linux下写服务端程序免不了用到命令行参数,这里我总结下C语言、bash脚本、python和go语言中的使用方法,也方便我以后查阅。这里我主要用的是getopt这个函数,首先看看c语言中的定义。
头文件:#include
函数定义:int getopt(int argc,char * const argv[ ],const char * optstring);
extern char *optarg;
extern int optind, opterr, optopt;
说明:
getopt函数是用来分析命令行参数的,参数argc和argv是由main()传递的参数个数和内容,参数 optstring为选项字符串, 告知 getopt()可以处理哪个选项以及哪个选项需要参数。
optstring中的指定的内容的意义(例如getopt(argc, argv, "ab:c:de::"):
-
单个字符,表示选项,(如上例中的abcde各为一个选项)
-
单个字符后接一个冒号:表示该选项后必须跟一个参数。参数紧跟在选项后或者以空格隔开。该参数的指针赋给optarg。(如上例中的b:c:)
-
单个字符后跟两个冒号,表示该选项后必须跟一个参数。参数必须紧跟在选项后不能以空格隔开。该参数的指针赋给optarg。(如上例中的e::)
getopt函数所设置的全局变量如下:
-
optarg : 指向当前选项参数(如果有)的指针
-
optind : 再次调用 getopt() 时的下一个 argv 指针的索引。
-
opterr : 是否打印出错信息,如果不希望getopt()印出错信息,则只要将全域变量opterr设为0即可。
-
optopt : 最后一个已知选项。
当然,在下面的例子中我也用到了getopt_long这个函数,这个和getopt类似,就不再赘述了。不懂的google下。
1、c语言实现
1.1 、getopt短命令
代码如下:
/* File : getoptShort.c Author : Mike E-Mail : [email protected] */ #include#include #include <string.h> extern char *optarg; extern int opterr; int main(int argc,char **argv) { int c,index; char host[128] = "127.0.0.1"; int port = 8000; opterr = 0; while((c=getopt(argc,argv,"h:p:")) != -1) { switch(c) { case 'h': strcpy(host,optarg); break; case 'p': port = atoi(optarg); break; case '?': printf("Usage : \n" "-h host : set ip address\n" "-p port : set port\n" ); return 1; default: break; } } printf( "ip : %s\n" "port : %d\n", host,port); for(index = optind;index < argc;index++) printf("Non-option argument %s\n",argv[index]); return 0; }
运行效果如下:
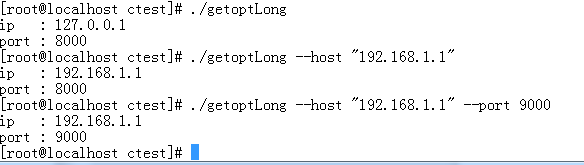
1.2 、getopt长命令
这个要用到getopt_long这个函数。
代码如下:
/* File : getoptLong.c Author : Mike E-Mail : [email protected] */ #include#include <string.h> #include extern char *optarg; extern int opterr; int main(int argc,char **argv) { int c,index; char host[128] = "127.0.0.1"; int port = 8000; struct option opts[] = { {"host",required_argument,NULL,'h'}, {"port",required_argument,NULL,'p'}, {0,0,0,0} }; opterr = 0; while((c=getopt_long(argc,argv,"h:p:",opts,NULL)) != -1) { switch(c) { case 'h': strcpy(host,optarg); break; case 'p': port = atoi(optarg); break; case '?': printf("Usage : \n" "-h host : set ip address\n" "-p port : set port\n" ); return 1; default: break; } } printf( "ip : %s\n" "port : %d\n", host,port); for(index = optind;index < argc;index++) printf("Non-option argument %s\n",argv[index]); return 0; }
运行效果如下:
2、Bash脚本实现
bash的和c语言的类似,这里只列举一个短命令的示例。
代码如下:
#! /bin/bash host="127.0.0.1" port=8000 if [ $# -gt 0 ] ; then while getopts ":h:p:" opt;do case $opt in h) host=$OPTARG ;; p) port=$OPTARG ;; *) echo "Usage :" echo "-h arg : set ip address" echo "-p arg : set port " exit 1;; esac done fi echo "ip : $host" echo "port : $port"
3.python实现
python里面的这个函数显然已经进化了,这个更简单,还是那个程序的功能,代码如下:
#! /usr/bin/python import getopt,sys if __name__ == "__main__": try: opts,args = getopt.getopt(sys.argv[1:],"h:p:",["host=","port="]) except getopt.GetoptError: print "Usage :" print "-h arg , --host=arg : set ip address" print "-p arg , --port=arg : set port" sys.exit(1) host = "127.0.0.1" port = 8000 for opt,arg in opts: if opt in ("-h","--host"): host = arg if opt in ("-p","--port"): port = arg print "ip : ",host print "port : ",port
4.go语言实现
go语言的flag库似乎更全面,下面是代码:
package main import ( "flag" "fmt" ) var ( ip = flag.String("host","127.0.0.1","ip address") port = flag.String("port","8000","listen port") ) func main() { flag.Parse() fmt.Println("ip : ",*ip) fmt.Println("port : ",*port) }