SpringBoot入门(1)RESTful风格api基本注解使用,Mockito测试,Swagger2文档
啊快入职了还是把框架学一下…虽然还不晓得是啥方向…
俺是跟着B站字母哥的视频梳理的(感觉他的视频比较精简的亚子)
概念知识
不得不说SpringBoot写CRUD还真比不用框架方便好多。
首先这玩意与Spring不同的地方在于它内置了Tomcat,所以无需另外启动Tomcat,而且可以自动装配(然后这玩意就又是个面试考点…算了以后再学),这就又比Spring方便不少。
只需引入一个Spring Boot Starter基本上就可以干活了,它引入了一些常用的类库。

SpringBoot若使用Maven,它的POM文件默认继承了spring-boot-starter-parent,方便对导入jar包进行版本控制,避免出现冲突。
方(偷)便(懒)插件(本机为IDEA)
lombok
这个介绍的应该很多,首先在Settings->Plugins中安装Lombok插件,然后再导入相关的Lombok包。
经常使用的的注解有:
1.@Data:生成get/set方法
2.@Buider:生成建造者模式
3.@AllArgsConstructor/@NoArgsConstructor:生成全域/空参构造器
4.@Slf4j:自动引入Logger日志常量
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
lombok中的注解是通过前端编译器(javac)在生成语法树时,扫描到如果存在注解,将对应的语法树插入到现语法树中,然后生成字节码。
devtools实现热加载
使用俩类加载器,一个用于加载依赖(这些一般不会变),一个用于加载自编代码。
导入以下jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
然后使用快捷键Ctrl+shift+alt+/,点击
选中
![]() 然后每次改动代码之后仅需要使用快捷键ctrl+F9即可重新编译
然后每次改动代码之后仅需要使用快捷键ctrl+F9即可重新编译
Codota
代码补全与可能的补全方式,同时提供一些类库的常见使用。
Auto filling Java call arguments
自动填充方法参数
点击ALT+回车,选中![]()
GsonFormat4DataBinding
将JSON转换为实体类
点击alt+D
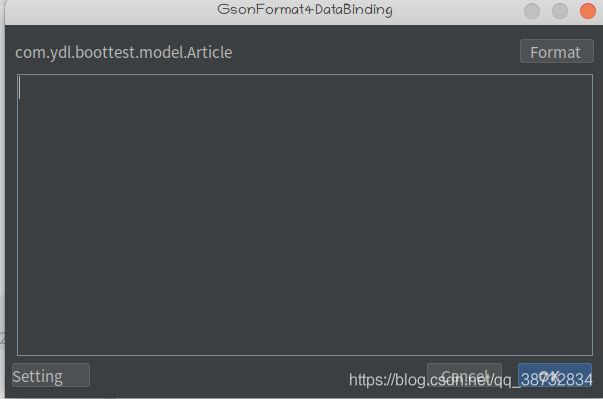 将JSON粘贴到其中,选中OK即可。
将JSON粘贴到其中,选中OK即可。
Rainbow Brackets
彩虹括号,方便看少了哪层括号
Maven Helper
方便看是否存在Jar包冲突
选中POM.xml下方多了一个Dependency Analyer

Key promoter X
方便记忆快捷键
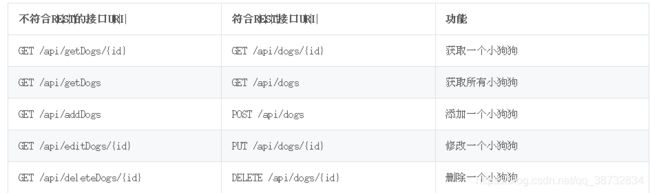
RESTful风格的API
SpringBoot常用注解
HTTP协议的四种传参方式
@RequestBody
修饰请求参数,注解用于接收HTTP的body,默认使用JSON格式,可用于复杂数据的传参
public AjaxResponse saveArticle(@RequestBody Article article)
@ResponseBody
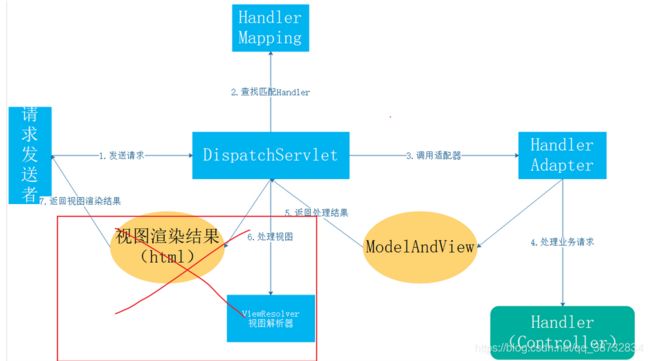
修饰返回值,说明携带响应数据,加上这个注解就说明为一个数据接口,不会走视图解析
public @ResponseBody AjaxResponse saveArticle(@RequestBody Article article)
@RequestMapping
用于标注服务端点。
@RequestMapping("/rest")
public class ArticleController

也有指定的方法的@DeleteMapping@PutMappin@PostMapping@GetMapping
@PostMapping("/articles")
public AjaxResponse saveArticle(@RequestBody Article article)
@RestController与@Controller
@RestController
public class ArticleController
@RestController: 说明被标注的类为Spring的Bean,需要被注入到Spring上下文环境中。所有被标注@RequestMapping的方法都是HTTP服务端点。
@RestController: 相当于@Controller+n×@ResponseBody
@PathVariable 与@RequestParam
@PathVariable: 将url后的参数传入API中
@GetMapping("/articles/{id}")
public AjaxResponse getArticle(@PathVariable("id") Integer id)
**@RequestParam:**通过表单或者ajax模拟表单传参
@DeleteMapping("/articles")
public AjaxResponse deleteArticle(@PathParam("id") Integer id)
CRUD测试代码
@Slf4j
//所有的方法都对外提供WEB服务
//默认给,每个方法加上@ResponseBody注解,表示响应json格式的内容
//@Controller+@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/rest")
@RestController
public class ArticleController {
// @Resource
// ArticleService articleService;
//查询一篇文章根据id
//@RequestMapping(value = "/articles/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
@GetMapping("/articles/{id}")
public AjaxResponse getArticle(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
Article article = Article.builder().id(id).email("[email protected]").firstName("y").lastName("dl").createTime(new Date()).build();
log.info("article:"+article);
AjaxResponse ajaxResponse = AjaxResponse.success(article);
return ajaxResponse;
}
@PostMapping("/articles")
public AjaxResponse saveArticle(@RequestBody Article article){
log.info("article:"+article);
//AjaxResponse ajaxResponse = AjaxResponse.success(article,articleService.saveArticle(article));
AjaxResponse ajaxResponse = AjaxResponse.success(article);
return ajaxResponse;
}
//修改
//@RequestMapping(value = "/articles",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@PutMapping("/articles")
public AjaxResponse updateArticle(@RequestBody Article article){
if(article.getId() == null){
//TODO 跑出一个自定义的异常
}
log.info("article:"+article);
AjaxResponse ajaxResponse = AjaxResponse.success(article);
return ajaxResponse;
}
//删除
// @RequestMapping(value = "/articles/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@DeleteMapping("/articles")
public AjaxResponse deleteArticle(@PathParam("id") Integer id){
log.info("id:"+id);
return AjaxResponse.success(null,"删除成功");
}
}
MVC中的M
之前一直以为M是指着实体模型,上次看慕课上一个项目才知道(课挺好的,不过有点名不副实,也还理解毕竟免费的),M指的是领域模型,在不同的领域,由于需要展示的数据不一样,所以需要不同的领域模型。
比如展现给前端的模型就不需要密码等敏感的个人信息,这时就需要一层视图模型。
而在中间处理中间数据为了方便需要将用户常规数据与密码建立到一个类中(一般这些信息是分表存放的),所以需要将两个数据库对应的实体模型融合到一起。
统一返回信息
这样可以携带上附带状态码,方便前端操作。
public class CommonReturnType {
private String status;
private Object data;
//定义一个通用的创建方法
public static CommonReturnType create(Object result){
return CommonReturnType.create(result,"success");
}
public static CommonReturnType create(Object result,String status){
CommonReturnType type = new CommonReturnType();
type.setStatus(status);
type.setData(result);
return type;
}
public String getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(String status) {
this.status = status;
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
统一错误信息
还是上次的慕课上那个项目,有个提示就是将错误信息,使用枚举进项管理,俺感觉是个不错的思路,这样不仅调试时清晰,返回给前端的错误或者异常信息也比较方便自定义。
比如:
public enum EmBusinessError implements CommonError {
//通用错误类型
PARAMETER_VALIDATION_ERROR(100001,"参数不合法"),
UNKNOWN_ERROR(100002,"未知错误"),
USER_NOT_EXIST(200001,"用户信息不存在"),
USER_LOGIN_FAIL(200002,"用户手机号或密码不正确"),
USER_NOT_LOGIN(200003,"用户还未登录"),
STOCK_NOT_ENOUGH(300001,"库存不足");
private int errCode;
private String errMsg;
EmBusinessError(int errCode, String errMsg) {
this.errCode = errCode;
this.errMsg = errMsg;
}
@Override
public int getErrCode() {
return this.errCode;
}
@Override
public String getErrMsg() {
return this.errMsg;
}
@Override
public CommonError setErrMsg(String errMsg) {
this.errMsg = errMsg;
return this;
}
}
JSON< —— > 对象
com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper -> writeValueAsString方法 实现对象转JSON
com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper -> readValue方法 实现JSON转对象
void testJackson() throws JsonProcessingException {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
List<Integer> ids= new ArrayList<>();
ids.add(1);
ids.add(2);
Article article = Article.builder().id(1).firstName("YDL").lastName("BD").email("93923").createTime(new Date()).ids(ids).build();
String jsonStr = mapper.writeValueAsString(article);
System.out.println(jsonStr);
Article article1 = mapper.readValue("{\"createTime\":\"2020/07/11 16:22:51\",\"ID\":1,\"firstName\":\"YDL\",\"lastName\":\"BD\",\"email\":\"93923\",\"ids\":[1,2]}",
Article.class);
System.out.println(article1);
}
JSON对象的一些其他常用注解,可在对外输出的Json生效。
**@JsonIgnore:**忽视某个属性
**@JsonProperty(“ID”):**给某个属性起别名
**@JsonFormat(pattern = “yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss”,timezone = “GMT+8”):**更改某个属性(这里是时间)的格式
**@JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL):**如果某个属性不为NULL则才包含它,设定包含条件。
**@JsonPropertyOrder(value = {“createTime”,“id”}):**设定Json中属性的顺序,默认是类中的顺序,这里就设定了创建时间优先于id,其他顺序保持不变。
@Data
@Builder
@JsonPropertyOrder(value = {"createTime","id"})
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Article {
/**
* firstName : Brett
* lastName : McLaughlin
* email : [email protected]
*/
@JsonIgnore
@JsonProperty("ID")
private Integer id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private String email;
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss",timezone = "GMT+8")
private Date createTime;
@JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL)
private List<Integer> ids;
}
Mockito测试
如果想要实现编码的方式测试,就需要使用Mockito了。
@Slf4j
public class ArticleRestControllerTest {
//标注此注解,就可以去除BeforeAll方法了
//@Resource
private static MockMvc mockMvc;
//在执行本类方法保证都会优先执行此方法
@BeforeAll
static void setUp(){
Object[] controllers;
//初始化
mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.standaloneSetup(new ArticleController()).build();
}
@Test
public void saveArticle() throws Exception {
//传入的JSON
String article = "{\"createTime\":\"2020/07/11 16:27:36\",\"ID\":1,\"firstName\":\"YDL\",\"lastName\":\"BD\",\"email\":\"93923\",\"ids\":[1,2]}";
MvcResult mvcResult = mockMvc.perform(
MockMvcRequestBuilders.request(HttpMethod.POST,"/rest/articles").
contentType("application/json").content(article)
//断言某状态是否为预期
).andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.data.lastName").value("BD"))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.data.firstName").value("YDL"))
//打印并返回
.andDo(MockMvcResultHandlers.print()).andReturn();
mvcResult.getResponse().setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
log.info(mvcResult.getResponse().getContentAsString());
}
}
如果有时候不同的接口由不同的程序员完成,未完成那部分不能很好的测试,则就无法使用实际测试或者使用POSTMAN测试,这时候也需要使用Mockito
@Slf4j
//启动Spring容器的上下文,如果不提供该注解就只能测试Controller层
@SpringBootTest
//自动构建MockMvc
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
//该注解功能与SpringBootTest类似,不过只加载配置的bean,而SpringBootTest加载所有的类,不可与@SpringBootTest一起用
//@WebMvcTest(ArticleController.class)
//提供容器环境
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
public class ArticleRestControllerTest3 {
@Resource
private MockMvc mockMvc;
//注明为一个虚拟类(接口)
@MockBean
private ArticleService articleService;
// @BeforeAll
// static void setUp(){
// Object[] controllers;
// mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.standaloneSetup(new ArticleController()).build();
// }
@Test
public void saveArticle() throws Exception {
String article = "{\"createTime\":\"2020/07/11 16:27:36\",\"ID\":1,\"firstName\":\"YDL\",\"lastName\":\"BD\",\"email\":\"93923\",\"ids\":[1,2]}";
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
Article articleObj = objectMapper.readValue(article,Article.class);
//打桩,预设对应该接口方法返回值
when(articleService.saveArticle(articleObj)).thenReturn("ok");
MvcResult mvcResult = mockMvc.perform(
MockMvcRequestBuilders.request(HttpMethod.POST,"/rest/articles").
contentType("application/json").content(article)
).andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk()).andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath(".message").value("成功"))
.andDo(MockMvcResultHandlers.print()).andReturn();
mvcResult.getResponse().setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
log.info(mvcResult.getResponse().getContentAsString());
}
}
使用Swagger2生成文档
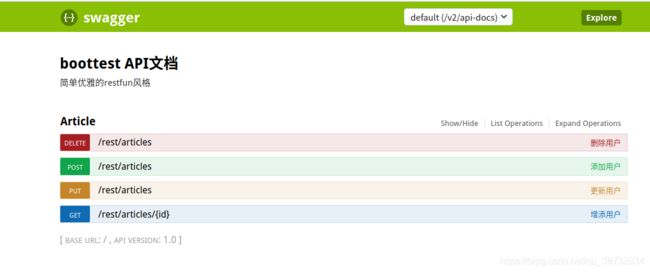

有点漂亮呀,使用Swagger2的好处在于及时和便利,几个注解就完事了。
首先导入如下jar包
io.springfox
springfox-swagger-ui
2.6.1
io.github.swagger2markup
swagger2markup
1.3.1
然后创建配置类
//标注为配置类
@Configuration
//标注为Swagger配置类
@EnableSwagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).
apiInfo(apiInfo()).select().apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.ydl.boottest")).
paths(PathSelectors.regex("/rest/.*")).build();
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
//设置标题,描述,服务器Url,版本号
return new ApiInfoBuilder().title("boottest API文档").description("简单优雅的restfun风格").
termsOfServiceUrl("NO terms of service").version("1.0").build();
}
}
可能一些朋友注意到了里面存在一些自定义的中文注释,那么这个怎么实现的呢?
比如删除方法就如下所示
//描述API
@ApiOperation(value = "删除用户",notes = "删除用户信息",tags = "Article",httpMethod = "DELETE")
//描述参数
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "article",value = "内容主体对象",required = true,dataType = "String")
})
//必填相关的返回类型,要不然try out无法执行
@ApiResponses({
@ApiResponse(code = 200,message = "成功",response = AjaxResponse.class)
})
//删除
// @RequestMapping(value = "/articles/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@DeleteMapping("/articles")
public AjaxResponse deleteArticle(@PathParam("id") Integer id)
@ApiModel(value = "通用响应数据结构类")
public class AjaxResponse {
@ApiModelProperty(value = "是否成功")
private boolean isOk;
//200\400\500
@ApiModelProperty(value = "状态码",example = "200,400,500")
private int code;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "请求结果描述")
private String message;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "请求结果数据")
private Object data;
将api文档保存于本地,有三种格式。markdown(md)、ASCIIDOC(adoc)、CONFLUENCE_MARKUP(txt)
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
//设定环境为设定的端口
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.DEFINED_PORT)
public class SwaggerExportTests {
@Test
public void generateAsciiDocs() throws URISyntaxException {
Swagger2MarkupConfig config = new Swagger2MarkupConfigBuilder().
//设定导出格式,这里为MARKDOWN,还有一个ASCIIDOC
withMarkupLanguage(MarkupLanguage.CONFLUENCE_MARKUP).
//自然语言选择为中文
withOutputLanguage(Language.ZH).
//按照TAGS分组
withPathsGroupedBy(GroupBy.TAGS).
//将生成的示例包括到文档中
withGeneratedExamples().build();
//禁用内联架构,虽然俺也不知道有啥用
//不知道是不是与java中后端优化中的内联是一个意思
//withoutInlineSchema().build();
Swagger2MarkupConverter.from(new URI("http://localhost:18888/v2/api-docs")).
withConfig(config).build().toFile(Paths.get("src/main/resources"));
}
}
导出为html格式,在maven中添加一个插件即可,而且需要有.adoc文档
<plugin>
<groupId>org.asciidoctor</groupId>
<artifactId>asciidoctor-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.5.6</version>
<configuration>
//设定输入文件夹
<sourceDirectory>src/main/resources/docs</sourceDirectory>
//输出文件夹
<outputDirectory>src/main/resources/html</outputDirectory>
<backend>html</backend>
<sourceHighlighter>coderay</sourceHighlighter>
<attributes>
<toc>left</toc>
<sectnums>true</sectnums>
</attributes>
</configuration>
</plugin>