Netty事件注册过程
Netty是对NIO的封装,通过事件驱动的网络编程框架,自然是要实现NIO中的事件注册与监听。在NIO中我们都是显式的注册每一个事件,但是Netty为开发人员封装了这些细节,提供了简单易用的API,底层是如何实现的呢,这就是本篇文章要讨论的问题。
NIO的SelectionKey中有四种事件,可读、可写、连接、接收连接
public abstract class SelectionKey {
public static final int OP_READ = 1 << 0; // 1
public static final int OP_WRITE = 1 << 2 // 4
public static final int OP_CONNECT = 1 << 3; // 8
public static final int OP_ACCEPT = 1 << 4; // 16
}Channel注册到Selector有两种方式,一种是调用Channel的register方法,第二种是设置SelectionKey的interestOps的值。Netty是用了第二种方式,通过设置SelectionKey的interestOps来注册Channel关心的事件,把实际的注册延迟了。
在分析Netty事件注册之前,我们在简单过一下NIO中的流程。NIO中Channel是连接的通道,服务端启动会新建一个ServerSocketChannel,接收到客户端连接时会创建一个SocketChannel,每个通道都会把自己感兴趣的事件注册到一个Selector上。然后在一个线程中循环调用Selector的select()方法查看是否有就绪事件,如果有就绪事件,遍历处理selectionKeys,如果是OP_ACCEPT事件,则创建一个SocketChannel并注册感兴趣的事件;如果是OP_READ事件则读socket数据。Netty也是这个原理,不过实现方式和直接使用NIO有很大的区别。
Netty新建一个Channel时也会执行一个注册过程,不管是NioServerSocketChannel还是NioSocketChannel被初始化时都会执行到父类AbstractNioChannel的doRegister方法
protected void doRegister() throws Exception {
boolean selected = false;
for (;;) {
try {
selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().selector, 0, this);
return;
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
if (!selected) {
// Force the Selector to select now as the "canceled" SelectionKey may still be
// cached and not removed because no Select.select(..) operation was called yet.
eventLoop().selectNow();
selected = true;
} else {
// We forced a select operation on the selector before but the SelectionKey is still cached
// for whatever reason. JDK bug ?
throw e;
}
}
}
}这个地方只是注册了一个0,并不是Channel真正感兴趣的事件,NioServerSocektChannel在之前的Netty服务端启动 ServerBootstrap中分析过调用register方法的过程。

在register0中最终调用什么的doRegister。
下面分析NioServerSocketChannel接收事件是在什么时候什么地方注册的。
OP_ACCEPT事件注册
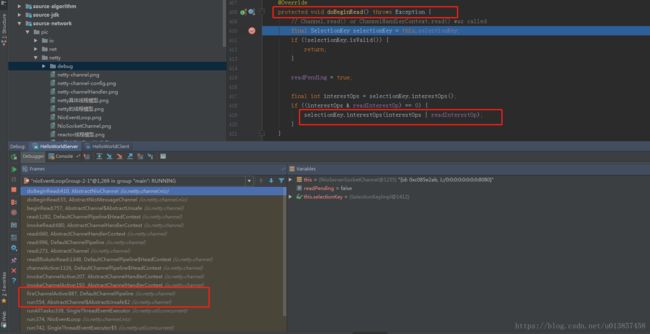
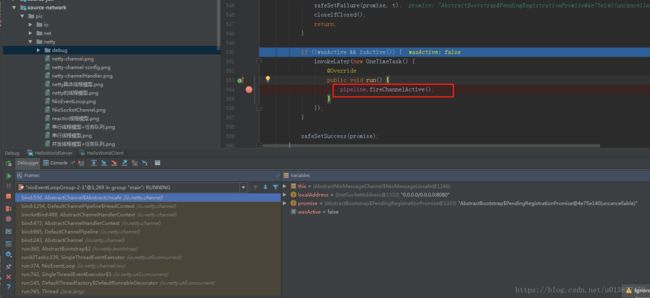
在AbstractChannel的bind方法中,在执行完doBind方法之后会起一个任务执行ChannelPipeline的fireChannelActive方法。粘源码设计的类比较多,下面以debug的图说明,DefaultChannelPipeline.fireChannelActive方法最终会调到AbstractNioChannel的doBeginRead()
AbstractNioChannel#doBeginRead()
@Override
protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {
// Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() was called
final SelectionKey selectionKey = this.selectionKey;
if (!selectionKey.isValid()) {
return;
}
readPending = true;
final int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & readInterestOp) == 0) {
selectionKey.interestOps(interestOps | readInterestOp);
}
}在这个方法中改变感兴趣的值,readInterestOp是什么呢?在NioServerSocketChannel构造方法中会传入OP_ACCEPT,最终赋值给readInterestOp
public NioServerSocketChannel(ServerSocketChannel channel) {
super(null, channel, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
config = new NioServerSocketChannelConfig(this, javaChannel().socket());
}
protected AbstractNioChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch, int readInterestOp) {
super(parent);
this.ch = ch;
this.readInterestOp = readInterestOp;
try {
ch.configureBlocking(false);
} catch (IOException e) {
try {
ch.close();
} catch (IOException e2) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn(
"Failed to close a partially initialized socket.", e2);
}
}
throw new ChannelException("Failed to enter non-blocking mode.", e);
}
}OP_READ事件注册
当有客户端连接请求过来时,前端的NioEventLoop会通过Selector找到响应的SelectionKey,Netty把OP_READ和OP_ACCEPT统一使用Unsafe的read来处理。
对于OP_ACCEPT事件,调用的是NioMessageUnsafe, 先会执行到NioServerSocketChannel的doReadMessage来处理连接请求
当NioServerSocketChannel通过调用ServerSocketChannel的accept来创建客户端SocketChannel时,会传递OP_READ事件到NioSocketChannel的构造函数,最后到了AbstractNioChannel的构造函数,和OP_ACCEPT一样,成为AbstractNioChannel的readInterestOps属性。
处理完之后NioMessageUnsafe会fireChannelRead来使用Pipeline传递事件,调用到ServerBootstrapAcceptor的channelRead方法来把Channel注册到selector,也只是注册了一个0到selector,把Channel作为Attachment绑定到SelectionKey。
和OP_ACCEPT一样,注册完之后会发出fireChannelActive事件,最后调用HeadHandler的read方法,在这个方法里面调用Unsafe的beginRead方法。这里的Unsafe的实例是NioByteUnsafe,最后又进入到AbstractNioChanel的doReadBegin来设置Selectionkey的interestOps为OP_READ
//SingleThreadEventExecutor
private void doStartThread() {
assert thread == null;
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
thread = Thread.currentThread();
if (interrupted) {
thread.interrupt();
}
boolean success = false;
updateLastExecutionTime();
try {
SingleThreadEventExecutor.this.run();
success = true;
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Unexpected exception from an event executor: ", t);
}
}
}
}
protected void run() {
for (;;) {
try {
switch (selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())) {
case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:
continue;
case SelectStrategy.SELECT:
select(wakenUp.getAndSet(false));
if (wakenUp.get()) {
selector.wakeup();
}
default:
// fallthrough
}
cancelledKeys = 0;
needsToSelectAgain = false;
final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;
if (ioRatio == 100) {
processSelectedKeys();
runAllTasks();
} else {
final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();
processSelectedKeys();
final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;
runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);
}
if (isShuttingDown()) {
closeAll();
if (confirmShutdown()) {
break;
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Unexpected exception in the selector loop.", t);
// Prevent possible consecutive immediate failures that lead to
// excessive CPU consumption.
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Ignore.
}
}
}
}
private void processSelectedKeys() {
if (selectedKeys != null) {
processSelectedKeysOptimized(selectedKeys.flip());
} else {
processSelectedKeysPlain(selector.selectedKeys());
}
}
private void processSelectedKeysOptimized(SelectionKey[] selectedKeys) {
for (int i = 0;; i ++) {
final SelectionKey k = selectedKeys[i];
if (k == null) {
break;
}
selectedKeys[i] = null;
final Object a = k.attachment();
if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) {
processSelectedKey(k, (AbstractNioChannel) a);
} else {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
NioTask task = (NioTask) a;
processSelectedKey(k, task);
}
}
}
// NioEventLoop处理事件分发
private void processSelectedKey(SelectionKey k, AbstractNioChannel ch) {
final AbstractNioChannel.NioUnsafe unsafe = ch.unsafe();
try {
int readyOps = k.readyOps();
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
unsafe.read();
if (!ch.isOpen()) {
return;
}
}
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) {
ch.unsafe().forceFlush();
}
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) {
int ops = k.interestOps();
ops &= ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT;
k.interestOps(ops);
unsafe.finishConnect();
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException ignored) {
unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
}
}
//AbstractNioMessageChannel
public void read() {
assert eventLoop().inEventLoop();
final ChannelConfig config = config();
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = unsafe().recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.reset(config);
boolean closed = false;
Throwable exception = null;
try {
try {
do {
int localRead = doReadMessages(readBuf);
if (localRead == 0) {
break;
}
if (localRead < 0) {
closed = true;
break;
}
allocHandle.incMessagesRead(localRead);
} while (allocHandle.continueReading());
} catch (Throwable t) {
exception = t;
}
int size = readBuf.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
readPending = false;
pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i));
}
readBuf.clear();
allocHandle.readComplete();
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof IOException && !(exception instanceof PortUnreachableException)) {
closed = !(AbstractNioMessageChannel.this instanceof ServerChannel);
}
pipeline.fireExceptionCaught(exception);
}
if (closed) {
inputShutdown = true;
if (isOpen()) {
close(voidPromise());
}
}
} finally {
if (!readPending && !config.isAutoRead()) {
removeReadOp();
}
}
}
}
NioServerSocketChannel.doReadMessage方法
protected int doReadMessages(List