HBase原理之HBase Region合并解析
1.概述
HBase表的基本单位是Region,日常调用HBase API操作一个表时,交互的数据也会以Region的形式进行呈现。前面介绍过HBase Region切分策略原理,一个表可以有若干个Region,本文主要介绍Region合并的一些问题和解决方法。
2.内容
在分析合并Region之前,我们先来了解一下Region的体系结构,如下图所示:
从图中可知,能够总结以下知识点:
-
HRegion:一个Region可以包含多个Store;
-
Store:每个Store包含一个Memstore和若干个StoreFile;
-
StoreFile:表数据真实存储的地方,HFile是表数据在HDFS上的文件格式。
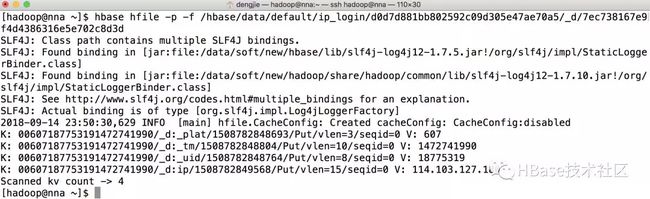
如果要查看HFile文件,HBase有提供命令,命令如下:
hbase hfile -p -f /hbase/data/default/ip_login/d0d7d881bb802592c09d305e47ae70a5/_d/7ec738167e9f4d4386316e5e702c8d3d
执行输出结果如图所示:
2.1 为什么需要合并Region
那为什么需要合并Region呢?这个需要从Region的Split来说。当一个Region被不断的写数据,达到Region的Split的阀值时(由属性hbase.hregion.max.filesize来决定,默认是10GB),该Region就会被Split成2个新的Region。随着业务数据量的不断增加,Region不断的执行Split,那么Region的个数也会越来越多。
一个业务表的Region越多,在进行读写操作时,或是对该表执行Compaction操作时,此时集群的压力是很大的。这里笔者做过一个线上统计,在一个业务表的Region个数达到9000+时,每次对该表进行Compaction操作时,集群的负载便会加重。而间接的也会影响应用程序的读写,一个表的Region过大,势必整个集群的Region个数也会增加,负载均衡后,每个RegionServer承担的Region个数也会增加。
因此,这种情况是很有必要的进行Region合并的。比如,当前Region进行Split的阀值设置为30GB,那么我们可以对小于等于10GB的Region进行一次合并,减少每个业务表的Region,从而降低整个集群的Region,减缓每个RegionServer上的Region压力。
2.2 如何进行Region合并
那么我们如何进行Region合并呢?HBase有提供一个合并Region的命令,具体操作如下:
# 合并相邻的两个Region
hbase> merge_region 'ENCODED_REGIONNAME', 'ENCODED_REGIONNAME'
# 强制合并两个Region
hbase> merge_region 'ENCODED_REGIONNAME', 'ENCODED_REGIONNAME', true
但是这种方式存在问题就是只能一次合并2个Region,如果这里有几千个Region需要合并,这种方式是不可取的。
2.2.1 批量合并
这里有一种批量合并的方式,通过编写脚本(merge_small_regions.rb)实现批量合并,实现源码如下所示:
# Test Mode:
#
# hbase org.jruby.Main merge_empty_regions.rb namespace.tablename
#
# Non Test - ie actually do the merge:
#
# hbase org.jruby.Main merge_empty_regions.rb namespace.tablename merge
#
# Note: Please replace namespace.tablename with your namespace and table, eg NS1.MyTable. This value is case sensitive.
require 'digest'
require 'java'
java_import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration
java_import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HBaseAdmin
java_import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.TableName
java_import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HRegionInfo;
java_import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Connection
java_import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.ConnectionFactory
java_import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Table
java_import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes
def list_bigger_regions(admin, table, low_size)
cluster_status = admin.getClusterStatus()
master = cluster_status.getMaster()
biggers = []
cluster_status.getServers.each do |s|
cluster_status.getLoad(s).getRegionsLoad.each do |r|
# getRegionsLoad returns an array of arrays, where each array
# is 2 elements
# Filter out any regions that don't match the requested
# tablename
next unless r[1].get_name_as_string =~ /#{table}\,/
if r[1].getStorefileSizeMB() > low_size
if r[1].get_name_as_string =~ /\.([^\.]+)\.$/
biggers.push $1
else
raise "Failed to get the encoded name for #{r[1].get_name_as_string}"
end
end
end
end
biggers
end
# Handle command line parameters
table_name = ARGV[0]
low_size = 1024
if ARGV[1].to_i >= low_size
low_size=ARGV[1].to_i
end
limit_batch = 1000
if ARGV[2].to_i <= limit_batch
limit_batch = ARGV[2].to_i
end
do_merge = false
if ARGV[3] == 'merge'
do_merge = true
end
config = HBaseConfiguration.create();
connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(config);
admin = HBaseAdmin.new(connection);
bigger_regions = list_bigger_regions(admin, table_name, low_size)
regions = admin.getTableRegions(Bytes.toBytes(table_name));
puts "Total Table Regions: #{regions.length}"
puts "Total bigger regions: #{bigger_regions.length}"
filtered_regions = regions.reject do |r|
bigger_regions.include?(r.get_encoded_name)
end
puts "Total regions to consider for Merge: #{filtered_regions.length}"
filtered_regions_limit = filtered_regions
if filtered_regions.length < 2
puts "There are not enough regions to merge"
filtered_regions_limit = filtered_regions
end
if filtered_regions.length > limit_batch
filtered_regions_limit = filtered_regions[0,limit_batch]
puts "But we will merge : #{filtered_regions_limit.length} regions because limit in parameter!"
end
r1, r2 = nil
filtered_regions_limit.each do |r|
if r1.nil?
r1 = r
next
end
if r2.nil?
r2 = r
end
# Skip any region that is a split region
if r1.is_split()
r1 = r2
r2 = nil
puts "Skip #{r1.get_encoded_name} bcause it in spliting!"
next
end
if r2.is_split()
r2 = nil
puts "Skip #{r2.get_encoded_name} bcause it in spliting!"
next
end
if HRegionInfo.are_adjacent(r1, r2)
# only merge regions that are adjacent
puts "#{r1.get_encoded_name} is adjacent to #{r2.get_encoded_name}"
if do_merge
admin.mergeRegions(r1.getEncodedNameAsBytes, r2.getEncodedNameAsBytes, false)
puts "Successfully Merged #{r1.get_encoded_name} with #{r2.get_encoded_name}"
sleep 2
end
r1, r2 = nil
else
puts "Regions are not adjacent, so drop the first one and with the #{r2.get_encoded_name} to iterate again"
r1 = r2
r2 = nil
end
end
admin.close
该脚本默认是合并1GB以内的Region,个数为1000个。如果我们要合并小于10GB,个数在4000以内,脚本(merging-region.sh)如下:
#! /bin/bash
num=$1
echo "[`date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"`] INFO : RegionServer Start Merging..."
if [ ! -n "$num" ]; then
echo "[`date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"`] INFO : Default Merging 10 Times."
num=10
elif [[ $num == *[!0-9]* ]]; then
echo "[`date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"`] INFO : Input [$num] Times Must Be Number."
exit 1
else
echo "[`date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"`] INFO : User-Defined Merging [$num] Times."
fi
for (( i=1; i<=$num; i++ ))
do
echo "[`date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"`] INFO : Merging [$i] Times,Total [$num] Times."
hbase org.jruby.Main merge_small_regions.rb namespace.tablename 10240 4000 merge
sleep 5
done
在merging-region.sh脚本中,做了参数控制,可以循环来执行批量合并脚本。可能在实际操作过程中,批量执行一次Region合并,合并后的结果Region还是有很多(可能此时又有新的Region生成),这是我们可以使用merging-region.sh这个脚本多次执行批量合并Region操作,具体操作命令如下:
# 默认循环10次,例如本次循环执行5次
sh merging-region.sh 5
2.3 如果在合并Region的过程中出现永久RIT怎么办
在合并Region的过程中出现永久RIT怎么办?笔者在生产环境中就遇到过这种情况,在批量合并Region的过程中,出现了永久MERGING_NEW的情况,虽然这种情况不会影响现有集群的正常的服务能力,但是如果集群有某个节点发生重启,那么可能此时该RegionServer上的Region是没法均衡的。因为在RIT状态时,HBase是不会执行Region负载均衡的,即使手动执行balancer命令也是无效的。
如果不解决这种RIT情况,那么后续有HBase节点相继重启,这样会导致整个集群的Region验证不均衡,这是很致命的,对集群的性能将会影响很大。经过查询HBase JIRA单,发现这种MERGING_NEW永久RIT的情况是触发了HBASE-17682的BUG,需要打上该Patch来修复这个BUG,其实就是HBase源代码在判断业务逻辑时,没有对MERGING_NEW这种状态进行判断,直接进入到else流程中了。源代码如下:
for (RegionState state : regionsInTransition.values()) {
HRegionInfo hri = state.getRegion();
if (assignedRegions.contains(hri)) {
// Region is open on this region server, but in transition.
// This region must be moving away from this server, or splitting/merging.
// SSH will handle it, either skip assigning, or re-assign.
LOG.info("Transitioning " + state + " will be handled by ServerCrashProcedure for " + sn);
} else if (sn.equals(state.getServerName())) {
// Region is in transition on this region server, and this
// region is not open on this server. So the region must be
// moving to this server from another one (i.e. opening or
// pending open on this server, was open on another one.
// Offline state is also kind of pending open if the region is in
// transition. The region could be in failed_close state too if we have
// tried several times to open it while this region server is not reachable)
if (state.isPendingOpenOrOpening() || state.isFailedClose() || state.isOffline()) {
LOG.info("Found region in " + state +
" to be reassigned by ServerCrashProcedure for " + sn);
rits.add(hri);
} else if(state.isSplittingNew()) {
regionsToCleanIfNoMetaEntry.add(state.getRegion());
} else {
LOG.warn("THIS SHOULD NOT HAPPEN: unexpected " + state);
}
}
}
修复之后的代码如下:
for (RegionState state : regionsInTransition.values()) {
HRegionInfo hri = state.getRegion();
if (assignedRegions.contains(hri)) {
// Region is open on this region server, but in transition.
// This region must be moving away from this server, or splitting/merging.
// SSH will handle it, either skip assigning, or re-assign.
LOG.info("Transitioning " + state + " will be handled by ServerCrashProcedure for " + sn);
} else if (sn.equals(state.getServerName())) {
// Region is in transition on this region server, and this
// region is not open on this server. So the region must be
// moving to this server from another one (i.e. opening or
// pending open on this server, was open on another one.
// Offline state is also kind of pending open if the region is in
// transition. The region could be in failed_close state too if we have
// tried several times to open it while this region server is not reachable)
if (state.isPendingOpenOrOpening() || state.isFailedClose() || state.isOffline()) {
LOG.info("Found region in " + state +
" to be reassigned by ServerCrashProcedure for " + sn);
rits.add(hri);
} else if(state.isSplittingNew()) {
regionsToCleanIfNoMetaEntry.add(state.getRegion());
} else if (isOneOfStates(state, State.SPLITTING_NEW, State.MERGING_NEW)) {
regionsToCleanIfNoMetaEntry.add(state.getRegion());
}else {
LOG.warn("THIS SHOULD NOT HAPPEN: unexpected " + state);
}
}
}
但是,这里有一个问题,目前该JIRA单只是说了需要去修复BUG,打Patch。但是,实际生产情况下,面对这种RIT情况,是不可能长时间停止集群,影响应用程序读写的。那么,有没有临时的解决办法,先临时解决当前的MERGING_NEW这种永久RIT,之后在进行HBase版本升级操作。
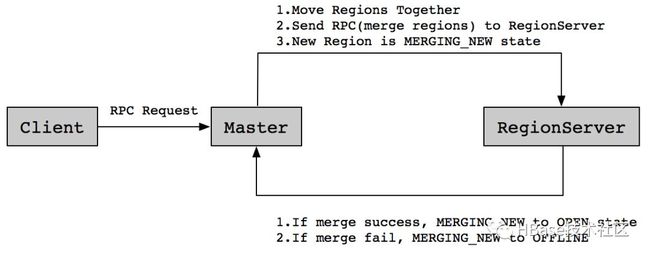
办法是有的,在分析了MERGE合并的流程之后,发现HBase在执行Region合并时,会先生成一个初始状态的MERGING_NEW。整个Region合并流程如下:
从流程图中可以看到,MERGING_NEW是一个初始化状态,在Master的内存中,而处于Backup状态的Master内存中是没有这个新Region的MERGING_NEW状态的,那么可以通过对HBase的Master进行一个主备切换,来临时消除这个永久RIT状态。而HBase是一个高可用的集群,进行主备切换时对用户应用来说是无感操作。因此,面对MERGING_NEW状态的永久RIT可以使用对HBase进行主备切换的方式来做一个临时处理方案。之后,我们在对HBase进行修复BUG,打Patch进行版本升级。
3.总结
HBase的RIT问题,是一个比较常见的问题,在遇到这种问题时,可以先冷静的分析原因,例如查看Master的日志、仔细阅读HBase Web页面RIT异常的描述、使用hbck命令查看Region、使用fsck查看HDFS的block等。分析出具体的原因后,我们在对症下药,做到大胆猜想,小心求证。
附:RIT问题解决方案参考文章:
HBase应用实践专场-HBase问题排查思路
HBase运维实践-聊聊RIT的那点事
号外:打开Kafka消息生态圈正确姿势
极速掌握HBase Netty源码剖析
精通HBase连接池核心源码通道
文章转载自 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/zIf81oJI4MgDpXMF0lTPMA