勿以恶小而为之,勿以善小而不为--------------------------刘备
劝诸君,多行善事积福报,莫作恶
上一章简单介绍了Hibernate实现简单的CRUD操作和常见类(三),如果没有看过,请观看上一章
Hibernate开发时,有两种形式,一种是XML配置的方式,另外一种是注解形式的开发。
XML配置是,需要写一个实体类User,还要在它的同级目录下创建一个相对应的User.hbm.xml,
而注解方式比较简单,只需要在User类中添加相应的注解即可。
一. Hibernate的注解开发
一.一 创建简单的实体类User
User.java 文件:
package com.yjl.pojo;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
/**
@author: 两个蝴蝶飞
@date: 2018年10月9日 下午8:53:39
@Description Hibernate操作时相应的实体类,实现序列化
*/
public class User implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* @param 主键id 用Integer包装类
* @param userName 用户名
* @param password 密码
* @param sex 性别
* @param age 年龄
* @param birthday 生日
* @param description 相关描述
*/
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String sex;
private Integer age;
private Date birthday;
private String description;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
}
一.二 在User.java中添加相应的注解
一.二.一 添加@Entity注解
直接在类User上使用 @Entity 注解即可。 这个注解@Entity 有一个属性 name,这个name指的是实体类的名称,通常省略不写.
这个这个Entity 注解位于
import javax.persistence.Entity;
下面所有的注解,都是位于这个包下。
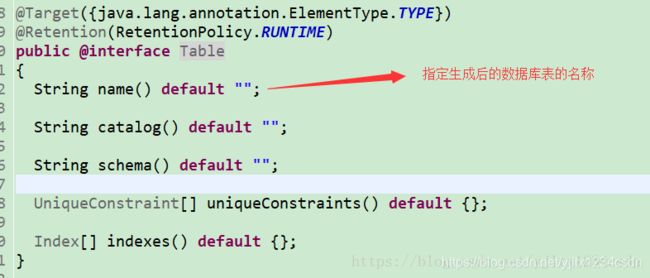
一.二.二 添加@Table 注解
@Table 与@Entity 联合使用。 其中@Table下有一个重要的name属性,这个值指向数据库中表的名称。表示生成后的表名为user. 如果省略不写的话,表示与User实体类名相同。 通常为了可读性,常常写。
联合使用后的User 修饰为:
@Entity
@Table(name="user")
public class User implements Serializable{
}
一.二.三 Id 标识
Id标识时用@Id 注解,默认生成策略是native, 自然的。可以省略不写。 用@GeneratedValue 注解。
@Id //表示是id
@GeneratedValue //表示生成策略是native, 是默认的。
private Integer id;
其中@Id注解为:
@Target({java.lang.annotation.ElementType.METHOD, java.lang.annotation.ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Id {}
@GeneratedValue 注解为:
@Target({java.lang.annotation.ElementType.METHOD, java.lang.annotation.ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface GeneratedValue
{
GenerationType strategy() default GenerationType.AUTO; //strategy 表示生成策略
String generator() default "";
}
其中GenerationType 可以取的值为:
package javax.persistence;
public enum GenerationType
{
TABLE, SEQUENCE, IDENTITY, AUTO; //枚举类型取值
private GenerationType() {}
}
如果是IDENTITY模式的话,那么需要写成:
@Id //表示是id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY) //表示生成策略是IDENTITY
private Integer id;
如果想显式说明的是native的话,可以这样:
@Id //表示是id
@GeneratedValue(generator="_native") //生成策略是native形式
@GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native")
private Integer id;
GeneratedValue与GenericGenerator联合使用。 Value中的generator的值要与Generator中name的值保持一致。
如果想表示是uuid形式的话,可以这样:
@Id //表示是id
@GeneratedValue(generator="_uuid") //生成策略是uuid
@GenericGenerator(name="_uuid",strategy="uuid")
private String uid;
其中GenericGenerator注解为:
@Target({java.lang.annotation.ElementType.PACKAGE, java.lang.annotation.ElementType.TYPE, java.lang.annotation.ElementType.METHOD, java.lang.annotation.ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Repeatable(GenericGenerators.class)
public @interface GenericGenerator
{
String name();
String strategy();
Parameter[] parameters() default {};
}
一.二.四 普通属性注解@Column
普通属性用@Column 常见的配置有:
@Column(name="userName",length=20)
private String userName;
可以直接@Column, 可以省略name,如果省略name的话,表示生成的表中字段与类中的属性名称一致。
其中@Column注解中有一些其他的配置,这样配置主要如下:
@Target({java.lang.annotation.ElementType.METHOD, java.lang.annotation.ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Column
{
String name() default "";
boolean unique() default false;
boolean nullable() default true;
boolean insertable() default true;
boolean updatable() default true;
String columnDefinition() default "";
String table() default "";
int length() default 255;
int precision() default 0;
int scale() default 0;
}
其中name表示生成表中字段的名称,如果省略不写的话,与类中属性值保持一致。
unique 表示是否是唯一的,默认为false. 如果为true,则表示唯一,是唯一约束关系。
nullable 表示是否可以为空,默认为true, 如果为false,表示不能为空。
insertable 表示是否可以插入,默认为true. 这个用的不多.
updateable 表示是否可以修改,默认为true. 如果为false的话,表示这个字段不能被修改。如sex字段。 一但被插入进去之后,就不能进行相应的修改了。
columnDefinition 表示列类型,即是int,还是varchar,date等。 但兼容性不好。
length 表示长度,即字段的长度。
precision 和scale共同构成了精度,如double类型时,precision 指的是总长度,scale 指的是位数。 即double(6,2) 样式的。
precision=6, scale=2。
一.二.五 修饰日期形式 @Temporal
如果是日期Date,Time,Timestamp 等形式,不能用普通的@Column 注解了,要用一个@Temporal 注解 。 中文意思是时间。
@Temporal(TemporalType.TIMESTAMP)
private Date birthday;
其中Temporal 注解:
@Target({java.lang.annotation.ElementType.METHOD, java.lang.annotation.ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(value=RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Temporal
{
TemporalType value();
}
而TemporalType是枚举,取值是:
public enum TemporalType
{
DATE, TIME, TIMESTAMP; //对应的是数据库中的日期,时间,时间戳
private TemporalType() {}
}
常用的值是TIMESTAMP. 其中value 可以省略。
一.二.六 指定类型 @Type
修饰列的类型,要用@Type 注解 。这个注解不像其他注解位于javax.persistence 包下
而是位于org.hibernate.annotations,与GenericGenerator 注解位于的包下相同。
@Type(type = "string")
private String description;
其中Type为:
@Target({java.lang.annotation.ElementType.FIELD, java.lang.annotation.ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Type
{
String type();
Parameter[] parameters() default {};
}
type="类型名称",与Hibernate中XML中的type 值相同,可以取double,int,long,string等常见的类型。 如果是Date,使用上面的@Temporal注解。
一.二.七 忽略注解@Transien
如果不想让User中的某个属性生成为表中的字段,可以在这个上面添加一个@Transien, 这样就可以避免生成表中的字段了。 如常见的User中的可能多余的属性,如确认密码,验证码等。
一.二.八 综合后的注解User.java
package com.yjl.pojo;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import javax.persistence.Temporal;
import javax.persistence.TemporalType;
import javax.persistence.Transient;
import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator;
import org.hibernate.annotations.Type;
/**
@author: 两个蝴蝶飞
@date: 2018年10月9日 下午8:53:39
@Description Hibernate操作时相应的实体类,实现序列化
*/
@Entity
@Table(name="user")
public class User implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* @param 主键id 用Integer包装类
* @param userName 用户名
* @param password 密码
* @param sex 性别
* @param age 年龄
* @param description 相关描述
*/
/**
* 主键生成策略为native
*/
@Id
@GeneratedValue(generator="_native")
@GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native")
private Integer id;
/**
* 类名为userName,长度是20,表示唯一
*/
@Column(name="userName",length=20,unique=true)
private String userName;
/**
* 去除password的生成
*/
@Transient
private String password;
/*
* 设置性别不为空,默认属性值为sex
*/
@Column(nullable=false)
private String sex;
/*
* int 类型,默认生成列属性值为age
*/
@Type(type="int")
private Integer age;
@Temporal(TemporalType.TIMESTAMP)
private Date birthday;
@Type(type = "string")
@Column(name="description",length=100)
private String description;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
}
一.三. hibernate.cfg.xml中配置引入.java注解文件
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hibernate?characterEncoding=utf8
root
abc123
org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect
true
update
true
一.四 测试运行
运行第三章的saveTest()方法
@Test
public void saveTest(){
//1 得到Session对象
Session session=HibernateUtil.getSession();
//2 打开事务
Transaction tran=session.beginTransaction();
//3 实例化对象
User user=new User();
user.setUserName("两个蝴蝶飞");
user.setSex("男");
user.setAge(24);
user.setPassword("123456");
user.setDescription("一个有梦想的程序员");
//4利用save()方法进行相应的保存
session.save(user);
//5 提交事务
tran.commit();
//6 关闭session
session.close();
}
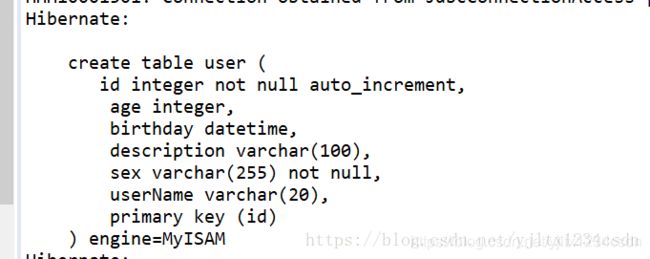
一.五 观察控制台日志输出
添加约束:
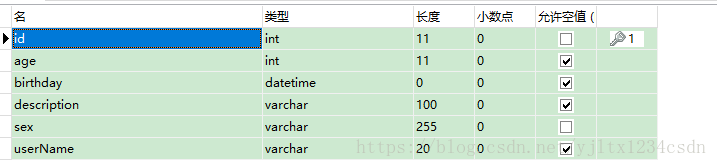
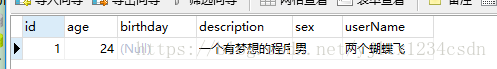
一.六 观察数据表
创建的结构正常. 没有生成password字段。
使用注解方式开发Hibernate,自动生成表正常。
二. Hibernate事务处理
具体代码形式为:
//1 得到Session对象
Session session=HibernateUtil.getSession();
//2 打开事务
Transaction tran=session.beginTransaction();
try{
//3 实例化对象
User user=new User();
user.setUserName("两个蝴蝶飞");
user.setSex("男");
user.setAge(24);
user.setPassword("123456");
user.setDescription("一个有梦想的程序员");
//4利用save()方法进行相应的保存
session.save(user);
//5 提交事务
tran.commit();
}catch(Exception e){
//出错了,进行回滚事务.
tran.rollback();
}finally{
//6 关闭session
session.close();
}
利用try ... catch ...finally 来进行处理异常。
谢谢您的观看,如果喜欢,请关注我,再次感谢 !!!