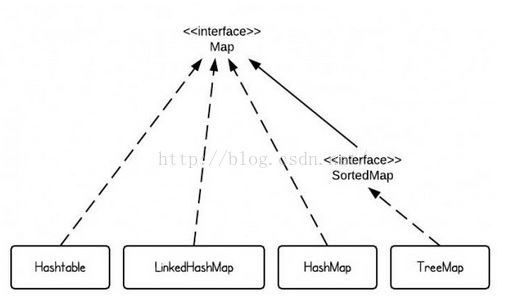
HashMap TreeMap Hashtable LinkedHashMap 区别
map是java中最常用的数据结构之一,在这篇文中,我将说明如何使用不同类型的maps,比如:HashMap,TreeMap,HashTable和LinkedHashMap。
Map概览
在java SE 中有4个Map常用的实现,分别是HashMap,TreeMap,HashTable和LinkedHashMap。用一句话来描述这四个实分别是:
HashMap是hash table的一个实现,它中的键值是无序的。
TreeMap是基于红黑树结构的一个实现,它是根据key来排序的。
LinkedHashMap保留了插入的顺序。
HashTabe是同步的,与HashMap相比,它有个同步的开销,因此如果程序是线程安全的,那么HashMap是个不错的选择。
HasMap
如果HashMap的key是自己定义的对象,那么equals()和hashCode()需要同样遵守规则:
class Dog {
String color;
Dog(String c) {
color = c;
}
public String toString(){
return color + " dog";
}
}
public class TestHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
Dog d1 = new Dog("red");
Dog d2 = new Dog("black");
Dog d3 = new Dog("white");
Dog d4 = new Dog("white");
hashMap.put(d1, 10);
hashMap.put(d2, 15);
hashMap.put(d3, 5);
hashMap.put(d4, 20);
//print size
System.out.println(hashMap.size());
//loop HashMap
for (Entry entry : hashMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey().toString() + " - " + entry.getValue());
}
}
} 输出的结果:
4
white dog - 5
black dog - 15
red dog - 10
white dog - 20注意:我们错误的添加了两个“white dogs”,但是HashMap都接受了,这并没有意义,因为现在很疑惑到底有多少个白狗
对Dog类的定义应该如下:
class Dog {
String color;
Dog(String c) {
color = c;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
return ((Dog) o).color.equals(this.color);
}
public int hashCode() {
return color.length();
}
public String toString(){
return color + " dog";
}
}现在的输出结果:
3
red dog - 10
white dog - 20
black dog - 15原因是HashMap不允许有两个相同的元素,默认情况下,hashcode()和equals()方法在对象的实现时使用,默认hashcode()方法给不同对象不同的整数,equals()方法只有在两个引用指向同一对象时才会返回true。
TreeMap
TreeMap是根据key进行排序的,让我们先来看看下边这个例子来理解什么事根据key排序
class Dog {
String color;
Dog(String c) {
color = c;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
return ((Dog) o).color.equals(this.color);
}
public int hashCode() {
return color.length();
}
public String toString(){
return color + " dog";
}
}
public class TestTreeMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog d1 = new Dog("red");
Dog d2 = new Dog("black");
Dog d3 = new Dog("white");
Dog d4 = new Dog("white");
TreeMap treeMap = new TreeMap();
treeMap.put(d1, 10);
treeMap.put(d2, 15);
treeMap.put(d3, 5);
treeMap.put(d4, 20);
for (Entry entry : treeMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " - " + entry.getValue());
}
}
} 输出的结果:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassCastException: collection.Dog cannot be cast to java.lang.Comparable
at java.util.TreeMap.put(Unknown Source)
at collection.TestHashMap.main(TestHashMap.java:35)因为TreeMaps是根据key来排序的,这个对象key必须能够互相比较,这就是为什么Dog要实现Comparable接口。例如,你利用String作为key,因为String实现了Comparable接口。
现在我们重新定义Dog,来实现comparable接口:
class Dog implements Comparable{
String color;
int size;
Dog(String c, int s) {
color = c;
size = s;
}
public String toString(){
return color + " dog";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Dog o) {
return o.size - this.size;
}
}
public class TestTreeMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog d1 = new Dog("red", 30);
Dog d2 = new Dog("black", 20);
Dog d3 = new Dog("white", 10);
Dog d4 = new Dog("white", 10);
TreeMap treeMap = new TreeMap();
treeMap.put(d1, 10);
treeMap.put(d2, 15);
treeMap.put(d3, 5);
treeMap.put(d4, 20);
for (Entry entry : treeMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " - " + entry.getValue());
}
}
} 输出结果:
red dog - 10
black dog - 15
white dog - 20它是根据键值进行排序的,例如dog的大小,
如果Dog d4 = new Dog("white",10),被替代为Dog d4 = new Dog("white", 40);输出结果则是
white dog - 20
red dog - 10
black dog - 15
white dog - 5Hashtable
来自java DOC的解释:
HashMap类大致相当于Hashtable,除了它是不同步的和允许是空值的之外。
LisnkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap是HashMap的子类,这意味着 它集成了HashMap的特点,除此之外,LinkedHashMap保留了插入时的顺序。让我们用LinkedHashMap代替HashMap,来看看刚才代码的实现:
class Dog {
String color;
Dog(String c) {
color = c;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
return ((Dog) o).color.equals(this.color);
}
public int hashCode() {
return color.length();
}
public String toString(){
return color + " dog";
}
}
public class TestHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog d1 = new Dog("red");
Dog d2 = new Dog("black");
Dog d3 = new Dog("white");
Dog d4 = new Dog("white");
LinkedHashMap linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap();
linkedHashMap.put(d1, 10);
linkedHashMap.put(d2, 15);
linkedHashMap.put(d3, 5);
linkedHashMap.put(d4, 20);
for (Entry entry : linkedHashMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " - " + entry.getValue());
}
}
} 输出结果:
red dog - 10
black dog - 15
white dog - 20red dog - 10
white dog - 20
black dog - 15
//下边是自己加的判断为空的情况
map == null 是指没有引用的对象。
map.size() == 0 指map中没有元素。是一个空的集合。
要判断map是空的。要先判断是不是null 再看size。
map.size() == 0 指map中没有元素。是一个空的集合。
要判断map是空的。要先判断是不是null 再看size。