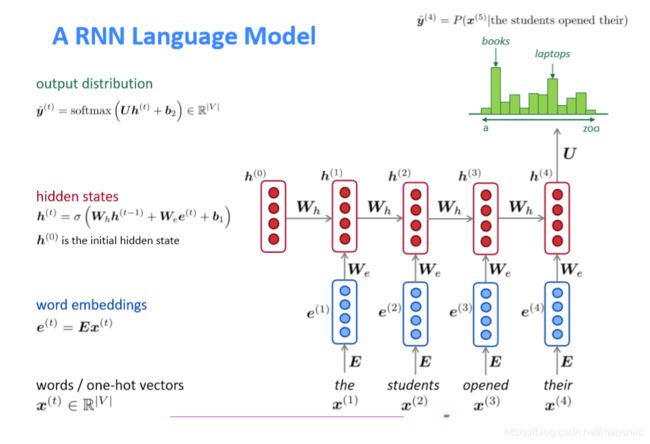
【pytorch实战02】RNN相关算法实现语言模型
本次实验在上次word-embeding基础上使用pytorch+torchtext完成
原理:
-
LSTM
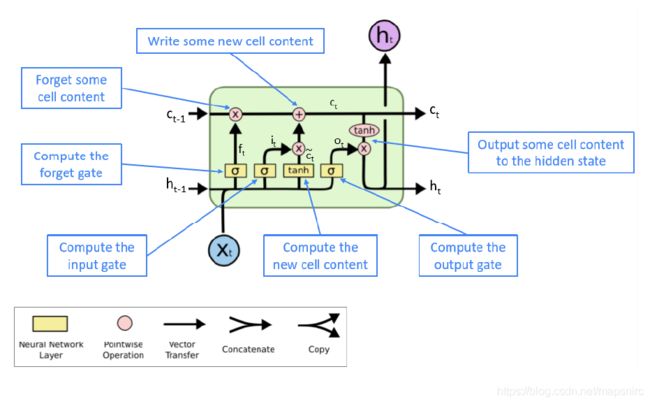
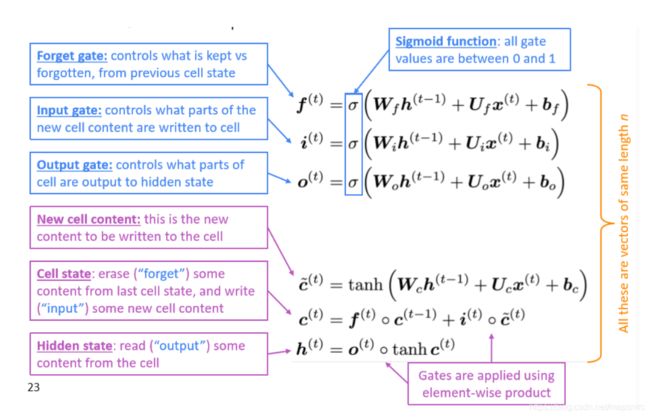

“相较于RNN,LSTM增加了cell state和门控单元从而保存长期依赖的信息,但实际上它并没有完全解决梯度消失问题,只是提供了一个简便的方法解决了模型难以学习长期依赖的问题。尽管如此,LSTM的表现也要比RNN好很多。在2013-2015年,LSTM在手写识别、语音识别、机器翻译等多个问题上取得了state-of-the-art的结果。不过现在(2019-2020年),LSTM渐渐淡出了人们的视野,取代它的是Transformers”
参考链接:LSTM介绍
USE_CUDA = torch.cuda.is_available()
# 为了保证实验结果可以复现,我们经常会把各种random seed固定在某一个值
random.seed(53113)
np.random.seed(53113)
torch.manual_seed(53113)
if USE_CUDA:
torch.cuda.manual_seed(53113)
BATCH_SIZE = 32
EMBEDDING_SIZE = 650
MAX_VOCAB_SIZE = 50000
# 利用torchtext进行数据预处理
TEXT = torchtext.data.Field(lower=True)
train, val, test = torchtext.datasets.LanguageModelingDataset.splits(path=".",
train="text8.train.txt",
validation="text8.dev.txt", test="text8.test.txt",
text_field=TEXT)
print(train.examples)
# print(len(train))
TEXT.build_vocab(train, max_size=MAX_VOCAB_SIZE)
print(len(TEXT.vocab))
VOCAB_SIZE = len(TEXT.vocab)
train_iter, val_iter, test_iter = torchtext.data.BPTTIterator.splits(
(train, val, test), batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, bptt_len=32, repeat=False, shuffle=True)
it = iter(train_iter)
batch = next(it)
print(" ".join([TEXT.vocab.itos[i] for i in batch.text[:, 1].data]))
print(" ".join([TEXT.vocab.itos[i] for i in batch.target[:, 1].data]))
# vocab.py
# stoi:一个collections.defaultdict实例,它将令牌字符串映射到数字标识符(string 2 index)
# itos:由其数字标识符索引的令牌字符串的列表(index 2 string)
class RNNModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, rnn_type, ntoken, ninp, nhid, nlayers, dropout=0.5):
''' 该模型包含以下几层:
- 词嵌入层
- 一个循环神经网络层(RNN, LSTM, GRU)
- 一个线性层,从hidden state到输出单词表
- 一个dropout层,用来做regularization
ntoken: vocab_size
nhid: hidden_size
ninp: embedding的维度
'''
super(RNNModel, self).__init__()
self.drop = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.encoder = nn.Embedding(ntoken, ninp)
if rnn_type in ['LSTM', 'GRU']:
self.rnn = getattr(nn, rnn_type)(ninp, nhid, nlayers, dropout=dropout)
else:
try:
nonlinearity = {'RNN_TANH': 'tanh', 'RNN_RELU': 'relu'}[rnn_type]
except KeyError:
raise ValueError("""An invalid option for `--model` was supplied,
options are ['LSTM', 'GRU', 'RNN_TANH' or 'RNN_RELU']""")
self.rnn = nn.RNN(ninp, nhid, nlayers, nonlinearity=nonlinearity, dropout=dropout)
# decoder 用来将RNN的输出转码成one-hot
self.decoder = nn.Linear(nhid, ntoken)
self.init_weights()
self.rnn_type = rnn_type
self.nhid = nhid
self.nlayers = nlayers
def init_weights(self):
initrange = 0.1
self.encoder.weight.data.uniform_(-initrange, initrange)
self.decoder.bias.data.zero_()
self.decoder.weight.data.uniform_(-initrange, initrange)
def forward(self, input, hidden):
''' Forward pass:
- word embedding
- 输入循环神经网络
- 一个线性层从hidden state转化为输出单词表
'''
# input:seq_length * batch_size
emb = self.drop(self.encoder(input)) # input: seq_length * batch_size * embed_size
# output: seq_length * batch_size * hidden_size
# hidden: (1 * batch_size * hidden_size, 1 * batch_size * hidden_size)
output, hidden = self.rnn(emb, hidden) # 这里输出的shape可以参考pytorch api
output = self.drop(output)
# decoded是三维的,Linear变换需要把decoded变成2层的
decoded = self.decoder(output.view(output.size(0) * output.size(1), output.size(2)))
# pytorch的view方法用于重构张量的维度
return decoded.view(output.size(0), output.size(1), decoded.size(1)), hidden
def init_hidden(self, bsz, requires_grad=True):
# bsz: batch_size
# 这里状态初始化为全0,因为不知道模型是否在CUDA上,所以利用param来创建全0的tenser
weight = next(self.parameters())
if self.rnn_type == 'LSTM':
# 如果是LSTM,则隐藏层需要两个权值矩阵,一个给hidden,一个给cell
return (weight.new_zeros((self.nlayers, bsz, self.nhid), requires_grad=requires_grad),
weight.new_zeros((self.nlayers, bsz, self.nhid), requires_grad=requires_grad))
else:
return weight.new_zeros((self.nlayers, bsz, self.nhid), requires_grad=requires_grad)
model = RNNModel("LSTM", VOCAB_SIZE, EMBEDDING_SIZE, EMBEDDING_SIZE, 2, dropout=0.5)