Week 12 作业
文章目录
- A - 必做题 - 1
- 输入
- 输出
- 样例输入
- 样例输出
- 思路
- 综述
- 总结
- 代码
- B - 必做题 - 2 三维bfs搜索
- 输入
- 输出
- 样例输入
- 样例输出
- 思路
- 综述
- 总结&&拓展
- 踩踩坑
- 代码
- C - 必做题 - 3 m段最长子串
- 输入
- 输出
- 样例输入
- 样例输出
- 思路
- 综述
- 状态定义
- 状态转移:
- 总结
- 最原始的没有滚动数组的
- 添加滚动数组,但是超时
- 完整的代码
- D - 选做题 - 1
- 输入
- 输出
- 样例输入
- 样例输出
- 思路
- 综述
- 状态定义
- 状态转移
- 总结
- 坑点
- 代码
- E - 选做题 - 2
- 输入
- 输出
- 样例输入
- 样例输出
- 综述
- 关于位运算:
- 状态
- 转移方程
- 如何保证字典序最小
- SUM求法
- 总结
- 注意
- 代码
A - 必做题 - 1
给出n个数,zjm想找出出现至少(n+1)/2次的数, 现在需要你帮忙找出这个数是多少?
输入
本题包含多组数据:
每组数据包含两行。
第一行一个数字N(1<=N<=999999) ,保证N为奇数。
第二行为N个用空格隔开的整数。
数据以EOF结束。
输出
对于每一组数据,你需要输出你找到的唯一的数。
样例输入
5
1 3 2 3 3
11
1 1 1 1 1 5 5 5 5 5 5
7
1 1 1 1 1 1 1
样例输出
3
5
1
思路
综述
最初:想的是没有说数据范围,想必可能超过int,所以干脆开了long long.于是写了个O(n^2)的算法,直接导致TLE;
改进:开1e6的数组来存储,i索引号对应的数字是数字i出现次数。
总结
最初拿到这个题感觉有点小坑:没有说数据范围,直接导致了第一次提交超时:(想必应该是题目不够严谨)
![]()
代码
#include B - 必做题 - 2 三维bfs搜索
zjm被困在一个三维的空间中,现在要寻找最短路径逃生!
空间由立方体单位构成。
zjm每次向上下前后左右移动一个单位需要一分钟,且zjm不能对角线移动。
空间的四周封闭。zjm的目标是走到空间的出口。
是否存在逃出生天的可能性?如果存在,则需要多少时间?
输入
输入第一行是一个数表示空间的数量。
每个空间的描述的第一行为L,R和C(皆不超过30)。
L表示空间的高度,R和C分别表示每层空间的行与列的大小。
随后L层,每层R行,每行C个字符。
每个字符表示空间的一个单元。’#‘表示不可通过单元,’.‘表示空白单元。
zjm的起始位置在’S’,出口为’E’。每层空间后都有一个空行。
L,R和C均为0时输入结束。
输出
每个空间对应一行输出。
如果可以逃生,则输出如下
Escaped in x minute(s).
x为最短脱离时间。
如果无法逃生,则输出如下
Trapped!
样例输入
3 4 5
S….
.###.
.##..
###.#
#####
#####
##.##
##…
#####
#####
#.###
####E
1 3 3
S##
#E#
###
0 0 0
样例输出
Escaped in 11 minute(s).
Trapped!
思路
综述
bfs搜索的模板题;
最初拿到题目的时候有点蒙。细细思考发现和二维空间并无差异。
不可以用dfs,dfs可以找到出口,但是找不到最短的路线。
总结&&拓展
二维地图可以轻易拓展到三维;
于是n维空间的种种题目也可以类比做出。
踩踩坑
scanf("%c",ch);这样会读入空格和回车符
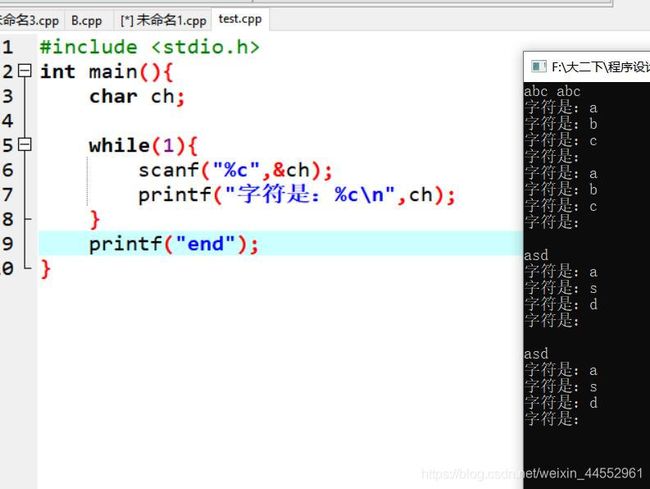 以下两种写法可以忽略回车符和空格
以下两种写法可以忽略回车符和空格
cin>>ch;
scanf(" %c",&ch);
代码
#include C - 必做题 - 3 m段最长子串
东东每个学期都会去寝室接受扫楼的任务,并清点每个寝室的人数。
每个寝室里面有ai个人(1<=i<=n)。从第i到第j个宿舍一共有sum(i,j)=a[i]+…+a[j]个人
这让宿管阿姨非常开心,并且让东东扫楼m次,每一次数第i到第j个宿舍sum(i,j)
问题是要找到sum(i1, j1) + … + sum(im,jm)的最大值。且ix <= iy <=jx和ix <= jy <=jx的情况是不被允许的。也就是说m段都不能相交。
注:1 ≤ i ≤ n ≤ 1e6 , -32768 ≤ ai ≤ 32767 人数可以为负数。。。。(1<=n<=1000000)
输入
输入m,输入n。后面跟着输入n个ai 处理到 EOF
输出
输出最大和
样例输入
1 3 1 2 3
2 6 -1 4 -2 3 -2 3
样例输出
6
8
思路
综述
该题用到方法有:dp+滚动数组;
题意归结为一句话就是m段最长子串问题;
难点就在定状态和状态转移方程以及滚动数组的应用。
状态定义
dp[i][j]表示前j个数据共i个区间所能取到的最大值;(注意其中第a[j]包含在内)
状态转移:
(注意其中第a[j]包含在内)
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j-1]+a[j] , dp[i-1][k] + a[j])(1<=k<=j-1)
总结
动态规划感觉有这么一个流程
写出最原始的状态定义和状态转移方程->滚动数组进行优化空间复杂度->其他方面优化时间复杂度
直接贴出多次不成功代码,供学习借鉴
最原始的没有滚动数组的
#include
}
int main(){
while(scanf("%d%d",&m,&n)!=EOF)
{
init();
in();
work();
}
}
添加滚动数组,但是超时
#include 完整的代码
#include D - 选做题 - 1
We give the following inductive definition of a “regular brackets” sequence:
the empty sequence is a regular brackets sequence,
if s is a regular brackets sequence, then (s) and [s] are regular brackets sequences, and
if a and b are regular brackets sequences, then ab is a regular brackets sequence.
no other sequence is a regular brackets sequence
For instance, all of the following character sequences are regular brackets sequences:
(), [], (()), ()[], ()[()]
while the following character sequences are not:
(, ], )(, ([)], ([(]
Given a brackets sequence of characters a1a2 … an, your goal is to find the length of the longest regular brackets sequence that is a subsequence of s. That is, you wish to find the largest m such that for indices i1, i2, …, im where 1 ≤ i1 < i2 < … < im ≤ n, ai1ai2 … aim is a regular brackets sequence.
Given the initial sequence ([([]])], the longest regular brackets subsequence is [([])].
输入
The input test file will contain multiple test cases. Each input test case consists of a single line containing only the characters (, ), [, and ]; each input test will have length between 1 and 100, inclusive. The end-of-file is marked by a line containing the word “end” and should not be processed.
输出
For each input case, the program should print the length of the longest possible regular brackets subsequence on a single line.
样例输入
((()))
()()()
([]])
)[)(
([][][)
end
样例输出
6
6
4
0
6
思路
综述
课上例题,是正常的动态规划,没有用到滚动数组之类的;
状态定义
总结共两种情况:
f[i][j]表示子序列[i,j]变成合法序列需要添加的最少括号的数量。
最终答案就应该是f[1][n]
状态转移
总结共两种情况:
* f[i][j] = min{f[i][k] + f[k+1][j]},( i≤k<j)
* 若S形如[S’]或(S’) ,那么f[i][ j] = min{f[i+1][ j-1]}
总结
动态规划的经典例题,动态规划题目最开始没有入门,做题多了之后发现有章可循;
坑点
初始化问题:
以后都单独写一个函数,多组数据之间需要初始化的变量都统一进行处理,这样不容易遗漏之类的;
void init(){
//初始化,因为合法数据是j>i所以,不需要初始化上三角
for(int i=0;i<110;i++)
for(int j=0;j<110;j++)
dp[i][j]=0;
}
match匹配函数
注意有两组可能
int match(int i,int j){
if( (s[i]=='('&&s[j]==')') || (s[i]=='['&&s[j]==']') ){
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
代码
#include E - 选做题 - 2
马上假期就要结束了,zjm还有 n 个作业,完成某个作业需要一定的时间,而且每个作业有一个截止时间,若超过截止时间,一天就要扣一分。
zjm想知道如何安排做作业,使得扣的分数最少。
Tips: 如果开始做某个作业,就必须把这个作业做完了,才能做下一个作业。
输入
有多组测试数据。第一行一个整数表示测试数据的组数
第一行一个整数 n(1<=n<=15)
接下来n行,每行一个字符串(长度不超过100) S 表示任务的名称和两个整数 D 和 C,分别表示任务的截止时间和完成任务需要的天数。
这 n 个任务是按照字符串的字典序从小到大给出。
输出
每组测试数据,输出最少扣的分数,并输出完成作业的方案,如果有多个方案,输出字典序最小的一个。
样例输入
2
3
Computer 3 3
English 20 1
Math 3 2
3
Computer 3 3
English 6 3
Math 6 3
样例输出
2
Computer
Math
English
3
Computer
English
Math
综述
是一道动态规划的题目;动态规划里面的状压dp;
主要是因为对于某些题目来说,状态尤其复杂,如果使用先前的多维数组 来表示,将会导致数组维度非常大,可操作性非常低
因此我们考虑使用一些编码技术,比如二进制编码,用一个数字来 表示一个状态,实现状态压缩的目的
关于位运算:
状态
f[S] 表示完成 S 作业集合后被扣的最少分数
假设S是5则转换为二进制就是101说明该状态完成了作业1和作业3;
转移方程
• sum = S 作业集合对应的总时间
• f[S|(1<<x)] = f[S] + tmp(作业 x 被扣的分数)
• c[x] = 作业 x 完成所需时间
• d[x] = 作业 x 的 DDL
• tmp = max ( sum + c[x] – d[x], 0 )
如何保证字典序最小
跟学长学到的套路,这类题可以按字典序排序试试,可能会有奇效;
SUM求法
注意sum在代码里面经常出现,但是求解的过程复杂,将其剥离开来,单独为一个子函数,增加可读性;
int sum(int node){
int time=0;
int cnt=1;
for(int i=1;i <= (1<<n)-1;i<<=1){
if(node & i){
time += TASK[cnt-1].day;
}
cnt++;
}
return time;
}
总结
最近养成的风格:
main函数里面将大部分的操作都分离开,这样一目了然,清晰爽快;
int main(){
cin>>T;
while(T--){
init();
in();
work();
cout<<ans[(1<<n)-1]<<endl;
print((1<<n)-1);
}
}
注意
注意print里面的状态还是某个作业的区分,一开始的时候入坑了。(没区分好状态和作业)
void print(int node){
if(node == 0) return;
print( node - ( 1 << way[node] ) );
cout<<TASK[way[node]].name<<endl;
}
代码
上文有详细注释
#include 