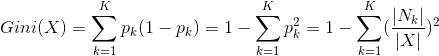决策树Decision Tree
决策树是一种有监督机器学习算法,可用于解决分类/回归问题,主要用于分类。决策树的算法主要有ID3算法、C4.5、CART三种。这些算法都是为了找到最合适的特征作为分裂属性,不断迭代直到找到整个决策树。
ID3算法:信息增益最大化。用信息增益来判断当前节点应该选用哪个特征来构建决策树,信息增益越大,越适合用来分类。
熵代表了事件的不确定性,熵越大,不确定性越大。ID3算法为计算每一个特征Y对数据集X的信息增益,信息增益最大值对应的特征作为分裂属性
随机变量X的熵表示为:表示X的不确定性
多个变量的联合熵:
根据联合熵的公式可以得到条件熵:表示已知Y后X的不确定性,![]() 表示特征Y中的不同取值情况(比如Y表示天气特征,
表示特征Y中的不同取值情况(比如Y表示天气特征,![]() 为阴天、晴天、雨天等)。
为阴天、晴天、雨天等)。
则信息增益表示为:表示已知Y后X的不确定性减少的程度
![]()
由于取值比较多的特征比取值少的特征信息增益大(比如成绩有ABCD四种,而出勤只有积极和不积极两种,成绩的信息增益会比较大),所以ID3算法倾向于选择取值多的特征作为分裂属性,C4.5可以解决这个问题。
C4.5:信息增益率。X为数据集,Y为某一特征。
CART(classfication and regression):基尼系数。为了避免过多的对数运算,CART采用基尼系数代替信息增益比,基尼系数代表模型的不纯度,基尼系数越小,特征越好。
样本X分为K类,基尼系数计算如下:![]() 。
。![]() 为X中k类的数目。
为X中k类的数目。
在决策树中基尼系数计算过程如下:表示根据Y将X分成了n个部分。
决策树停止分裂的条件:节点数小于某个指定值时;熵或基尼系数小于设定阈值;决策树深度达到设定的最大深度;所有特征使用完毕。
ID3和CART存在偏向细小分割,导致决策树过于复杂可能出现过拟合,需要进行优化,优化方法主要有剪枝和组合树。
随机森林:随机森林集成了多棵决策树,每棵决策树有一个分类结果,将投票次数最多的类别作为最终输出。随机森林可以处理大量的输入变数,可以产生高准确度的分类器。
随机森林算法步骤:
1)假设训练集的大小为N,对每棵树,有放回地随机抽取N个样本(包括可能重复的样本)
2)假设每个样本的特征为M,随机地从M中抽取m个特征,每次树进行分裂时,从这m个特征中选取最优的特征
3)对每棵决策树选定样本和特征后,使用CART进行计算,不剪枝
4)得到决策树后,对每棵树的输出进行投票,投票最多的类作为随机森林的决策。
python的sklearn实现分类和回归:
#决策树用于分类
import numpy as np
from sklearn import tree
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from pydotplus.graphviz import graph_from_dot_data
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
iris=datasets.load_iris()
X=iris.data
y=iris.target
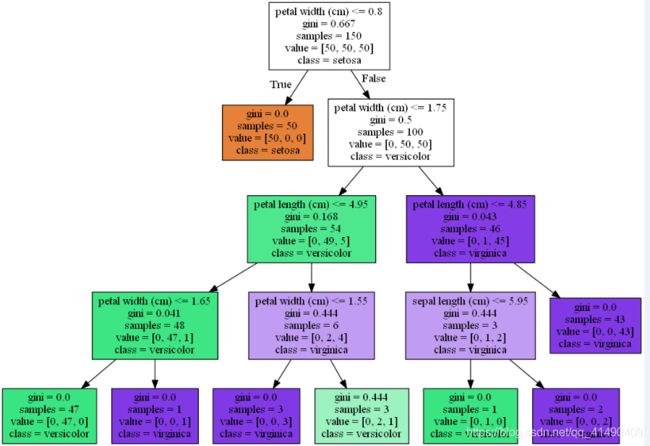
clf=tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=4,criterion='gini',random_state=1)#criterion='gini'/'entropy'
clf.fit(X,y)
# score=cross_val_score(clf,X,y,cv=10)
# acc=score.mean()
# print(acc)
dot_data=tree.export_graphviz(clf,filled=True,class_names=iris.target_names,feature_names=iris.feature_names,out_file=None)
graph=graph_from_dot_data(dot_data)
graph.write_png('tree.png')
#回归
from sklearn import tree
from sklearn import datasets
boston=datasets.load_boston()
data=boston.data[:,12]
y=boston.target
sort_idx=data.flatten().argsort()
X=data[sort_idx].reshape(-1,1)
y=y[sort_idx]
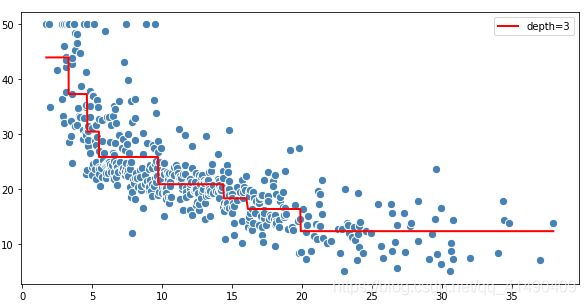
clf=tree.DecisionTreeRegressor(criterion='mse',max_depth=3)
clf.fit(X,y)
y_pre=clf.predict(X)
plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
plt.scatter(X,y,c='steelblue',edgecolor='white',s=70)
plt.plot(X,y_pre,color='r',linewidth=2)
plt.legend(['depth=3',])
plt.show()from math import log
import operator
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
def creatDataSet():
dataSet=[[0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 'yes'],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'],
[2, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'],
[2, 0, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[2, 1, 0, 2, 'yes'],
[2, 0, 0, 0, 'no']]
labels=['年龄','有工作','有自己的房子','信贷情况']
return dataSet,labels
def calcShannonEnt(dataSet):
numEntries=len(dataSet)
labelcounts={}
for featVec in dataSet:
currentLabel=featVec[-1]
if currentLabel not in labelcounts.keys():
labelcounts[currentLabel]=0
labelcounts[currentLabel]+=1
shannonEnt=0.0
for key in labelcounts:
prob=float(labelcounts[key])/numEntries
shannonEnt-=prob*log(prob,2)
return shannonEnt
def splitDataSet(dataSet,axis,value):
retDataSet=[]
for featVec in dataSet:
if featVec[axis]==value:
reduceFeatVec=featVec[:axis]
reduceFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:])
retDataSet.append(reduceFeatVec)
return retDataSet
def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet):
numFeatures=len(dataSet[0])-1
baseEntropy=calcShannonEnt(dataSet)
bestInfoGain=0.0
bestFeature=-1
for i in range(numFeatures):
featList=[example[i] for example in dataSet]
uniqueVals=set(featList)
newEntropy=0.0
for value in uniqueVals:
subDataSet=splitDataSet(dataSet,i,value)
prob=len(subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet))
newEntropy+=prob*calcShannonEnt((subDataSet))
infoGain=baseEntropy-newEntropy
print("第%d个特征的增益为:%.3f"%(i,infoGain))
if (infoGain>bestInfoGain):
bestInfoGain=infoGain
bestFeature=i
return bestFeature
def majortyCnt(classList):
classCount={}
for vote in classList:
if vote not in classCount.keys():
classCount[vote]=0
classCount[vote]+=1
sortedClassCount=sorted(classCount.items(),key=operator.itemgetter(1),reverse=True)
return sortedClassCount[0][0]
def createTree(dataSet,labels,featLabels):
classList=[example[-1] for example in dataSet]
if classList.count(classList[0])==len(classList):
return classList[0]
if len(dataSet[0])==1:
return majortyCnt(classList)
bestFeat=chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet)
bestFeatLabel=labels[bestFeat]
featLabels.append(bestFeatLabel)
myTree={bestFeatLabel:{}}
del(labels[bestFeat])
featValues=[example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet]
uniqueVals=set(featValues)
for value in uniqueVals:
myTree[bestFeatLabel][value]=createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet,bestFeat,value),labels,featLabels)
return myTree
def getNumLeafs(myTree):
numLeafs=0
firstStr=next(iter(myTree))
secondDict=myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':
numLeafs+=getNumLeafs(secondDict[key])
else:
numLeafs+=1
return numLeafs
def getTreeDepth(mTree):
maxDepth=0
firstStr=next(iter(myTree))
secondDict=myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dic':
thisDepth=1+getTreeDepth(secondDic[key])
else:
thisDepth=1
if thisDepth>maxDepth:
maxDepth=thisDepth
return maxDepth
def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType):
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-")
font = FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc", size=14)
createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction',
xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction',
va="center", ha="center", bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args, FontProperties=font)
def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString):
xMid = (parentPt[0]-cntrPt[0])/2.0 + cntrPt[0]
yMid = (parentPt[1]-cntrPt[1])/2.0 + cntrPt[1]
createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30)
def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):
decisionNode = dict(boxstyle="sawtooth", fc="0.8")
leafNode = dict(boxstyle="round4", fc="0.8")
numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree)
depth = getTreeDepth(myTree)
firstStr = next(iter(myTree))
cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs))/2.0/plotTree.totalW, plotTree.yOff)
plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt)
plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode)
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0/plotTree.totalD
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':
plotTree(secondDict[key],cntrPt,str(key))
else:
plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalW
plotNode(secondDict[key], (plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, leafNode)
plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, str(key))
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalD
def createPlot(inTree):
fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white')#创建fig
fig.clf()#清空fig
axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[])
createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops)
plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree))
plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree))
plotTree.xOff = -0.5/plotTree.totalW; plotTree.yOff = 1.0
plotTree(inTree, (0.5,1.0), '')
plt.show()
def classify(inputTree,fratLabels,testVec):
firstStr=next(iter(inputTree))
secondDict=inputTree[firstStr]
featIndex=featLabels.index(firstStr)
for key in secondDict.keys():
if testVec[featIndex]==key:
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':
classLabel=classify(secondDict[key],fratLabels,testVec)
else:
classLabel=secondDict[key]
return classLabel
if __name__=='__main__':
dataSet,labels=creatDataSet()
featLabels=[]
myTree=createTree(dataSet,labels,featLabels)
print(myTree)
createPlot(myTree)
testVec=[0,1]
result=classify(myTree,featLabels,testVec)
print(result)算法实现原理参考:https://blog.csdn.net/jiaoyangwm/article/details/79525237