pytorch源码解读——RNN/LSTM篇
文章的字母中:
b: batch_size
t: time_step
n: num_feature
h: hidden_size
假设输入数据维度input = (b, t, n)
所设计的LSTM模型如下:
class MYLSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, out_size):
super(MYLSTM, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.input_size = input_size
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(
input_size=self.input_size + self.hidden_size,
hidden_size=self.hidden_size,
num_layers=1,
batch_first=True,
)
self.out = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, out_size)
def forward(self, x):
hidden, cell = Variable(torch.zeros(1, x.size(0), self.hidden_size)),\
Variable(torch.zeros(1, x.size(0), self.hidden_size))
for i in range(x.size(1)):
curx = x[:, i, :].unsqueeze(1)
curx = torch.cat((curx, hidden.permute(1, 0, 2)), dim=2)
_, lstm_state = self.lstm(curx, (hidden, cell))
hidden, cell = lstm_state[0], lstm_state[1]
outs = self.out(hidden)
return outs
由于num_layer=1,因此hidden,cell的维度均为(1, b, h)
对于每一个时间步,将其与hidden拼接,得到(b, 1, h + n)维度的curx,此对应下图中红框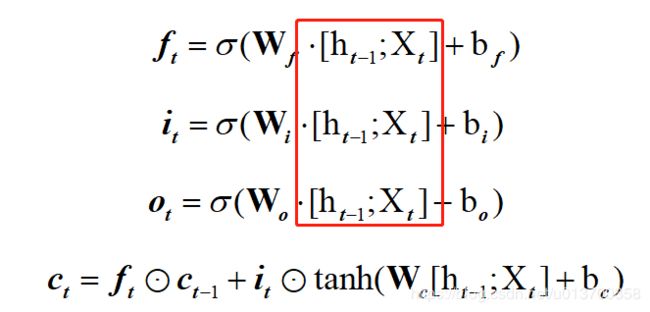
这个整体作为torch中LSTM单元的输入
在modules\rnn.py中,存在这样一段代码:
if mode == 'LSTM':
gate_size = 4 * hidden_size
elif mode == 'GRU':
gate_size = 3 * hidden_size
else:
gate_size = hidden_size
self._all_weights = []
for layer in range(num_layers):
for direction in range(num_directions):
layer_input_size = input_size if layer == 0 else hidden_size * num_directions
w_ih = Parameter(torch.Tensor(gate_size, layer_input_size))
w_hh = Parameter(torch.Tensor(gate_size, hidden_size))
b_ih = Parameter(torch.Tensor(gate_size))
b_hh = Parameter(torch.Tensor(gate_size))
layer_params = (w_ih, w_hh, b_ih, b_hh)
suffix = '_reverse' if direction == 1 else ''
param_names = ['weight_ih_l{}{}', 'weight_hh_l{}{}']
if bias:
param_names += ['bias_ih_l{}{}', 'bias_hh_l{}{}']
param_names = [x.format(layer, suffix) for x in param_names]
for name, param in zip(param_names, layer_params):
setattr(self, name, param)
self._all_weights.append(param_names)
这里的符号跟我上面的图略有不符,因为我习惯于纵向拼接,放下面这个原始的LSTM状态公式可能更好对应一些:
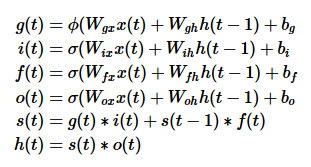
首先根据LSTM网络的特点,或直接看状态计算公式,共有四个地方用到了拼接的输入即计算,因此gate_size = 4 * hidden_size,即相当于把上面的四个Wh和Wx各自合并在一起,各自偏置也合并,方便定义域运算,这个后面还会拆分,分别用于各部分的计算
而由于我们每次的输入均为(b, 1, n + h),因此layer_input_size = n + h
这样所有需要用到的权重和偏置均已求得,用_all_weights进行包装
此后,同样是在modules\rnn.py文件中
func = self._backend.RNN(
self.mode,
self.input_size,
self.hidden_size,
num_layers=self.num_layers,
batch_first=self.batch_first,
dropout=self.dropout,
train=self.training,
bidirectional=self.bidirectional,
dropout_state=self.dropout_state,
variable_length=is_packed,
flat_weight=flat_weight
)
output, hidden = func(input, self.all_weights, hx, batch_sizes)
func将所有参数重新包装并计算,计算过程在_functions\rnn.py中:
def forward(input, weight, hidden, batch_sizes):
if batch_first and not variable_length:
input = input.transpose(0, 1)
nexth, output = func(input, hidden, weight, batch_sizes)
if batch_first and not variable_length:
output = output.transpose(0, 1)
return output, nexth
上面提到input = (b, 1, n + h),第一维为batch_size, 即batch_first = True, 于是先将其前两维转置,即此时input = (1, b, n + h)
第一维的1实际代表了LSTM的层数与是否双向,因此此后的运算仅针对单层LSTM进行运算,即此后的input = (b, n + h)
_functions\rnn.py
hx, cx = hidden
gates = F.linear(input, w_ih, b_ih) + F.linear(hx, w_hh, b_hh)
ingate, forgetgate, cellgate, outgate = gates.chunk(4, 1)
ingate = torch.sigmoid(ingate)
forgetgate = torch.sigmoid(forgetgate)
cellgate = torch.tanh(cellgate)
outgate = torch.sigmoid(outgate)
cy = (forgetgate * cx) + (ingate * cellgate)
hy = outgate * torch.tanh(cy)
return hy, cy
input = (b, n + h), w_hh = (4 * h, h), w_ih = (4* h, n + h)
F.linear是线性操作,无论是CNN、RNN都很常用,其定义如下:
def linear(input, weight, bias=None):
r"""
Applies a linear transformation to the incoming data: :math:`y = xA^T + b`.
Shape:
- Input: :math:`(N, *, in\_features)` where `*` means any number of
additional dimensions
- Weight: :math:`(out\_features, in\_features)`
- Bias: :math:`(out\_features)`
- Output: :math:`(N, *, out\_features)`
"""
if input.dim() == 2 and bias is not None:
# fused op is marginally faster
return torch.addmm(bias, input, weight.t())
output = input.matmul(weight.t())
if bias is not None:
output += bias
return output
比较容易看懂,返回input * weight.t() + bias这样的矩阵
于是经过线性变换后,返回的gates = (b, 4 * h)
然后通过chunk()函数,将gates的第一维切分为四份
于是ingate, forgetgate, cellgate, outgate = (b, h)
分别对ingate forgetgate outgate作sigmoid,对cellgate作tanh,注意 * 运算是点积,而不是矩阵乘法,前述代码配合下图饮用更佳,感觉均能一一对应:
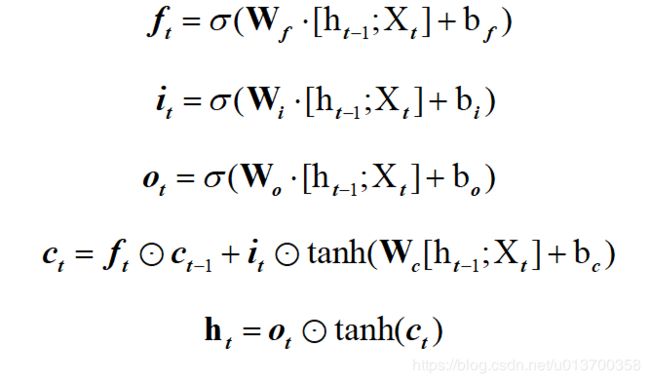
如此即结束了第一个时间步的hidden、cell计算,有多少个时间步,循环迭代即可,最后一步的hidden即可作为最终输出