halcon拓展系列—计算任意矩形的四个角点坐标算子find_rectangle2_points
计算任意矩形的四个角点坐标,基本数学方法利用到了初中高中数学知识:正弦定理和余弦定理
一、基础知识
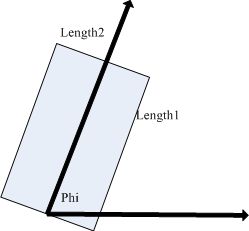
1、halcon的矩形rectangle2定义
draw_rectangle2( : : WindowHandle : Row, Column, Phi, Length1, Length2)
smallest_rectangle2(Regions : : : Row, Column, Phi, Length1, Length2)
draw_rectangle2:窗口有个箭头方向,这个方向就是矩形的角度Phi,和Phi方向一致的边为Length1,和Phi方向垂直的边为Length2
smallest_rectangle2:Length1为长度较长的边,Length2为长度较短的边,且满足Phi为长边Length1方向的角度,角度范围
- pi / 2 < Phi && Phi <= pi / 2
两者相同点:Phi都是Length1的角度
两者不同点:draw_rectangle2的Length1,Length2和Phi与边长度无关,smallest_rectangle2与边长度有关
2、正弦定理和余弦定理
二、计算任意矩形的四个角点坐标
步骤
1、统一矩形描述
把rectangle2转为PI/2>Phi>PI/4,或者-PI/4>Phi>-PI/2,修改矩形的的描述方式,让矩形的Phi较大,这样保证矩形纵方向是Length1,横方向是Length2,
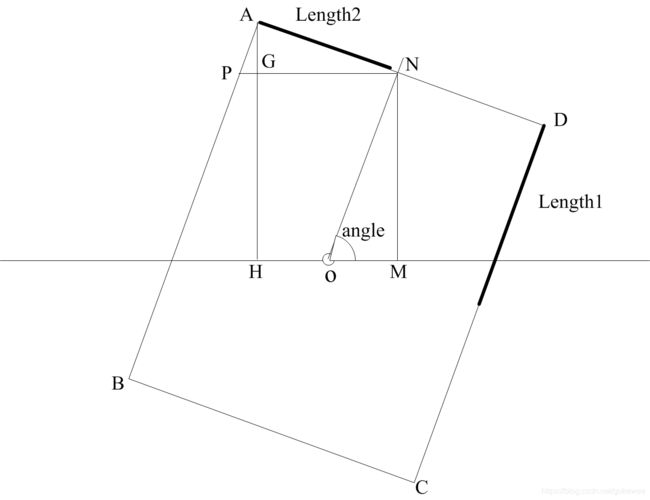
2、计算点A坐标
x=x(OM) - x(AM) = Length1*cos(angle) - Length2*sin(angle)---------------------1.1
y=y(ON) + y(AN) = Length1*sin(angle) + Length2*cos(angle)---------------------1.2
设xLengh1 = Length1*cos(angle)
xLength2 = Length2*sin(angle)
yLength1 = Length1*sin(angle)
yLength2 = Length2*cos(angle)
简化1.1和1.2为
x = xLength1 - xLength2------------------------------------------1.3
y = yLength1 + yLength2------------------------------------------1.4
即A(xLength1 - xLength2, yLength1 + yLength2 )
同理,可以计算出B,C,D点的坐标,过程中要考虑到Phi有正负之分
详细代码如下
* ****************************************
* * 求rectangle2的四个直角点
* * 0********|*********2
* * *********|**********
* * *********|**********
* * *********|**********
* * *********|**********
* * *********|**********
* * 1********|*********3
* *注:以与水平方向所成角度较大的边中线为轴线
* ****************************************
pi := acos(0)*2
if (phi >= 0 and phi < pi/4)
phi := phi - pi/2
Tem := length1
length1 := length2
length2 := Tem
elseif (phi > -pi/4 and phi < 0)
phi := phi + pi/2
Tem := length1
length1 := length2
length2 := Tem
endif
*
if (phi >= 0)
la := phi ///63
lb := la - pi/2 -26
tuple_tan (la, tem1)
tuple_tan (lb, tem2)
tuple_sqrt ((length1 * length1) / (1 + tem1 * tem1), xLength1)
tuple_sqrt ((length2 * length2) / (1 + tem2 * tem2), xLength2)
tuple_sqrt ((tem1*tem1*length1*length1) / (1 + tem1 * tem1), yLength1)
tuple_sqrt ((tem2 * tem2 * length2 * length2) / (1 + tem2 * tem2), yLength2)
* 左上
gen_cross_contour_xld (Cross, 1, columnCenter + xLength1- xLength2, 6, 0.785398)
mColumnUpLeft := columnCenter + xLength1 - xLength2
nRowUpLeft := rowCenter - yLength1 - yLength2
* 左下
mColumnDownLeft := columnCenter - xLength1 - xLength2
nRowDownLeft := rowCenter + yLength1 - yLength2
* 右上
mColumnUpRight := columnCenter + xLength1 + xLength2
nRowUpRight := rowCenter - yLength1 + yLength2
* 右下
mColumnDownRight := columnCenter - xLength1 + xLength2
nRowDownRight := rowCenter + yLength1 + yLength2
else
la := phi
lb := la - pi/2
tuple_tan (la, tem1)
tuple_tan (lb, tem2)
tuple_sqrt ((length1 * length1) / (1 + tem1 * tem1), xLength1)
tuple_sqrt ((length2 * length2) / (1 + tem2 * tem2), xLength2)
tuple_sqrt ((tem1*tem1*length1*length1) / (1 + tem1 * tem1), yLength1)
tuple_sqrt ((tem2 * tem2 * length2 * length2) / (1 + tem2 * tem2), yLength2)
* 左上
mColumnUpLeft := columnCenter - xLength1 - xLength2
nRowUpLeft := rowCenter - yLength1 + yLength2
* disp_cross (3600, nRowUpLeft, mColumnUpLeft, 16, 0)
* 左下
mColumnDownLeft := columnCenter + xLength1 - xLength2
nRowDownLeft := rowCenter + yLength1 + yLength2
* disp_cross (3600, nRowDownLeft, mColumnDownLeft, 16, 0)
* 右上
mColumnUpRight := columnCenter - xLength1 + xLength2
nRowUpRight := rowCenter - yLength1 - yLength2
* 右下
mColumnDownRight := columnCenter + xLength1 + xLength2
nRowDownRight := rowCenter + yLength1 - yLength2
endif
row := []
column := []
row[0] := nRowUpLeft
column[0] := mColumnUpLeft
row[1] := nRowDownLeft
column[1] := mColumnDownLeft
row[2] := nRowUpRight
column[2] := mColumnUpRight
row[3] := nRowDownRight
column[3] := mColumnDownRight
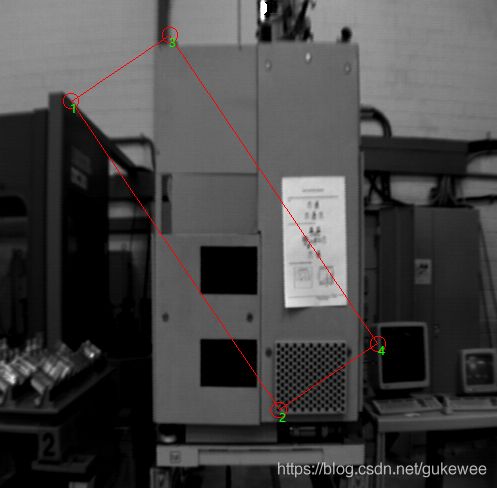
return ()运行效果图如下
注:代码里面推导过程稍有不同,用到了tan(angle)=sin(angle)/cos(angle),最终结果都是一样的;基于这个方法,可以做很多算法,比如Blob粗定位,Blob精定位,直线滤波等;
因为方法没有引用其他方法,上述代码就是所有源码,这里就不上传源码
如需要hdvp函数请留言个人邮箱
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「谷棵」的原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/gukewee/article/details/105787343