一.分析网页结构并编写程序
import requests
import csv
import time
import math
import random
from lxml import etree
from multiprocessing.dummy import Pool
def getPage(url):
time.sleep(random.choice([2, 2.5, 3, 3.5]))
page = requests.get(url, headers={
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/70.0.3538.102 Safari/537.36 OPR/57.0.3098.110"})
return etree.HTML(page.text)
def csvWrite(item):
with open("lianjia_sh_ershoufang_data.csv", "a", encoding="utf-8", newline="") as f:
csv.writer(f).writerow(item)
def get_areas_regions_urls():
areas = [
"pudong",
"minhang",
"baoshan",
"xuhui",
"putuo",
"yangpu",
"changning",
"songjiang",
"jiading",
"huangpu",
"jingan",
"zhabei",
"hongkou",
"qingpu",
"fengxian",
"jinshan",
"chongming",
"shanghaizhoubian"]
areas_regions_urls = []
for area in areas:
page = getPage("https://sh.lianjia.com/ershoufang/" + area)
region_names = page.xpath("/html/body/div[3]/div/div[1]/dl[2]/dd/div[1]/div[2]/a/text()")
region_urls = page.xpath("/html/body/div[3]/div/div[1]/dl[2]/dd/div[1]/div[2]/a/@href")
for url in region_urls:
areas_regions_urls.append((area,region_names[region_urls.index(url)], "https://gz.lianjia.com"+url))
print("All regions urls have been added")
return areas_regions_urls
def region_spider(x):
info_num = int(getPage(x[2]).xpath("/html/body/div[4]/div[1]/div[2]/h2/span/text()")[0])
page_num = math.ceil(info_num/30)
for url in [x[2]+"pg" + str(num+1) for num in range(page_num)]:
page = getPage(url)
for house in page.xpath("/html/body/div[4]/div[1]/ul/li"):
try:
Area = x[0]
Region = x[1]
info = house.xpath("div[1]/div[2]/div/text()")[0].split("|")
if info[1].strip()[-2:]=="别墅":
Garden = house.xpath("div[1]/div[2]/div/a/text()")[0]
Layout = info[2]
Acreage = info[3].strip()
Direction = info[4].strip()
Renovation = info[5].strip()
Elevator = info[6].strip()
Price = int(house.xpath("div[1]/div[6]/div[1]/span/text()")[0])
BuiltYear = re.search("\d{4}",house.xpath("div[1]/div[3]/div/text()")[0]).group()
Height = re.search("\d层",house.xpath("div[1]/div[3]/div/text()")[0]).group()
Building = info[1].strip()
else:
Garden = house.xpath("div[1]/div[2]/div/a/text()")[0]
Layout = info[1]
Acreage = info[2].strip()
Direction = info[3].strip()
Renovation = info[4].strip()
try:
Elevator = info[5].strip()
except:
Elevator = "无数据"
Price = house.xpath("div[1]/div[6]/div[1]/span/text()")[0]
try:
BuiltYear = re.search("\d{4}",house.xpath("div[1]/div[3]/div/text()")[0]).group()
except:
BuiltYear = 0
Height = house.xpath("div[1]/div[3]/div/text()")[0][0:3]
try:
Building = re.search("..楼",house.xpath("div[1]/div[3]/div/text()")[0]).group()[-2:]
except:
Building = "无数据"
except:
print("Error")
else:
csvWrite([Area,Region,Garden,Acreage,Direction,Layout,Renovation,Height,Elevator,BuiltYear,Building,Price])
print("All data of District{} in Area {} have sbeen downloaded!".format(x[1],x[0]))
if __name__ == "__main__":
url_list = get_areas_regions_urls()
pool = Pool()
pool.map(region_spider,url_list)
pool.close()
pool.join()
二.数据分析
import pandas as pd
import pandas_profiling as pp
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
%matplotlib inline
/opt/conda/lib/python3.6/importlib/_bootstrap.py:219: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility. Expected 96, got 88
return f(*args, **kwds)
/opt/conda/lib/python3.6/importlib/_bootstrap.py:219: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility. Expected 96, got 88
return f(*args, **kwds)
df = pd.read_csv("/home/kesci/work/lianjia_sh_ershoufang_data.csv", header = None)
df.columns = ["Area", "Region", "Garden", "Acreage", "Direction", "Layout", "Renovation", \
"Height", "Elevator", "BuiltYear", "Building", "Price"]
df.head()
|
Area |
Region |
Garden |
Acreage |
Direction |
Layout |
Renovation |
Height |
Elevator |
BuiltYear |
Building |
Price |
| 0 |
pudong |
潍坊 |
富丽家园中行宿舍 |
95.3平米 |
南 |
3室2厅 |
简装 |
中楼层 |
无数据 |
0 |
无数据 |
172.0 |
| 1 |
pudong |
潍坊 |
金沙湾花园 |
108.8平米 |
北 |
3室2厅 |
精装 |
高楼层 |
无数据 |
0 |
无数据 |
215.0 |
| 2 |
pudong |
潍坊 |
中海誉城南苑 |
71.68平米 |
东北 |
2室1厅 |
精装 |
低楼层 |
无数据 |
0 |
无数据 |
190.0 |
| 3 |
pudong |
潍坊 |
万科东荟城 |
70平米 |
北 |
2室2厅 |
精装 |
高楼层 |
无数据 |
0 |
无数据 |
222.0 |
| 4 |
pudong |
潍坊 |
恒宝华庭 |
66.75平米 |
东 西 |
2室1厅 |
简装 |
低楼层 |
无数据 |
0 |
无数据 |
318.0 |
数据清洗
爬取的数据存在瑕疵,在进行数据分析前需检查数据。观察数据具有重复值,故需对数据去重。
df.info()
RangeIndex: 314674 entries, 0 to 314673
Data columns (total 12 columns):
Area 314674 non-null object
Region 314674 non-null object
Garden 314674 non-null object
Acreage 314674 non-null object
Direction 314674 non-null object
Layout 314674 non-null object
Renovation 314674 non-null object
Height 314674 non-null object
Elevator 314674 non-null object
BuiltYear 314674 non-null int64
Building 314674 non-null object
Price 314674 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(1), int64(1), object(10)
memory usage: 28.8+ MB
df.isnull().sum()
Area 0
Region 0
Garden 0
Acreage 0
Direction 0
Layout 0
Renovation 0
Height 0
Elevator 0
BuiltYear 0
Building 0
Price 0
dtype: int64
df_clean = df.drop_duplicates()
观察数据,房龄,电梯和建筑皆为无用特征,在此删除
df_clean["BuiltYear"].value_counts()
df_clean["Building"].value_counts()
df_clean["Elevator"].value_counts()
df_clean = df_clean.drop(["BuiltYear", "Building", "Elevator"], axis=1)
df_clean.head()
|
Area |
Region |
Garden |
Acreage |
Direction |
Layout |
Renovation |
Height |
Price |
| 0 |
pudong |
潍坊 |
富丽家园中行宿舍 |
95.3平米 |
南 |
3室2厅 |
简装 |
中楼层 |
172.0 |
| 1 |
pudong |
潍坊 |
金沙湾花园 |
108.8平米 |
北 |
3室2厅 |
精装 |
高楼层 |
215.0 |
| 2 |
pudong |
潍坊 |
中海誉城南苑 |
71.68平米 |
东北 |
2室1厅 |
精装 |
低楼层 |
190.0 |
| 3 |
pudong |
潍坊 |
万科东荟城 |
70平米 |
北 |
2室2厅 |
精装 |
高楼层 |
222.0 |
| 4 |
pudong |
潍坊 |
恒宝华庭 |
66.75平米 |
东 西 |
2室1厅 |
简装 |
低楼层 |
318.0 |
房屋面积转化成数字型,便于后面的分析建模。
df_clean["Acreage"] = df_clean["Acreage"].str[:-2].astype(float)
定义函数,分类特征和标签
def feature_label(data):
feature = data.drop("Price", axis = 1)
label = data["Price"]
return feature, label
去除异常点
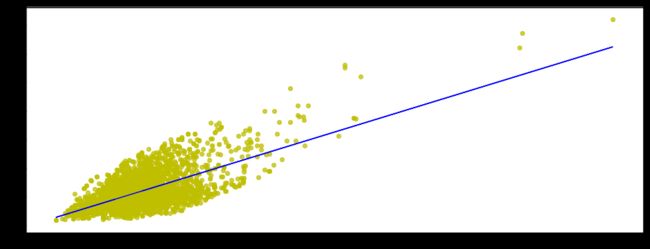
首先通过拟合线性回归模型,求出拟合值与实际值的差。此时问题 [去除异常点] 转化成 [去除残差中的异常点]
未处理前
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
def LR(data):
LR = LinearRegression()
LR.fit(np.array(data["Acreage"]).reshape(-1, 1), data["Price"])
res = LR.predict(np.array(data["Acreage"]).reshape(-1, 1))
return res
pred = LR(df_clean)
def pl(data, res):
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16,6))
plt.plot(data["Acreage"], res, color = "b")
plt.scatter(data["Acreage"], data["Price"], color = "y", alpha = 0.5);
pl(df_clean, pred)
数据中存在极端值,不利于建模和泛化,在建模前需去除异常点
def rem_error(res, data):
bias = res - data["Price"]
bias_max = 2.5*bias.describe()[6] - 1.5*bias.describe()[4]
bias_min = 2.5*bias.describe()[4] - 1.5*bias.describe()[6]
index = bias[(bias >= bias_min) & (bias <= bias_max)].index
return index
index = rem_error(pred, df_clean)
除去异常点后的模型
df_clean = df_clean.ix[index]
pred = LR(df_clean)
pl(df_clean, pred);
/opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:1: DeprecationWarning:
.ix is deprecated. Please use
.loc for label based indexing or
.iloc for positional indexing
See the documentation here:
http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#ix-indexer-is-deprecated
"""Entry point for launching an IPython kernel.
对于X室X厅,考虑转换成数值型变量
df_clean["厅"] = df_clean["Layout"].str[1].astype(float)
df_clean["室"] = df_clean["Layout"].str[3].astype(float)
df_clean.drop(columns = "Layout", inplace=True)
对装修状况进行编码
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
df_clean["Renovation"].unique()
array(['简装', '精装', '毛坯', '其他'], dtype=object)
le = LabelEncoder()
le.fit(df_clean["Renovation"])
df_clean["Renovation"] = le.transform(df_clean["Renovation"])
将房屋朝向用one-hot编码
观察数据存在多种朝向混合,直接对列one-hot编码,特征数过大,所以这里采用对朝向列的字符串进行one-hot编码
df_clean["Direction"].unique()
array(['南', '北', '东北', '东 西', '东南', '西北', '西', '南 北', '东南 西南', '西南', '东',
'东 东南', '西北 北', '南 西南', '东北 东南', '西南 西', '西南 北', '东南 北', '东 西北',
'北 东北', '东南 南', '西北 东北', '南 西', '西南 东北', '东南 南 西南', '东 西 北', '东 南',
'南 西 北', '东 南 北', '东 北', '北 南', '南 东北', '东 南 北 西', '南 东南', '东 东北',
'西 北', '东南 西 北', '西 东北', '西南 西北', '东南 西北', '南 东', '东南 南 北', '西 西南',
'东南 东', '西北 西南', '东 南 西 北'], dtype=object)
Direction = df_clean["Direction"].str.get_dummies(sep=" ")
df_clean = df_clean.join(Direction)
df_clean.drop(columns = "Direction", inplace=True)
df_clean.head()
|
Area |
Region |
Garden |
Acreage |
Renovation |
Height |
Price |
厅 |
室 |
东 |
东北 |
东南 |
北 |
南 |
西 |
西北 |
西南 |
| 0 |
pudong |
潍坊 |
富丽家园中行宿舍 |
95.30 |
2 |
中楼层 |
172.0 |
3.0 |
2.0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| 1 |
pudong |
潍坊 |
金沙湾花园 |
108.80 |
3 |
高楼层 |
215.0 |
3.0 |
2.0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| 2 |
pudong |
潍坊 |
中海誉城南苑 |
71.68 |
3 |
低楼层 |
190.0 |
2.0 |
1.0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| 3 |
pudong |
潍坊 |
万科东荟城 |
70.00 |
3 |
高楼层 |
222.0 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| 4 |
pudong |
潍坊 |
恒宝华庭 |
66.75 |
2 |
低楼层 |
318.0 |
2.0 |
1.0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
观察楼层主要集中在中楼层,高楼层,低楼层,在这考虑将楼层分类为中,高,低,其他,以降低维度
Height = df_clean["Height"].str[0]
index = Height[(Height != "高") & (Height.str[0] != "中") & (Height.str[0] != "低")].index
Height[index] = "其他楼层"
Height = pd.get_dummies(Height)
看下清洗完的数据
df_clean.drop(columns = "Height", inplace=True)
df_clean = df_clean.join(Height)
df_clean.head()
|
Area |
Region |
Garden |
Acreage |
Renovation |
Price |
厅 |
室 |
东 |
东北 |
东南 |
北 |
南 |
西 |
西北 |
西南 |
中 |
低 |
其他楼层 |
高 |
| 0 |
pudong |
潍坊 |
富丽家园中行宿舍 |
95.30 |
2 |
172.0 |
3.0 |
2.0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| 1 |
pudong |
潍坊 |
金沙湾花园 |
108.80 |
3 |
215.0 |
3.0 |
2.0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
| 2 |
pudong |
潍坊 |
中海誉城南苑 |
71.68 |
3 |
190.0 |
2.0 |
1.0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
| 3 |
pudong |
潍坊 |
万科东荟城 |
70.00 |
3 |
222.0 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
| 4 |
pudong |
潍坊 |
恒宝华庭 |
66.75 |
2 |
318.0 |
2.0 |
1.0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
房屋所在地合并,降低维度
location = df_clean["Area"] + df_clean["Region"] + df_clean["Garden"]
df_clean = df_clean.join(pd.get_dummies(location))
df_clean.drop(columns=["Area", "Region", "Garden"], inplace=True)
df_clean.head()
|
Acreage |
Renovation |
Price |
厅 |
室 |
东 |
东北 |
东南 |
北 |
南 |
... |
pudong碧云鸿城花园 |
pudong碧云鸿福花园(番禺) |
pudong碧云鸿禧华庭 |
pudong碧云鸿翔大厦 |
pudong碧云鸿运花园 |
pudong碧云鹤林苑 |
pudong碧云黄埔花园 |
pudong碧云黄船生活区 |
pudong碧云龙光峰景华庭 |
pudong碧云龙口东路 |
| 0 |
95.30 |
2 |
172.0 |
3.0 |
2.0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
... |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| 1 |
108.80 |
3 |
215.0 |
3.0 |
2.0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
... |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| 2 |
71.68 |
3 |
190.0 |
2.0 |
1.0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
... |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| 3 |
70.00 |
3 |
222.0 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
... |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| 4 |
66.75 |
2 |
318.0 |
2.0 |
1.0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
... |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
5 rows × 3790 columns
交叉验证
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score, mean_squared_error
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold, cross_val_score
kf = KFold(n_splits=12, random_state=42, shuffle=True)
def rmsle(y, y_pred):
return np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y, y_pred))
def cv_rmse(model, X, y):
rmse = np.sqrt(-cross_val_score(model, X, y,
scoring="neg_mean_squared_error", cv=kf))
return (rmse)
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
features_raw, label = feature_label(df_clean)
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
features = scaler.fit_transform(features_raw)
/opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/data.py:323: DataConversionWarning: Data with input dtype uint8, int64, float64 were all converted to float64 by MinMaxScaler.
return self.partial_fit(X, y)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(features, label, test_size=0.25, random_state=40)
lr = LinearRegression().fit(X_train, y_train)
pred = lr.predict(X_test)
train_pred = lr.predict(X_train)
test_pred = lr.predict(X_test)
print('MSE train data: %.3f, MSE test data: %.3f' % (
mean_squared_error(y_train, train_pred),
mean_squared_error(y_test, test_pred)))
print('R2 train data: %.3f, R2 test data: %.3f' % (
r2_score(y_train, train_pred),
r2_score(y_test, test_pred)))
MSE train data: 539.724, MSE test data: 16170516411079238651010351104.000
R2 train data: 0.977, R2 test data: -694086926740721479188480.000
训练结果明显过拟合,选用网格,调整超参数来选取最佳模型
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.metrics import make_scorer
from sklearn.model_selection import ShuffleSplit
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
def performance_metric(y_true, y_predict):
""" Calculates and returns the performance score between
true and predicted values based on the metric chosen. """
score = r2_score(y_true, y_predict)
return score
def fit_model(X, y):
""" Performs grid search over the 'max_depth' parameter for a
decision tree regressor trained on the input data [X, y]. """
cv_sets = ShuffleSplit(n_splits=10, test_size=0.20, random_state=42)
regressor = RandomForestRegressor()
params = {'max_depth': [i for i in range(1,11)]}
scoring_fnc = make_scorer(performance_metric)
grid = GridSearchCV(regressor, param_grid=params, scoring=scoring_fnc, cv=4)
grid = grid.fit(X, y)
return grid.best_estimator_
reg = fit_model(features, label)
print("Parameter 'max_depth' is {} for the optimal model.".format(reg.get_params()['max_depth']));
Parameter 'max_depth' is 10 for the optimal model.
train_pred = reg.predict(X_train)
test_pred = reg.predict(X_test)
print('MSE train data: %.3f, MSE test data: %.3f' % (
mean_squared_error(y_train, train_pred),
mean_squared_error(y_test, test_pred)))
print('R2 train data: %.3f, R2 test data: %.3f' % (
r2_score(y_train, train_pred),
r2_score(y_test, test_pred)))
MSE train data: 9356.258, MSE test data: 8988.234
R2 train data: 0.847, R2 test data: 0.864
reg.score(X_test, test_pred)
1.0
总结
- 爬虫爬取的数据是存在瑕疵的,数据格式也不利于建模,在此需要花费大量时间清洗。
- 一个最优的模型不一定是一个健壮模型。有的时候模型会过于复杂或者过于简单,以致于难以泛化新增添的数据;有的时候模型采用的学习算法并不适用于特定的数据结构;有的时候样本本身可能有太多噪点或样本过少,使得模型无法准确地预测目标变量。这些情况下我们会说模型是欠拟合的。
- 尝试多个模型,调整超参数,混合模型等方式让模型更加健壮
