Faster RCNN源码解读(Tensorflow 版)
(二)anchors的产生
我们fork下来的项目里,lib文件下有如下文件:

config:配置文件,一些超参数和项目路径的配置
nets:网络的类定义文件,基类:network,派生类:vgg16或resnet
datasets:处理数据集的代码包,主要用到factory.py,imdb.py,pascal_voc.py,roidb.py;
layer_utils:一些网络训练或测试时需要用到的辅助函数,比如proposal_layer.py:产生约2000个boxes,以及其得分,这里我们要解析的是generate_anchors.py和snippets.py文件实现的功能,现在我们直接跳转到vgg16的build_rpn函数处,我们发现,在创建RPN 之前,首先运行了self._anchor_componet()函数,该函数定义于network.py中,我们找到他:
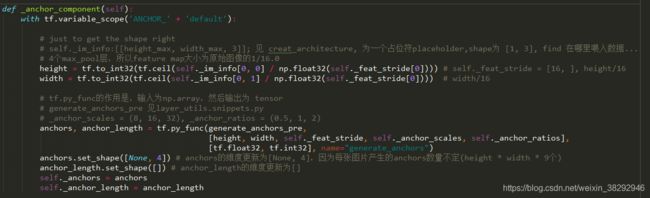
height即为图像放缩后的高/16,width即为图像放缩后的宽/16的向上取整,后面我们将二者简记为H,W,其实这也是feature map的尺寸;接着执行tf.py_func函数,该函数的功能是:将输入为ndarray的参数输出为一个tensor(为何如此操作?因为,训练时我们‘喂入’单张图片,而每张图片的尺寸可能不一样,这样H,W的值就会变化,通过设置tensor的某个维度为None,以接收可变的维度); 该函数输入五个参数:H,W,self._feat_stride,self._anchor_scales,self._anchor_ratios
该函数定义在layer_utils文件夹下的snippets.py中,详见第二段代码
首先我们关注一下generate_anchors这个函数,其返回9个中心点在(7.5,7.5),w = (128,256,512,184, 368, 736,88,187,352),h = (128,256,512,96,192,384,176,352,704)
可见w:h的比例有3种:即1,2,0.5; scales也有三种(8,16,32),例如16*(8,16,32)=(128,256,512),23*(8,16,32)=(184,368,736)…
def generate_anchors(base_size=16, ratios=[0.5, 1, 2],
scales=2 ** np.arange(3, 6)):
# scales: [8 16 32]
"""
Generate anchor (reference) windows by enumerating aspect ratios X
scales wrt a reference (0, 0, 15, 15) window.
"""
base_anchor = np.array([1, 1, base_size, base_size]) - 1 # base_anchor = [0 0 15 15]
ratio_anchors = _ratio_enum(base_anchor, ratios)
#print(ratio_anchors)
'''
[[-3.5 2. 18.5 13. ]
[ 0. 0. 15. 15. ]
[ 2.5 -3. 12.5 18. ]]
'''
#print([_scale_enum(ratio_anchors[i, :], scales) for i in range(ratio_anchors.shape[0])]) # scales = [8, 16, 32]
# scales = [8, 16, 32]
anchors = np.vstack([_scale_enum(ratio_anchors[i, :], scales) for i in range(ratio_anchors.shape[0])]) # 合并行
## scales = [8, 16, 32] ratio_anchors.shape[0] = 3
return anchors
# anchors:
''' ->1.w = 23, h = 12, x_ctr = 7.5, y_ctr = 7.5时:
ws = [184, 368, 736]; hs = [96,192,384]
np.stack(7.5-0.5*([184,368,736]-1),7.5-0.5*([96,192,384]-1),7.5+0.5*([184,368,736]-1),7.5+0.5*([96,192,384])-1)
=np.stack(7.5-[91.5,183.5,367.5], 7.5-[47.5, 95.5, 191.5],7.5+[91.5,183.5,367.5], 7.5+[47.5, 95.5, 191.5])
=np.stack([-84,-176,-360],[99,191,375],[-40,-88,-184],[55,103,199])
=[[ -84. -40. 99. 55.] # [x1,y1,x2,y2]
[-176. -88. 191. 103.]
[-360. -184. 375. 199.]]
->2.w=16, h=16, x_ctr = 7.5, y_ctr = 7.5时:
ws = [128,256,512], hs = [128,256,512]
np.stack(7.5-0.5*([128,256,512]-1), 7.5-0.5*([128,256,512]-1),7.5+0.5([128,256,512]-1),, 7.5+0.5*([128,256,512]-1))
=np.stack(7.5-[63.5,127.5,255.5], 7.5-[63.5,127.5,255.5], 7.5+[63.5,127.5,255.5], 7.5+[63.5,127.5,255.5])
=np.stack([-56,-120,-248],[-56,-120,-248],[71,135,263],[71,135,263])
=[[-56,-120,-248]
[-56,-120,-248]
[ 71, 135, 263]
[ 71, 135, 263]]
->3.w=11,h=22,x_ctr=7.5,y_ctr=7.5
ws = [88,187,352], hs = [176,352,704]
np.stack(7.5-0.5*([88,187,352]-1),7.5-0.5*([176,352,704]-1), 7.5+0.5*([88,187,352]-1), 7.5+0.5*([176,352,704]-1))
=np.stack(7.5-[43.5,93.5,175.5],7.5-[87.5,175.5,351.5],7.5+[43.5,93.5,175.5], 7.5+[87.5,175.5,351.5])\
=[[ -36. -80. 51. 95.]
[ -80. -168. 95. 183.]
[-168. -344. 183. 359.]]
# [x1,y1,x2,y2]
[[ -84. -40. 99. 55.]
[-176. -88. 191. 103.]
[-360. -184. 375. 199.] w:h = 2:1
[ -56. -56. 71. 71.]
[-120. -120. 135. 135.]
[-248. -248. 263. 263.] w:h = 1:1
[ -36. -80. 51. 95.]
[ -80. -168. 95. 183.]
[-168. -344. 183. 359.]]w:h = 1:2
'''
# 返回对于一个anchor窗口的width, height, 和中心坐标(x, y)
def _whctrs(anchor): # anchor = [0 0 15 15]
"""
Return width, height, x center, and y center for an anchor (window).
"""
w = anchor[2] - anchor[0] + 1 # w = 16
h = anchor[3] - anchor[1] + 1 # h = 16
x_ctr = anchor[0] + 0.5 * (w - 1) # x_ctr = 7.5
y_ctr = anchor[1] + 0.5 * (h - 1) # y_ctr = 7.5
return w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr
# 给定一组宽高向量,输出各个anchor,即预测窗口(包括左上角、右下角坐标),各个anchors的面积相等,只是宽高比不同
def _mkanchors(ws, hs, x_ctr, y_ctr):
"""
Given a vector of widths (ws) and heights (hs) around a center
(x_ctr, y_ctr), output a set of anchors (windows).
"""
ws = ws[:, np.newaxis] # ws = array([[23], [16], [11]])
hs = hs[:, np.newaxis] # hs = array([[12], [16], [22]])
anchors = np.hstack((x_ctr - 0.5 * (ws - 1),
y_ctr - 0.5 * (hs - 1),
x_ctr + 0.5 * (ws - 1),
y_ctr + 0.5 * (hs - 1))) # 按水平方向进行合并(合并列)
#print(anchors) 如下:面积大小为16*16,中心点都是(7.5,7.5),但长宽比为(0.5,1,2)
'''
[[-3.5 2. 18.5 13. ]
[ 0. 0. 15. 15. ]
[ 2.5 -3. 12.5 18. ]]
'''
return anchors
# 枚举一个anchor三种宽高比的具体数值
def _ratio_enum(anchor, ratios):
""" 列举关于一个anchors的三种宽高比 1:2, 1:1, 2:1
Enumerate a set of anchors for each aspect ratio wrt an anchor.
"""
w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr = _whctrs(anchor) # w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr = 16, 16, 7.5, 7.5
size = w * h # size = 256
# 解释: sqrt(S/a)*a*sqrt(S/a) = S
size_ratios = size / ratios # size_ratios = [512, 256, 128]
ws = np.round(np.sqrt(size_ratios)) # ws = [round(16*1.414=22.6)=23, 16, 11]
hs = np.round(ws * ratios) # ws * ratios = [11.5, 16, 22]; hs = [12, 16, 22]
# print(np.round(11.5)) 得到12
#print(np.round(4.5)) 得到4
#print(ws)
#print(hs)
anchors = _mkanchors(ws, hs, x_ctr, y_ctr) # 给定一组宽高向量,输出各个窗口的中心坐标、左上角、右下角坐标
return anchors
# 枚举一个anchor的各种尺度(width&height的放大倍数)scales = [8, 16, 32],以anchor[0 0 15 15]为例
# anchor = [-3.5 2. 18.5 13. ], [ 0. 0. 15. 15. ], [ 2.5 -3. 12.5 18. ]
def _scale_enum(anchor, scales):
""" 列举一个关于anchor的三种尺度 128*128 256*256 512*512
Enumerate a set of anchors for each scale wrt an anchor.
"""
# 以anchor = [-3.5 2. 18.5 13. ]为例
w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr = _whctrs(anchor) # w = 23, h = 12, x_ctr = 7.5, y_ctr = 7.5(当然anchor的中心点坐标不会变化)
ws = w * scales # ws = [184, 368, 736]
hs = h * scales # hs = [96, 192, 384]
anchors = _mkanchors(ws, hs, x_ctr, y_ctr) # 给定一组宽高向量,输出各个窗口的中心坐标、左上角、右下角坐标
return anchors
理解了中心点在(7.5,7.5),base_size = 16处(其实就是feature map上最左上角的那个点在原图的感受野)9个anchors的产生过程,其实后面那些anchors只需要在此9个anchors上做w,h方向的偏移即可,因为每次偏移一个像素点,故在横轴方向偏移时,x的坐标+16,y的坐标不变,而在纵轴方向偏移时,y的坐标+16,x的坐标不变,因为有HxW个像素点,故偏移向量有WxH个,最后总的anchors的维度为:(HxWx9,4)
import numpy as np
from lib.layer_utils.generate_anchors import generate_anchors
# height = ceil(height/16.0): 向正无穷方向取整,width = ceil(width/16.0)
def generate_anchors_pre(height, width, feat_stride, anchor_scales=(8, 16, 32), anchor_ratios=(0.5, 1, 2)):
# 产生位置:调用函数 generate_anchors得到 shape为(9,4)的ndarray.(9个anchors,每个anchors有四个参数x1,y1,x2,y2)
anchors = generate_anchors(ratios=np.array(anchor_ratios), scales=np.array(anchor_scales))
#print(anchors)
# anchors:
''' base = [0,0,15,15],scales = [8,16,32],ratios = [0.5,1,2]的
[ x1, y1, x2, y2 ]:
[[ -84. -40. 99. 55.]
[-176. -88. 191. 103.]
[-360. -184. 375. 199.]
[ -56. -56. 71. 71.]
[-120. -120. 135. 135.]
[-248. -248. 263. 263.]
[ -36. -80. 51. 95.]
[ -80. -168. 95. 183.]
[-168. -344. 183. 359.]]
'''
A = anchors.shape[0] # 9
# 以 height:32(ceil(500/16)), width:23(ceil(353/16)) 为例; 得到feature maps上每个点的anchors之间的h和w的偏移量(以16等差)
shift_x = np.arange(0, width) * feat_stride # np.arange(0,width) * [16,], width = 23
# shift_x: [ 0 16 32 48 64 80 96 112 128 144 160 176 192 208 224 240 256 272 288 304 320 336 352]
shift_y = np.arange(0, height) * feat_stride # np.arange(0, height) * [16,], height = 32
'''shift_y = [ 0 16 32 48 64 80 96 112 128 144 160 176 192 208 224 240 256 272
288 304 320 336 352 368 384 400 416 432 448 464 480 496]
'''
'''
a, b = np.meshgrid(x,y): x变成矩阵 a 的行向量,y变成矩阵 b 的列向量 ,a,b的维度相同
'''
shift_x, shift_y = np.meshgrid(shift_x, shift_y)
# shift_x: 32个shift_x(每个shift_x为行向量); shift_y: 23列shift_y(每个shift_y为列向量)
#print(shift_y)
'''
print(shift_x) (32,23)
[[ 0 16 32 48 64 80 96 112 128 144 160 176 192 208 224 240 256 272 288 304 320 336 352]
[ 0 16 32 48 64 80 96 112 128 144 160 176 192 208 224 240 256 272 288 304 320 336 352]
[ 0 16 32 48 64 80 96 112 128 144 160 176 192 208 224 240 256 272 288 304 320 336 352]
...
[ 0 16 32 48 64 80 96 112 128 144 160 176 192 208 224 240 256 272 288 304 320 336 352]
]
print('--------------------------')
print(shift_y):
[[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ] #23个
[16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16]
...
[496 496 496 496 496 496 496 496 496 496 496 496 496 496 496 496 496 496 496 496 496 496 496]
]
print('--------------------------')
print(shift_x.shape) # (32, 23)
print(shift_y.shape) # (32, 23)
'''
#print(shift_y.ravel()) # 功能和flatten相同,即将多维数组降至一维,区别在于 flatten不改变原始矩阵,但ravel会改变原始矩阵。
#print(np.vstack((shift_x.ravel(), shift_y.ravel(), shift_x.ravel(), shift_y.ravel()))[1,:])
shifts = np.vstack((shift_x.ravel(), shift_y.ravel(), shift_x.ravel(), shift_y.ravel())).transpose() # 不转置之前的 shape 为(4, 736)
#print(shifts.shape) # (736, 4)
K = shifts.shape[0] # K = 736
#print(shifts[0:48])
#output:
'''
[[ 0 0 0 0]
[ 16 0 16 0]
[ 32 0 32 0]
[ 48 0 48 0]
[ 64 0 64 0]
[ 80 0 80 0]
[ 96 0 96 0]
[112 0 112 0]
[128 0 128 0]
[144 0 144 0]
[160 0 160 0]
[176 0 176 0]
[192 0 192 0]
[208 0 208 0]
[224 0 224 0]
[240 0 240 0]
[256 0 256 0]
[272 0 272 0]
[288 0 288 0]
[304 0 304 0]
[320 0 320 0]
[336 0 336 0]
[352 0 352 0] # feature map第一行的点的锚框的偏移(23个偏移量)
[ 0 16 0 16]
[ 16 16 16 16]
[ 32 16 32 16]
[ 48 16 64 16]
[ 80 16 80 16]
[ 96 16 96 16]
[112 16 112 16]
[128 16 128 16]
[144 16 144 16]
[160 16 160 16]
[176 16 176 16]
[192 16 192 16]
[208 16 208 16]
[224 16 224 16]
[240 16 240 16]
[256 16 256 16]
[272 16 272 16]
[288 16 288 16]
[304 16 304 16]
[320 16 320 16]
[336 16 336 16]
[352 16 352 16]] # feature map第二行的点的锚框的偏移(23个偏移量,相比于第一行,只有y1,y2发生16像素点的偏移)
'''
# width changes faster, so here it is H, W, C
#print(anchors.reshape((1, 9, 4)))
#print(shifts.reshape((1, K, 4)).transpose((1,0,2)).shape) # (736, 1, 4)
# transpose((1, 0, 2))多维数组的转置:原来数组的第一、二维索引调换一下;
# 给每一个点的anchors加上该位置对应的x,y方向的偏移量(H*W个点对应H*W个偏移量数组)
anchors = anchors.reshape((1, A, 4)) + shifts.reshape((1, K, 4)).transpose((1, 0, 2))
#print(shifts.reshape((1, K, 4)).transpose((1, 0, 2)).shape) # (736, 1, 4)
#print(anchors.shape) # (736, 9, 4)
#print(anchors[23,:,:])
anchors = anchors.reshape((K * A, 4)).astype(np.float32, copy=False) # anchors.shape = (6624, 4)
# 一共得到 H*W*9个anchors,每个anchors有四个参数值
length = np.int32(anchors.shape[0]) # 736*9 = 6624
return anchors, length # 返回的是一个 (height * width * 9, 4)的ndarray, length = height * width * 9.
# 每张图片产生的anchors及其数量
# if __name__ == '__main__':
# a,b =generate_anchors_pre(32, 23, [16,], anchor_scales=(8, 16, 32), anchor_ratios=(0.5, 1, 2))
# print(a[0:8])
至此,在HxW大小的feature map上,产生了HxWx9个anchors…接下来做什么呢?下一篇讲解~