HttpSession与JSESSIONID的"盗用"
先说一下什么是HttpSession,Http协议是一种无状态的协议,当我们从客户端发起一个浏览器请求的时候,服务器端如果说需要保留我们的登录信息的话,我们就需要通过某种方式解决这个登录问题。
在B/S模式中不可能每次访问服务器都把自己的登录信息传递到服务器端,如果说我们不考虑单点登录系统和cookie没有被禁用的情况下,首选的就是HttpSession技术实现保存客户端传递过来的信息或者是根据参数对数据库查询后的结果。如果说是cookie技术被禁用的话,导致的结果就是HttpSession对象被废掉,也无法使用。HttpSession如果说没有设置声明周期的话,它会在浏览器关闭的时候清除在浏览器上对应的存储的信息(JSESSIONID)。当我们开着浏览器,默认30min不操作的情况下,当前会话会自动死亡。
下面我们用一个项目模拟一下JSESSIONID盗用问题。

首先清除一下浏览器的缓存,这样更方便于查看我们的测试效果。这个框框弹出来的快捷键是shift+ctrl+del
。做好这个基本工作之后我们就来进入编码阶段:
下面这是我们测试使用的javaBean 一个User实体类
package com.test.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class User implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String role;
private Integer companyId;
private String lastLoginTime;
public User() {
super();
}
public User(Integer id, String username, String password, String phone,
String role, Integer companyId, String lastLoginTime) {
this();
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.phone = phone;
this.role = role;
this.companyId = companyId;
this.lastLoginTime = lastLoginTime;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getRole() {
return role;
}
public void setRole(String role) {
this.role = role;
}
public Integer getCompanyId() {
return companyId;
}
public void setCompanyId(Integer companyId) {
this.companyId = companyId;
}
public String getLastLoginTime() {
return lastLoginTime;
}
public void setLastLoginTime(String lastLoginTime) {
this.lastLoginTime = lastLoginTime;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result
+ ((companyId == null) ? 0 : companyId.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((id == null) ? 0 : id.hashCode());
result = prime * result
+ ((lastLoginTime == null) ? 0 : lastLoginTime.hashCode());
result = prime * result
+ ((password == null) ? 0 : password.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((phone == null) ? 0 : phone.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((role == null) ? 0 : role.hashCode());
result = prime * result
+ ((username == null) ? 0 : username.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
User other = (User) obj;
if (companyId == null) {
if (other.companyId != null)
return false;
} else if (!companyId.equals(other.companyId))
return false;
if (id == null) {
if (other.id != null)
return false;
} else if (!id.equals(other.id))
return false;
if (lastLoginTime == null) {
if (other.lastLoginTime != null)
return false;
} else if (!lastLoginTime.equals(other.lastLoginTime))
return false;
if (password == null) {
if (other.password != null)
return false;
} else if (!password.equals(other.password))
return false;
if (phone == null) {
if (other.phone != null)
return false;
} else if (!phone.equals(other.phone))
return false;
if (role == null) {
if (other.role != null)
return false;
} else if (!role.equals(other.role))
return false;
if (username == null) {
if (other.username != null)
return false;
} else if (!username.equals(other.username))
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", username=" + username + ", password="
+ password + ", phone=" + phone + ", role=" + role
+ ", companyId=" + companyId + ", lastLoginTime="
+ lastLoginTime + "]";
}
}
JavaBean必须实现序列化接口,重写hashCode( )方法和equals( )方法。
我们再数据库中对应的表是 :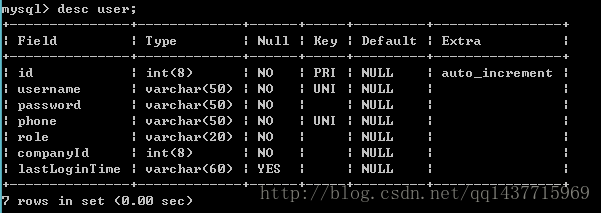
准备完毕,我们开始准备Servlet提供一个访问的方法。
在这里,大家一定要知道的是这里的Servlet是HttpServelt,这个类声明周期方法必须烂熟于心。
package com.test.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.Cookie;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import com.test.entity.User;
import com.test.utils.JDBCUtils;
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
String sql = "select * from user where username = ? and password = ?";
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try {
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1,username);
pstmt.setString(2,password);
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
if(rs.next()){
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String DBUsername = rs.getString("username");
String DBPassword = rs.getString("password");
String phone = rs.getString("phone");
String role = rs.getString("role");
int companyId = rs.getInt("companyId");
String lastLoginTime = rs.getString("lastLoginTime");
User user = new User(id, DBUsername, DBPassword, phone, role, companyId, lastLoginTime);
request.getSession().setAttribute("user",user);
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
for(Cookie cookie:cookies){
System.out.println(cookie.getName());
System.out.println(cookie.getValue());
}
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
在上面的Servlet中我们使用到了JDBCUtils方法,这个就是我们自己封装的一个方法,不要想着它有多么的高大上,就是很普通的一个工具类而已。
我们还是展示一下我们的JDBCUtils方法的具体编码 :
package com.test.utils;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JDBCUtils {
private static String driverName;
private static String url;
private static String username;
private static String password;
private static Properties props;
static {
props = new Properties();
InputStream in = JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
try {
props.load(in);
driverName = props.getProperty("mysql.driver");
url = props.getProperty("mysql.url");
username = props.getProperty("mysql.username");
password = props.getProperty("mysql.password");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getConnection() {
Connection conn = null;
try {
Class.forName(driverName);
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return conn;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(getConnection());
}
}
然后是我们的jdbc配置文件 :
mysql.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
mysql.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/cctrace
mysql.username=root
mysql.password=123456这样的话,我们还差一个设置JSESSIONID的servlet。其代码实现如下所示 :
package com.test.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.Cookie;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class SetJeSessionIdServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String JESESSIONID = request.getParameter("JSESSIONID");
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("JSESSIONID",JESESSIONID);
response.addCookie(cookie);
}
}
以上基本上已经把准备工作做完,还差一个展示页面,我们就用欢迎页中的index.jsp页面配合EL表达式来做展示功能。
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'index.jsp' starting pagetitle>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
head>
<body>
${sessionScope.user.username}
body>
html>
上述是我们的展示页面,使我们第一次访问该站点时要访问的页面,HttpSession在jsp页面第一次被访问时或者在Servlet中第一次被调用request(HttpServletRequest).getSession()时创建。但是当前会话中不存在这个对象,所以不会显示任何信息。
看一下web.xml中的配置信息,我们对应的映射之后,我们就可以对该项目进行测试了 :
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"
id="WebApp_ID" version="3.1">
<display-name>JSessionIdDBTestdisplay-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.htmlwelcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.htmwelcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.jspwelcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.htmlwelcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.htmwelcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.jspwelcome-file>
welcome-file-list>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>loginServletservlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.test.servlet.LoginServletservlet-class>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>loginServletservlet-name>
<url-pattern>/login.dourl-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>setJeSessionservlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.test.servlet.SetJeSessionIdServletservlet-class>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>setJeSessionservlet-name>
<url-pattern>/setSession.dourl-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
web-app>
访问结果是空白,下面我们登陆一下,登陆之后,HttpSession中会保存一个user对象,就是当前登录用户。
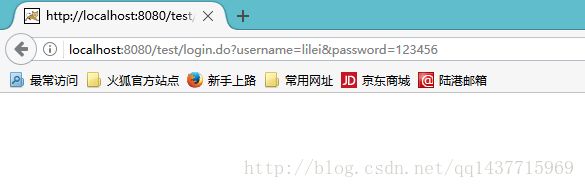
简单的模拟了登录之后,我们看一下控制台打印效果 :

登录之后的结果是 :
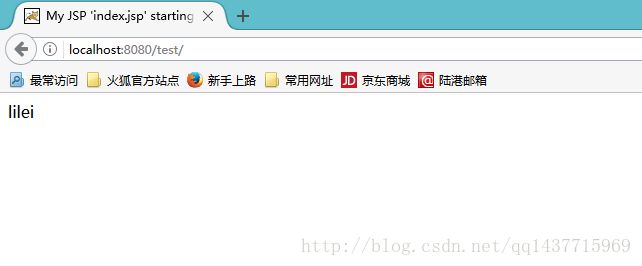
此处获取到了前台传递过来的Cookie中的JSESSIONID,也就是说我们获取到了一个HttpSession对象的灵魂。
调用了这个方法之后,我们换一个浏览器,但是不登录,去添加一个Cookie,访问我们写好的Servlet就OK了。

我们的servlet中的处理如图 :

我们没有调用登录方法,换了个浏览器,我们去首页测试一下。
 ,没有登录,盗取JSESSIONID成功。
,没有登录,盗取JSESSIONID成功。