Java线程等待中Thread.sleep()、Object.wait()、LockSupport.park、UNSAFE.park()的原理与区别
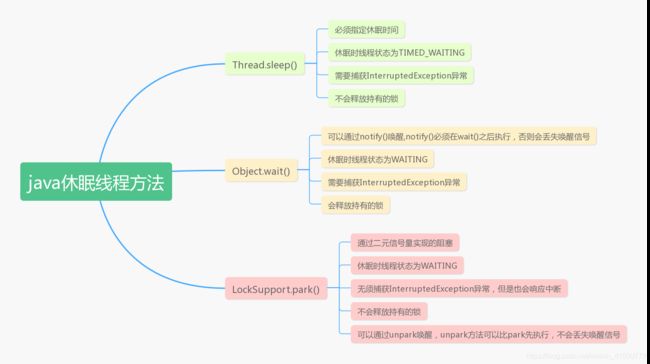
Thread.sleep()
源码如下:
public static native void sleep(long millis) throws InterruptedException;
public static void sleep(long millis, int nanos)
throws InterruptedException {
if (millis < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
}
if (nanos < 0 || nanos > 999999) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"nanosecond timeout value out of range");
}
if (nanos >= 500000 || (nanos != 0 && millis == 0)) {
millis++;
}
sleep(millis);
}
说明:
- Thread.sleep()必须指定休眠时间,所以线程状态为TIMED_WAITING。
- 如果休眠时发生中断,会抛出InterruptedException异常,并必须处理。
- 等待期间,不会释放所持有的锁
Object.wait()
源码如下:
public final native void wait(long timeout) throws InterruptedException;
public final void wait(long timeout, int nanos) throws InterruptedException {
if (timeout < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
}
if (nanos < 0 || nanos > 999999) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"nanosecond timeout value out of range");
}
if (nanos > 0) {
timeout++;
}
wait(timeout);
}
public final void wait() throws InterruptedException {
wait(0);
}
说明:
- 线程状态为WAITING表示一直等待,通过Object.notify()唤醒。
- 如果休眠时发生中断,会抛出InterruptedException异常,并必须处理。
- 等待期间,会释放所持有的锁
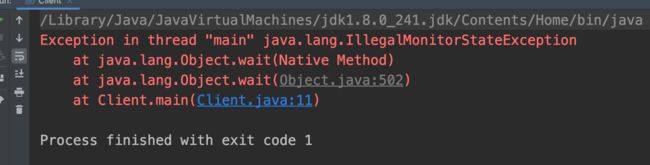
- 必须获取到对象锁时才可以进入等待状态,否则会抛出java.lang.IllegalMonitorStateException异常。
错误使用示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object waitObject = new Object();
try {
//没获取到waitObject的锁,调用该方法抛出IllegalMonitorStateException异常
waitObject.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
wait释放锁示例:
public class ObjeactWaitDemo {
public static final Object WAIT_OBJECT = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MyThread1().start();
new MyThread2().start();
}
public static class MyThread1 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
synchronized (WAIT_OBJECT) {
System.out.println("线程1获取锁" + System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("线程1结束sleep" + System.currentTimeMillis());
WAIT_OBJECT.wait();
System.out.println("线程1唤醒时间" + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static class MyThread2 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (WAIT_OBJECT) {
System.out.println("线程2获取锁" + System.currentTimeMillis());
// 唤醒
WAIT_OBJECT.notify();
System.out.println("线程2结束" + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
}
}
Output:
线程1获取锁 1583052064070
线程1结束sleep 1583052065070
线程2获取锁 1583052065070
线程2结束 1583052065070
线程1唤醒时间 1583052065070
LockSupport.park()与UNSAFE.park()
源码如下:
public static void park() {
UNSAFE.park(false, 0L);
}
public static void unpark(Thread thread) {
if (thread != null)
UNSAFE.unpark(thread);
}
public native void unpark(Thread jthread);
// true为毫秒
// false为纳秒
public native void park(boolean isAbsolute, long time);
说明:
- 线程状态为WAITING。
- 如果休眠时发生中断,不会抛出InterruptedException异常。也会响应中断。当外部线程对阻塞线程调用interrupt方法时,park阻塞的线程也会立刻返回。
- 等待期间,不会释放所持有的锁。
- 如果先调用unpark,会导致许可为1,当调用park时则直接返回导致并不会阻塞线程。看下面代码。
先调用unpark在调用park情况:
直接输出结结果,park生效会等待30秒
public class Demo {
public static Unsafe unsafe;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Field f = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
f.setAccessible(true);
unsafe = (Unsafe) f.get(null);
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
myThread.start();
System.out.println(100);
}
public static class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(1);
// 注视这里park生效会等待30秒
unsafe.unpark(Thread.currentThread());
// 先unpark会让park失效
unsafe.park(false, 30000000000L);
System.out.println(2);
}
}
}
Output:
100
1
2
原理:
LockSupport.park() 通过UNSAFE.park来实现。在Linux系统下,是用的Posix线程库pthread中的mutex(互斥量),condition(条件变量)来实现的。mutex和condition保护了一个_counter的变量,当park时,这个变量被设置为0,当unpark时,这个变量被设置为1。每个Java线程都有一个Parker实例,Parker实际上用Posix的mutex,condition来实现的。
class Parker : public os::PlatformParker {
private:
//表示许可
volatile int _counter ;
Parker * FreeNext ;
JavaThread * AssociatedWith ; // Current association
public:
Parker() : PlatformParker() {
//初始化_counter
_counter = 0 ;
FreeNext = NULL ;
AssociatedWith = NULL ;
}
protected:
~Parker() { ShouldNotReachHere(); }
public:
void park(bool isAbsolute, jlong time);
void unpark();
// Lifecycle operators
static Parker * Allocate (JavaThread * t) ;
static void Release (Parker * e) ;
private:
static Parker * volatile FreeList ;
static volatile int ListLock ;
};
park步骤:
void Parker::park(bool isAbsolute, jlong time) {
if (_counter > 0) {
//已经有许可了,用掉当前许可
_counter = 0 ;
//使用内存屏障,确保 _counter赋值为0(写入操作)能够被内存屏障之后的读操作获取内存屏障事前的结果,也就是能够正确的读到0
OrderAccess::fence();
//立即返回
return ;
}
Thread* thread = Thread::current();
assert(thread->is_Java_thread(), "Must be JavaThread");
JavaThread *jt = (JavaThread *)thread;
if (Thread::is_interrupted(thread, false)) {
// 线程执行了中断,返回
return;
}
if (time < 0 || (isAbsolute && time == 0) ) {
//时间到了,或者是代表绝对时间,同时绝对时间是0(此时也是时间到了),直接返回,java中的parkUtil传的就是绝对时间,其它都不是
return;
}
if (time > 0) {
//传入了时间参数,将其存入absTime,并解析成absTime->tv_sec(秒)和absTime->tv_nsec(纳秒)存储起来,存的是绝对时间
unpackTime(&absTime, isAbsolute, time);
}
//进入safepoint region,更改线程为阻塞状态
ThreadBlockInVM tbivm(jt);
if (Thread::is_interrupted(thread, false) || pthread_mutex_trylock(_mutex) != 0) {
//如果线程被中断,或者是在尝试给互斥变量加锁的过程中,加锁失败,比如被其它线程锁住了,直接返回
return;
}
//这里表示线程互斥变量锁成功了
int status ;
if (_counter > 0) {
// 有许可了,返回
_counter = 0;
//对互斥变量解锁
status = pthread_mutex_unlock(_mutex);
assert (status == 0, "invariant") ;
OrderAccess::fence();
return;
}
#ifdef ASSERT
// Don't catch signals while blocked; let the running threads have the signals.
// (This allows a debugger to break into the running thread.)
//debug用
sigset_t oldsigs;
sigset_t* allowdebug_blocked = os::Linux::allowdebug_blocked_signals();
pthread_sigmask(SIG_BLOCK, allowdebug_blocked, &oldsigs);
#endif
//将java线程所拥有的操作系统线程设置成 CONDVAR_WAIT状态 ,表示在等待某个条件的发生
OSThreadWaitState osts(thread->osthread(), false /* not Object.wait() */);
//将java的_suspend_equivalent参数设置为true
jt->set_suspend_equivalent();
// cleared by handle_special_suspend_equivalent_condition() or java_suspend_self()
if (time == 0) {
//把调用线程放到等待条件的线程列表上,然后对互斥变量解锁,(这两是原子操作),这个时候线程进入等待,当它返回时,互斥变量再次被锁住。
//成功返回0,否则返回错误编号
status = pthread_cond_wait (_cond, _mutex) ;
} else {
//同pthread_cond_wait,只是多了一个超时,如果超时还没有条件出现,那么重新获取胡吃两然后返回错误码 ETIMEDOUT
status = os::Linux::safe_cond_timedwait (_cond, _mutex, &absTime) ;
if (status != 0 && WorkAroundNPTLTimedWaitHang) {
//WorkAroundNPTLTimedWaitHang 是JVM的运行参数,默认为1
//去除初始化
pthread_cond_destroy (_cond) ;
//重新初始化
pthread_cond_init (_cond, NULL);
}
}
assert_status(status == 0 || status == EINTR ||
status == ETIME || status == ETIMEDOUT,
status, "cond_timedwait");
#ifdef ASSERT
pthread_sigmask(SIG_SETMASK, &oldsigs, NULL);
#endif
//等待结束后,许可被消耗,改为0 _counter = 0 ;
//释放互斥量的锁
status = pthread_mutex_unlock(_mutex) ;
assert_status(status == 0, status, "invariant") ;
// If externally suspended while waiting, re-suspend
if (jt->handle_special_suspend_equivalent_condition()) {
jt->java_suspend_self();
}
//加入内存屏障指令
OrderAccess::fence();
}
unpark步骤:
当unpark时,直接设置_counter为1,再unlock mutex返回。如果_counter之前的值是0,则还要调用pthread_cond_signal唤醒在park中等待的线程:
void Parker::unpark() {
int s, status ;
//给互斥量加锁,如果互斥量已经上锁,则阻塞到互斥量被解锁
//park进入wait时,_mutex会被释放
status = pthread_mutex_lock(_mutex);
assert (status == 0, "invariant") ;
//存储旧的_counter
s = _counter;
//许可改为1,每次调用都设置成发放许可
_counter = 1;
if (s < 1) {
//之前没有许可
if (WorkAroundNPTLTimedWaitHang) {
//默认执行 ,释放信号,表明条件已经满足,将唤醒等待的线程
status = pthread_cond_signal (_cond) ;
assert (status == 0, "invariant") ;
//释放锁
status = pthread_mutex_unlock(_mutex);
assert (status == 0, "invariant") ;
} else {
status = pthread_mutex_unlock(_mutex);
assert (status == 0, "invariant") ;
status = pthread_cond_signal (_cond) ;
assert (status == 0, "invariant") ;
}
} else {
//一直有许可,释放掉自己加的锁,有许可park本身就返回了
pthread_mutex_unlock(_mutex);
assert (status == 0, "invariant") ;
}
}