_predict, real_y_test, real_y_predict, fig1 = test_model(model, X_test, Y_test, unnormalized_bases)#Show the plotplt.show(fig1)
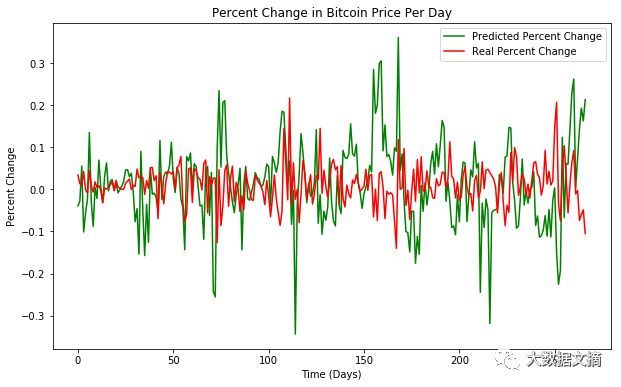
然后是预测的百分比变化vs实际的百分比变化,值得注意的是,这里的预测相对实际来说波动更大,这是模型可以提高的部分:
Y_daybefore, Y_test, delta_predict, delta_real, fig2 = price_change(Y_daybefore, Y_test, y_predict)
Show the plot
plt.show(fig2)
最终模型表现是这样的:
Precision: 0.62
Recall: 0.553571428571
F1 score: 0.584905660377
Mean Squared Error: 0.0430756924477
怎么样,看完有没有跃跃欲试呢?
代码下载地址:
https://github.com/llSourcell/ethereum_future/blob/master/A%20Deep%20Learning%20Approach%20to%20Predicting%20Cryptocurrency%20Prices.ipynb
原视频地址:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G5Mx7yYdEhE
作 者 | Siraj Raval 大数据文摘经授权译制
翻 译 | 糖竹子、狗小白、邓子稷
时间轴 | 韩振峰、Barbara、菜菜Tom
监 制 | 龙牧雪