游戏排行榜的实现
在没有接触游戏行业的排行版时,就觉得排行版的实现非常不简单,也不知道是不是自己想的太过于复杂,然后自己特意去百度了游戏排行版的算法设计的比较(http://www.cocoachina.com/game/20150930/13638.html),发现排行榜可大可小吧,具体看你如何做这个功能,我借鉴了别人写的方法,然后自己也实现了一波,发现算法真是一个好东西。
需求背景:
查看前top N的排名用户
查看自己的排名
用户积分变更后,排名及时更新
方案一
利用MySQL来实现,存放一张用户积分表user_score,结构如下
表 t_u_userscore
CREATE TABLE `t_u_userscore` (
`UserId` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户ID',
`Score` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '当前分数',
PRIMARY KEY (`UserId`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='玩家积分表';表 t_u_user
CREATE TABLE `t_u_user` (
`UserId` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户ID',
`Username` varchar(255) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户名',
`CurAllRank` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '当前所有用户排名',
`CurFriendRank` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '当前所有用户排名',
PRIMARY KEY (`UserId`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='玩家信息表';
表t_u_friend
CREATE TABLE `t_u_friend` (
`FriendId` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '朋友ID',
`UserId` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户ID',
`FriendRelation` varchar(255) DEFAULT '好友' COMMENT '关系描述',
PRIMARY KEY (`FriendId`,`UserId`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='玩家交际描述';表里面的数据就自己填写吧,这里我使用的是存储过程,自己写的存储过程并不多,如果大家有更好的方法,可以在下方评论告知我,不胜感激。
存储过程friendorder
CREATE DEFINER=`root`@`%` PROCEDURE `friendorder`(IN `userId` int)
BEGIN
DECLARE curFriendRank INT DEFAULT 1; /*当前朋友圈排名*/
DECLARE friendScore INT DEFAULT 0; /*好友分数*/
DECLARE friendCount INT DEFAULT 0; /*好友总数量*/
DECLARE v_curScore INT DEFAULT 0; /*userId当前分数*/
DECLARE v_friendId INT DEFAULT 0; /*朋友id*/
DECLARE v_index INT DEFAULT 0; /*循环索引值*/
SELECT count(1) INTO friendCount FROM `t_u_friend` f WHERE f.UserId = userId;
SELECT `Score` INTO v_curScore FROM `t_u_userscore` f WHERE f.UserId = userId;
WHILE v_index < friendCount DO
SELECT f.FriendId INTO v_friendId FROM `t_u_user` u,`t_u_friend` f WHERE u.UserId = f.UserId AND u.UserId = userId LIMIT v_index,1;
SELECT `score` INTO friendScore FROM `t_u_userscore` u WHERE u.UserId = v_friendId;
IF friendScore > v_curScore THEN
SET curFriendRank = curFriendRank + 1;
END IF;
SET v_index = v_index +1;
END WHILE;
UPDATE `t_u_user` u SET u.curFriendRank = CurFriendRank WHERE u.UserId = userId;
END存储过程orderInfo
CREATE DEFINER=`root`@`%` PROCEDURE `orderInfo`()
BEGIN
DECLARE count INT(11) DEFAULT 0; /*总共的数量*/
DECLARE Startcur INT(11) DEFAULT 0; /*排名值*/
DECLARE v_userId INT(11);
SELECT COUNT(1) INTO count FROM `t_u_userscore`;
WHILE Startcur < count DO
SELECT `UserId` INTO v_userId FROM `t_u_userscore` ORDER BY `Score` DESC LIMIT Startcur, 1;
SET Startcur = Startcur + 1;
UPDATE `t_u_user` SET `CurAllRank` = Startcur WHERE `userId` = v_userId;
CALL friendOrder(v_userId); /*同时更新好友圈排行*/
END WHILE;
END最后结果如下:

方案二
实现Comparable接口实现排序
对象类 Command
public class Command implements Comparable<Command> {
private String commandName;
private int commandTime;
public Command(String commandName, int commandTime) {
super();
this.commandName = commandName;
this.commandTime = commandTime;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Command o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (this.getCommandTime() > o.getCommandTime()) {
return -1;
} else if (this.getCommandTime() < o.getCommandTime()) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}使用Collections.sort方法进行排序,之后是用list的indexof得到对象的索引值,这个索引值就是他的排名.
TestClass类
Command command1 = new Command("ssd", ran);
Command command2= new Command("ssd", ran);
Command command3 = new Command("ssd", ran);
Command command4 = new Command("ssd", ran);
Vector vector = new Vector();
vector.add(command1);
vector.add(command2);
vector.add(command3);
vector.add(command4);
Collections.sort(vector); 方案三
上述方法可以实现排行榜的功能,不过尽管是用线程安全的vector,但是在高并发的问题还是无法解决,而且在效率上也不是很快,所以可以使用skiplist。这里就简单的介绍下skipList。
SkipList这个数据结构名为跳跃表,再插入数据的同时就给它排序好,然后随机的生成层。Skip List是一种随机化的数据结构,基于并联的链表,其效率可比拟于二叉查找树(对于大多数操作需要O(log n)平均时间)。基本上,跳跃列表是对有序的链表增加上附加的前进链接,增加是以随机化的方式进行的,所以在列表中的查找可以快速的跳过部分列表(因此得名)。所有操作都以对数随机化的时间进行。Skip List可以很好解决有序链表查找特定值的困难。
在Java的API中已经有了实现:分别是
1: ConcurrentSkipListMap. 在功能上对应HashTable、HashMap、TreeMap。 在并发环境下,Java也提供ConcurrentHashMap这样的类来完成hashmap功能。
2: ConcurrentSkipListSet . 在功能上对应HashSet.
SkipList中的每一个对象的数据结构是这样的:
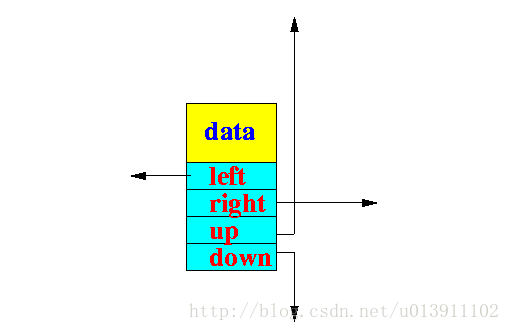
SkipList使用的时候是这样的
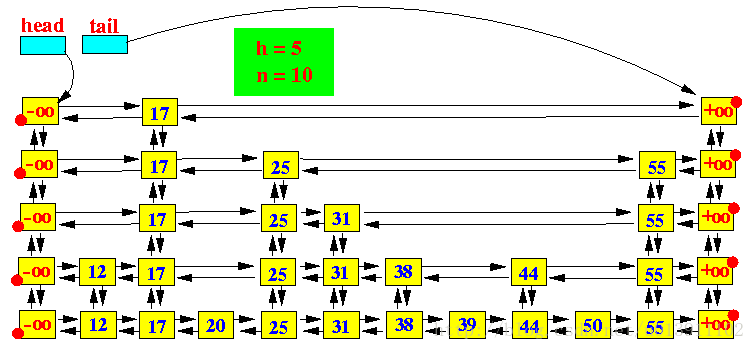
代码实现:
SkipListEntry.java
public Integer key;
public Integer value;
public int rank; // 排名
public int pos; // 标志位,主要方便打印内容
public SkipListEntry left;
public SkipListEntry right;
public SkipListEntry up;
public SkipListEntry down;
public static int negInf = Integer.MIN_VALUE; //边界值
public static int posInf = Integer.MAX_VALUE; //边界值
public SkipListEntry(Integer key, Integer value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
rank = 0;
this.left = this.right = this.up = this.down = null;
}SkipList.java
public class NSkipList {
public SkipListEntry head; // 顶层的第一个元素
public SkipListEntry tail; // 顶层的最后一个元素
public int n; // 跳跃表中的元素个数
public int h; // 跳跃表的高度
public Random r; // 投掷硬币
// 默认构造函数
public NSkipList()
{
SkipListEntry p1, p2;
p1 = new SkipListEntry(SkipListEntry.negInf, null);
p2 = new SkipListEntry(SkipListEntry.posInf, null);
head = p1;
tail = p2;
p1.right = p2;
p2.left = p1;
n = 0;
h = 0;
r = new Random();
}
/** 返回 包含的元素个数 */
public int size() {
return n;
}
/** 跳跃表是否为空 */
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (n == 0);
}
// 在最下面一层,找到要插入的位置前面的那个key
public SkipListEntry findEntry(Integer k) {
SkipListEntry p;
p = head;
while (true) {
while (p.right.key != Integer.MAX_VALUE && p.right.key >= k) {
p = p.right;
}
// 如果还有下一层,就到下一层继续查找
if (p.down != null) {
p = p.down;
} else
break; // 到了最下面一层 就停止查找
}
return (p); // p.key <= k
}
// 在最下面一层,这个方法主要是用于查询相同k值不同value的情况
public SkipListEntry findEntry(Integer k, Integer value) {
SkipListEntry p;
p = head;
// flag用来标识是否已经向左查询了
boolean flag = false;
while (true) {
// 找到跳表位置,然后一直向右找,如果找到了直接返回
while (p.right.key != Integer.MAX_VALUE && p.right.key >= k) {
if(p.value != null && p.value.equals(value)){
return p;
}
p = p.right;
}
// 如果还有下一层,就到下一层继续查找
if (p.down != null) {
p = p.down;
}
// 如果没有下一层
else {
// 如果找到这个key值继续操作,否则返回null
if (p.key == k) {
//如果已经向左查询过了,还没有找到,直接返回null
if(flag){
return null;
}
// 需要考虑跳表的时候,在上一层跳过了当前要查找的key值,所以需要往前找
if (p.left.key == k && !flag) {
flag = !flag;
while (p.left.key != Integer.MIN_VALUE && p.left.key <= k) {
if (p.value.equals(value)) {
return p;
}
p = p.left;
}
}
}
else{
return null;
}
}
}
}
/** 返回和key绑定的值 */
public Integer get(Integer k) {
SkipListEntry p;
p = findEntry(k);
if (k.equals(p.getKey()))
return (p.value);
else
return (null);
}
/** 放一个key-value到跳跃表中, 同时排序 */
public Integer put(Integer k, Integer v) {
SkipListEntry p, q;
int i;
p = findEntry(k);
q = new SkipListEntry(k, v);
q.left = p;
q.right = p.right;
p.right.left = q;
p.right = q;
i = 0; // 当前层 level = 0
// 随机生成跳表层
while (r.nextDouble() < 0.5) {
// 如果超出了高度,需要重新建一个顶层
if (i >= h) {
SkipListEntry p1, p2;
h = h + 1;
p1 = new SkipListEntry(SkipListEntry.negInf, null);
p2 = new SkipListEntry(SkipListEntry.posInf, null);
p1.right = p2;
p1.down = head;
p2.left = p1;
p2.down = tail;
head.up = p1;
tail.up = p2;
head = p1;
tail = p2;
}
while (p.up == null) {
p = p.left;
}
p = p.up;
SkipListEntry e;
e = new SkipListEntry(k, null);
e.left = p;
e.right = p.right;
e.down = q;
p.right.left = e;
p.right = e;
q.up = e;
q = e; // q 进行下一层迭代
i = i + 1; // 当前层 +1
}
n = n + 1;
getRank(k); //put一个value值时就排名一次
return (null); // No old value
}
/** 排序方法 */
public void getRank(Integer k) {
SkipListEntry p;
p = findEntry(k);
while (p != null) {
if (p.key != p.left.key) {
p.rank = p.left.rank + 1;
} else {
p.rank = p.left.rank;
}
p = p.right;
}
}
/** 移除一个key */
public Integer remove(Integer key,Integer value) {
SkipListEntry p = findEntry(key,value);
if (p.key != key)
return (null);
while (p != null) {
p.left.right = p.right;
p.right.left = p.left;
p = p.up;
}
getRank(key);
return value;
}
public void printHorizontal() {
String s = "";
int i;
SkipListEntry p;
p = head;
while (p.down != null) {
p = p.down;
}
i = 0;
while (p != null) {
p.pos = i++;
p = p.right;
}
p = head;
while (p != null) {
s = getOneRow(p);
System.out.println(s);
p = p.down;
}
}
// 用了打印测试
public String getOneRow(SkipListEntry p) {
String s;
int a, b, i;
a = 0;
s = "" + getStrKey(p.key) + "(" + p.value + ")";
p = p.right;
while (p != null) {
SkipListEntry q;
q = p;
while (q.down != null)
q = q.down;
b = q.pos;
s = s + " <-";
for (i = a + 1; i < b; i++)
s = s + "--------";
s = s + "> " + getStrKey(p.key) + "(" + p.value + ")";
a = b;
p = p.right;
}
return (s);
}
// 用了打印测试
public void printVertical() {
String s = "";
SkipListEntry p;
p = head;
while (p.down != null)
p = p.down;
while (p != null) {
s = getOneColumn(p);
System.out.println(s);
p = p.right;
}
}
// 用了打印测试
public String getOneColumn(SkipListEntry p) {
String s = "";
while (p != null) {
s = s + " " + p.key;
p = p.up;
}
return (s);
}
// 为了替换边界值
public String getStrKey(Integer key) {
if (key == SkipListEntry.negInf) {
return "-oo";
} else if (key == SkipListEntry.posInf) {
return "+oo";
} else {
return "" + key;
}
}测试代码 TestClass.java
NSkipList S = new NSkipList();
S.printHorizontal();
System.out.println("------");
// S.printVertical();
// System.out.println("======");
S.put(123, 123);
S.printHorizontal();
System.out.println("------");
// S.printVertical(); // System.out.println("======");
S.put(456, 123);
S.printHorizontal();
System.out.println("------");
// S.printVertical(); // System.out.println("======");
S.put(1245, 123);
S.printHorizontal();
System.out.println("------");
// S.printVertical(); // System.out.println("======");
S.put(12378, 123);
S.printHorizontal();
System.out.println("------");
// S.printVertical(); // System.out.println("======");
S.put(664, 123);
S.printHorizontal();
System.out.println("------");
// S.printVertical(); // System.out.println("======");
S.put(510, 123);
S.printHorizontal();
System.out.println("------");
// S.printVertical(); // System.out.println("======"); S.put(5, 123);
S.put(1, 1234);
S.put(1, 1574);
S.put(1, 978);
S.put(3, 123);
S.put(5678, 123);
S.put(1167, 123);
S.printHorizontal();
System.out.println("------");
SkipListEntry s = S.findEntry(1,1234);
System.out.println("1234的排名是" + s.rank + ",value值是" + s.value);
S.remove(1,1574);
S.printHorizontal();
System.out.println("------");
s = S.findEntry(1,978);
System.out.println("978的排名是" + s.rank + ",value值是" + s.value);
s = S.findEntry(4568,222);
if (s == null){
System.out.println("没有找到!");
}运行结果:

上述代码参考地址:http://www.acmerblog.com/skip-list-impl-java-5773.html
skipList可以在不使用同步和锁的情况下,解决高并发问题。
方案四
使用redis的Sorted sets (有序集合)
将你要排序的值设置成sorted set的score,将具体的数据设置成相应的value,每次只需要执行一条ZADD命令即可
redis我自己也不是很了解,所以我附上这个链接
http://lib.csdn.net/article/34/40010?knId=1006
想学习的小伙伴就去看看吧 0.0.