Mysql系列——详解mysql数据类型
详解mysql数据类型
- MySQL的数据类型
- 整数类型
- 示例1:有符号类型
- 示例2:无符号类型
- 类型(n)说明
- 浮点类型(容易懵,注意看)
- 示例1(重点)
- 示例2
- 再看一下下面代码:
- 日期类型
- mysql类型和java类型对应关系
- 数据类型选择的一些建议
环境:mysql5.7.25,cmd命令中进行演示。
- 介绍mysql中常用的数据类型
- mysql类型和java类型对应关系
- 数据类型选择的一些建议
MySQL的数据类型
主要包括以下五大类
- 整数类型:
bit、bool、tinyint、smallint、mediumint、int、bigint - 浮点数类型:
float、double、decimal - 字符串类型:
char、varchar、tinyblob、blob、mediumblob、longblob、tinytext、text、mediumtext、longtext - 日期类型:
Date、DateTime、TimeStamp、Time、Year - 其他数据类型:暂不介绍,用的比较少。
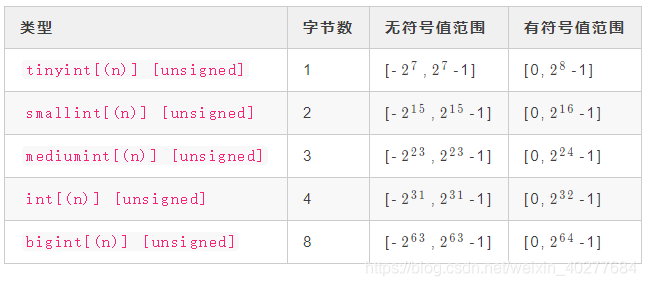
整数类型
上面表格中有符号和无符号写反了,[]包含的内容是可选的,默认是无符号类型的,无符号的需要在类型后面跟上unsigned
示例1:有符号类型
mysql> create table demo1(
c1 tinyint
);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into demo1 values(-pow(2,7)),(pow(2,7)-1);
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from demo1;
+------+
| c1 |
+------+
| -128 |
| 127 |
+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into demo1 values(pow(2,7));
ERROR 1264 (22003): Out of range value for column 'c1' at row 1
demo1表中c1字段为tinyint有符号类型的,可以看一下上面的演示,有超出范围报错的。
关于数值对应的范围计算方式属于计算机基础的一些知识,可以去看一下计算机的二进制表示相关的文章。
示例2:无符号类型
mysql> create table demo2(
c1 tinyint unsigned
);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into demo2 values (-1);
ERROR 1264 (22003): Out of range value for column 'c1' at row 1
mysql> insert into demo2 values (pow(2,8)+1);
ERROR 1264 (22003): Out of range value for column 'c1' at row 1
mysql> insert into demo2 values (0),(pow(2,8));
mysql> insert into demo2 values (0),(pow(2,8)-1);
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from demo2;
+------+
| c1 |
+------+
| 0 |
| 255 |
+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
c1是无符号的tinyint类型的,插入了负数会报错。
类型(n)说明
在开发中,我们会碰到有些定义整型的写法是int(11),这种写法个人感觉在开发过程中没有什么用途,不过还是来说一下,int(N)我们只需要记住两点:
- 无论N等于多少,int永远占4个字节
N表示的是显示宽度,不足的用0补足,超过的无视长度而直接显示整个数字,但这要整型设置了unsigned zerofill才有效
看一下示例,理解更方便:
mysql> CREATE TABLE test3 (
`a` int,
`b` int(5),
`c` int(5) unsigned,
`d` int(5) zerofill,
`e` int(5) unsigned zerofill,
`f` int zerofill,
`g` int unsigned zerofill
);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into test3 values (1,1,1,1,1,1,1),(11,11,11,11,11,11,11),(12345,12345,12345,12345,12345,12345,12345);
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from test3;
+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+------------+------------+
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g |
+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+------------+------------+
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 00001 | 00001 | 0000000001 | 0000000001 |
| 11 | 11 | 11 | 00011 | 00011 | 0000000011 | 0000000011 |
| 12345 | 12345 | 12345 | 12345 | 12345 | 0000012345 | 0000012345 |
+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+------------+------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> show create table test3;
| Table | Create Table
| test3 | CREATE TABLE `test3` (
`a` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`b` int(5) DEFAULT NULL,
`c` int(5) unsigned DEFAULT NULL,
`d` int(5) unsigned zerofill DEFAULT NULL,
`e` int(5) unsigned zerofill DEFAULT NULL,
`f` int(10) unsigned zerofill DEFAULT NULL,
`g` int(10) unsigned zerofill DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
show create table test3;输出了表test3的创建语句,和我们原始的创建语句不一致了,原始的d字段用的是无符号的,可以看出当使用了zerofill自动会将无符号提升为有符号。
说明:
int(5)输出宽度不满5时,前面用0来进行填充
int(n)中的n省略的时候,宽度为对应类型无符号最大值的十进制的长度,如bigint无符号最大值为2的64次方-1等于18,446,744,073,709,551,615;
长度是20位,来个bigint左边0填充的示例看一下
mysql> CREATE TABLE test4 (
`a` bigint zerofill
);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into test4 values(1);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select *from test4;
+----------------------+
| a |
+----------------------+
| 00000000000000000001 |
+----------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
上面的结果中1前面补了19个0,和期望的结果一致。
浮点类型(容易懵,注意看)
float数值类型用于表示单精度浮点数值,而double数值类型用于表示双精度浮点数值,float和double都是浮点型,而decimal是定点型。
浮点型和定点型可以用类型名称后加(M,D)来表示,M表示该值的总共长度,D表示小数点后面的长度,M和D又称为精度和标度。
float和double在不指定精度时,默认会按照实际的精度来显示,而DECIMAL在不指定精度时,默认整数为10,小数为0。
示例1(重点)
mysql> create table test5(a float(5,2),b double(5,2),c decimal(5,2));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into test5 values (1,1,1),(2.1,2.1,2.1),(3.123,3.123,3.123),(4.125,4.125,4.125),(5.115,5.115,5.115),(6.126,6.126,6.126),(7.116,7.116,7.116),(8.1151,8.1151,8.1151),(9.1251,9.1251,9.1251),(10.11501,10.11501,10.11501),(11.12501,11.12501,11.12501);
Query OK, 7 rows affected, 5 warnings (0.01 sec)
Records: 7 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 5
mysql> select * from test5;
+-------+-------+-------+
| a | b | c |
+-------+-------+-------+
| 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 2.10 | 2.10 | 2.10 |
| 3.12 | 3.12 | 3.12 |
| 4.12 | 4.12 | 4.13 |
| 5.12 | 5.12 | 5.12 |
| 6.13 | 6.13 | 6.13 |
| 7.12 | 7.12 | 7.12 |
| 8.12 | 8.12 | 8.12 |
| 9.13 | 9.13 | 9.13 |
| 10.12 | 10.12 | 10.12 |
| 11.13 | 11.13 | 11.13 |
+-------+-------+-------+
11 rows in set (0.00 sec)
结果说明(注意看):
c是decimal类型,认真看一下输入和输出,发现decimal采用的是四舍五入
认真看一下a和b的输入和输出,尽然不是四舍五入,一脸闷逼,float和double采用的是四舍六入五成双
decimal插入的数据超过精度之后会触发警告。
什么是四舍六入五成双?
就是5以下舍弃5以上进位,如果需要处理数字为5的时候,需要看5后面是否还有不为0的任何数字,如果有,则直接进位,如果没有,需要看5前面的数字,若是奇数则进位,若是偶数则将5舍掉
示例2
我们将浮点类型的(M,D)精度和标度都去掉,看看效果:
mysql> create table test6(a float,b double,c decimal);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> insert into test6 values (1,1,1),(1.234,1.234,1.4),(1.234,0.01,1.5);
Query OK, 3 rows affected, 2 warnings (0.00 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 2
mysql> select * from test6;
+-------+-------+------+
| a | b | c |
+-------+-------+------+
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1.234 | 1.234 | 1 |
| 1.234 | 0.01 | 1 |
+-------+-------+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
说明:
a和b的数据正确插入,而c被截断了
浮点数float、double如果不写精度和标度,则会按照实际显示
decimal不写精度和标度,小数点后面的会进行四舍五入,并且插入时会有警告!
再看一下下面代码:
mysql> select sum(a),sum(b),sum(c) from test5;
+--------+--------+--------+
| sum(a) | sum(b) | sum(c) |
+--------+--------+--------+
| 67.21 | 67.21 | 67.22 |
+--------+--------+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select sum(a),sum(b),sum(c) from test6;
+--------------------+--------------------+--------+
| sum(a) | sum(b) | sum(c) |
+--------------------+--------------------+--------+
| 3.4679999351501465 | 2.2439999999999998 | 4 |
+--------------------+--------------------+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
从上面sum的结果可以看出float、double会存在精度问题,decimal精度正常的,比如银行对统计结果要求比较精准的建议使用decimal。
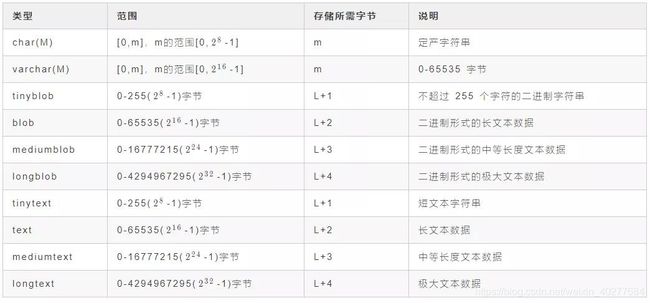
日期类型
char类型占用固定长度,如果存放的数据为固定长度的建议使用char类型,如:手机号码、身份证等固定长度的信息。
表格中的L表示存储的数据本身占用的字节,L 以外所需的额外字节为存放该值的长度所需的字节数。
MySQL 通过存储值的内容及其长度来处理可变长度的值,这些额外的字节是无符号整数。
请注意,可变长类型的最大长度、此类型所需的额外字节数以及占用相同字节数的无符号整数之间的对应关系:
例如,MEDIUMBLOB 值可能最多2的24次方 - 1字节长并需要3个字节记录其长度,3 个字节的整数类型MEDIUMINT 的最大无符号值为2的24次方 - 1。
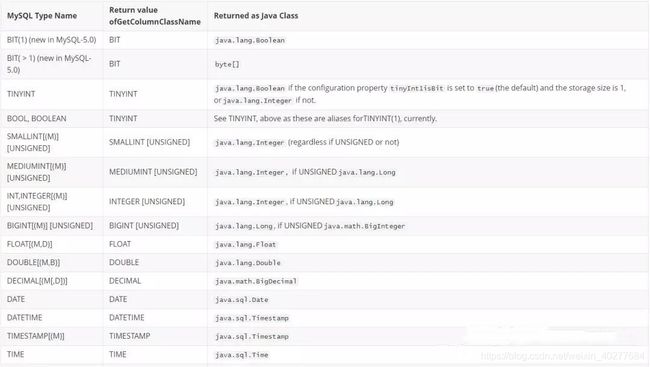
mysql类型和java类型对应关系
数据类型选择的一些建议
-
选小不选大:一般情况下选择可以正确存储数据的最小数据类型,越小的数据类型通常更快,占用磁盘,内存和CPU缓存更小。 -
简单就好:简单的数据类型的操作通常需要更少的CPU周期,例如:整型比字符操作代价要小得多,因为字符集和校对规则(排序规则)使字符比整型比较更加复杂。 -
尽量避免NULL:尽量制定列为NOT NULL,除非真的需要NULL类型的值,有NULL的列值会使得索引、索引统计和值比较更加复杂。 -
浮点类型的建议统一选择decimal -
记录时间的建议使用int或者bigint类型,将时间转换为时间戳格式,如将时间转换为秒、毫秒,进行存储,方便走索引