纯Vue 原生JS JQuery 三种方式实现无限滚动到底部加载更多
原生js实现思路
需要三个高度:scrollHeight(文档内容实际高度,包括超出视窗的溢出部分)、scrollTop(滚动条滚动距离)、clientHeight(窗口可视范围高度)。当 clientHeight + scrollTop >= scrollHeight 时,表示已经抵达内容的底部了,可以加载更多内容。
scrollHeight:通过 document.documentElement.scrollHeight 、document.body.scrollHeight 可以获取;
scrollTop:通过window.pageYOffset 、 document.documentElement.scrollTop 、 document.body.scrollTop 可以获取;(window.scrollY也可以,只是ie根本不支持。)
clientHeight:通过window.innerHeight 、 document.documentElement.clientHeight 、 document.body.clientHeight 可以获取;
下面我先附上我的大致测试结果图(页面代码和测试表格数据最后附上)
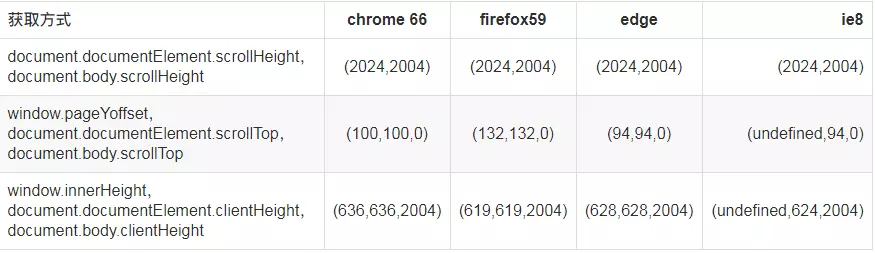
从第一行数据可以看出来,2000(content)+2*2(border)+20(margin-top)=2024才是全部内容。故var scrollHeight = Math.max(document.documentElement.scrollHeight, document.body.scrollHeight); 。
第二行数据,window.pageYOffset 不支持ie8;另外查询其他文档得知,document.documentElement.scrollTop 和 document.body.scrollTop 只会生效一个;window.scrollY也是一样的功能,但是兼容性比第一个还差(点此查看)。故var scrollTop = window.pageYOffset || document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTop;。
第三行数据:显而易见,数字小的那个才是窗口可是区域高度。故var clientHeight = window.innerHeight || Math.min(document.documentElement.clientHeight,document.body.clientHeight);。
所以最后的js代码如下:
window.onscroll= function(){
//文档内容实际高度(包括超出视窗的溢出部分)
var scrollHeight = Math.max(document.documentElement.scrollHeight, document.body.scrollHeight);
//滚动条滚动距离
var scrollTop = window.pageYOffset || document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTop;
//窗口可视范围高度
var clientHeight = window.innerHeight || Math.min(document.documentElement.clientHeight,document.body.clientHeight);
if(clientHeight + scrollTop >= scrollHeight){
console.log("===加载更多内容……===");
}
}
jquery的实现方式
代码如下:
<script>
$(window).on("resize scroll",function(){
var windowHeight = $(window).height();//当前窗口的高度
var scrollTop = $(window).scrollTop();//当前滚动条从上往下滚动的距离
var docHeight = $(document).height(); //当前文档的高度
console.log(scrollTop, windowHeight, docHeight);
//当 滚动条距底部的距离 + 滚动条滚动的距离 >= 文档的高度 - 窗口的高度
//换句话说:(滚动条滚动的距离 + 窗口的高度 = 文档的高度) 这个是基本的公式
if (scrollTop + windowHeight >= docHeight) {
console.log("===加载更多数据===");
}
});
</script>
测试页面代码:
<!-- <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/strict.dtd"> -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>test</title>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,minimum-scale=1.0,maximum-scale=1.0,user-scalable=no">
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.scroll{
margin-top: 20px;
border: 2px solid #00f;
height: 2000px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="scroll">
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br>
sdhfiahdifashdifhid
<span id="js_con"></span>
</div>
<script>
window.onscroll= function(){
var str = '';
// str += window.scrollY+",";//ie不支持。
str += "("+document.documentElement.scrollHeight+","+document.body.scrollHeight+"),";
str += "("+window.pageYOffset+","+document.documentElement.scrollTop+","+document.body.scrollTop+"),";
str += "("+window.innerHeight+","+document.documentElement.clientHeight+","+document.body.clientHeight+"),";
document.getElementById('js_con').innerHTML = str;
console.log(str);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
测试结果:
| 获取方式 | chrome 66 | firefox59 | edge | ie8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| document.documentElement.scrollHeight,document.body.scrollHeight | (2024,2004) | (2024,2004) | (2024,2004) | (2024,2004) |
| window.pageYoffset,document.documentElement.scrollTop,document.body.scrollTop | (100,100,0) | (132,132,0) | (94,94,0) | (undefined,94,0) |
| window.innerHeight,document.documentElement.clientHeight,document.body.clientHeight | (636,636,2004) | (619,619,2004) | (628,628,2004) | (undefined,624,2004) |
VUE方式加载更多
将使用 Random User API(模拟后端返回数据)。对于模仿未来项目的用户配置文件也非常有用。
获取初始用户数据
有各种实现无限滚动的 npm 包,你可以使用你的 Vue 应用程序,但其中一些可能是太繁琐了。此文中,我们将不用那些插件或包,仅仅编写一个简单的 JavaScript 函数来实现无限滚动功能(当滚动到浏览器窗口底部时,获取一组新数据)。
在我们开始集成无限滚动之前,让我们在页面加载中获取并设置一些初始数据:
App.vue
data () {
return {
persons: []
}
},
methods: {
getInitialUsers () {
for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
axios.get(`https://randomuser.me/api/`)
.then(response => {
this.persons.push(response.data.results[0]);
});
}
}
},
beforeMount() {
this.getInitialUsers();
}
注意:
Random User API 一次只会返回一个随机用户数据,为了获得5个用户数据,需要发起五次请求。
如果您在 console 看到了五个用户数据,那就OK了!让我们通过模板中的这些数据进行迭代,然后继续:
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>Random User</h1>
<div class="person" v-for="person in persons">
<div class="left">
<img :src="person.picture.large">
</div>
<div class="right">
<p>{{ person.name.first }} {{ person.name.last }}</p>
<ul>
<li>
<strong>Birthday:</strong> {{ formatDate(person.dob) }}
</li>
<li class="text-capitalize">
<strong>Location:</strong> {{ person.location.city }},
{{ person.location.state }}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
...
</script>
<style lang="scss">
/* Optional Styles */
.person {
background: #ccc;
border-radius: 2px;
width: 20%;
margin: 0 auto 15px auto;
padding: 15px;
img {
width: 100%;
height: auto;
border-radius: 2px;
}
p:first-child {
text-transform: capitalize;
font-size: 2rem;
font-weight: 900;
}
.text-capitalize {
text-transform: capitalize;
}
}
</style>
实现无限滚动逻辑
现在你在此的目的…无限的滚动! 在组件的方法中,您需要创建一个名为scroll()的新函数,并将其加载到mounted()生命周期方法中。
这个scroll()方法应该有一个简单的条件来计算页面的底部,判断它为true或false,并执行一些操作。我们将利用文档对象的documentElement.scrollTop,documentElement.offsetHeight属性和窗口的innerHeight属性来确定是否滚动到底部:
window.onscroll = () => {
let bottomOfWindow = document.documentElement.scrollTop + window.innerHeight === document.documentElement.offsetHeight;
if (bottomOfWindow) {
// Do something, anything!
}
};
在这种情况下,让我们添加一个GET方法,使用Axios从随机用户API中获取另一个随机用户。
methods: {
...,
scroll (person) {
window.onscroll = () => {
let bottomOfWindow = document.documentElement.scrollTop + window.innerHeight === document.documentElement.offsetHeight;
if (bottomOfWindow) {
axios.get(`https://randomuser.me/api/`)
.then(response => {
person.push(response.data.results[0]);
});
}
};
},
},
mounted() {
this.scroll(this.person);
}
此功能只会在用户滚动到页面底部时发起服务请求,并向人员数组添加一个新的随机“用户”。此时,您应该可以无限滚动…并每次看到新的“用户”。