什么是MyBatis
MyBatis 本是apache的一个开源项目iBatis, 2010年这个项目由apache software foundation 迁移到了google code,并且改名为MyBatis。是一个基于Java的持久层框架
为什么我们要用Mybatis?
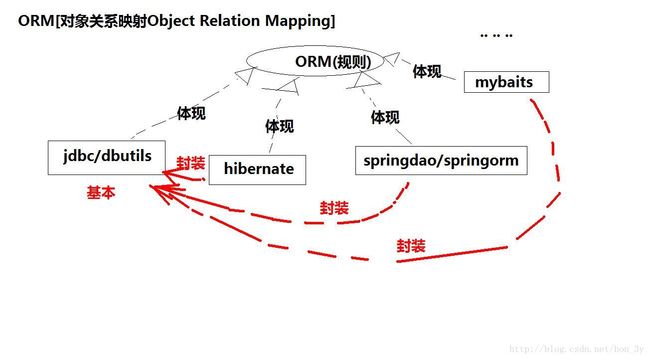
无论是Mybatis、Hibernate都是ORM的一种实现框架,都是对JDBC的一种封装!
到目前为止,我们已经在持久层中学了几种技术了...
- Hibernate
- jdbc
- SpringDAO
那我们为啥还要学Mybatis呢???现在Mybatis在业内大行其道,那为啥他能那么火呢??
Hibernate是一个比较老旧的框架,用过他的同学都知道,只要你会用,用起来十分舒服...啥sql代码都不用写...但是呢,它也是有的缺点::处理复杂业务时,灵活度差, 复杂的HQL难写难理解,例如多表查询的HQL语句
而JDBC很容易理解,就那么几个固定的步骤,就是开发起来太麻烦了,因为什么都要我们自己干..
而SpringDAO其实就是JDBC的一层封装,就类似于dbutils一样,没有特别出彩的地方....
我们可以认为,Mybatis就是jdbc和Hibernate之间的一个平衡点...毕竟现在业界都是用这个框架,我们也不能不学呀!
Mybatis快速入门
其实我们已经学过了Hibernate了,对于Mybatis入门其实就非常类似的。因此就很简单就能掌握基本的开发了...
导入开发包
导入Mybatis开发包
- mybatis-3.1.1.jar
- commons-logging-1.1.1.jar
- log4j-1.2.16.jar
- cglib-2.2.2.jar
- asm-3.3.1.jar
导入mysql/oracle开发包
- mysql-connector-java-5.1.7-bin.jar
- Oracle 11g 11.2.0.1.0 JDBC_ojdbc6.jar
准备测试工作
创建一张表
create table students(
id int(5) primary key,
name varchar(10),
sal double(8,2)
);
创建实体:
/**
* Created by ozc on 2017/7/21.
*/
public class Student {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Double sal;
public Student() {
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Double getSal() {
return sal;
}
public void setSal(Double sal) {
this.sal = sal;
}
}
创建mybatis配置文件
创建mybatis的配置文件,配置数据库的信息....数据库我们可以配置多个,但是默认的只能用一个...
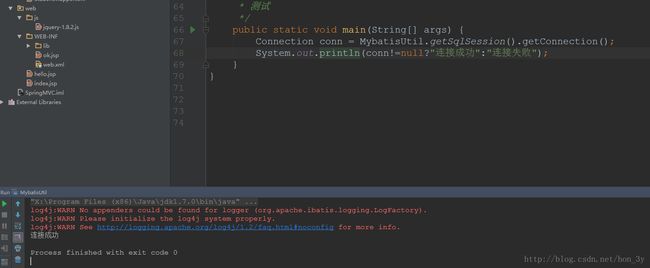
编写工具类测试是否获取到连接
使用Mybatis的API来创建一个工具类,通过mybatis配置文件与数据库的信息,得到Connection对象
package cn.itcast.javaee.mybatis.util;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Reader;
import java.sql.Connection;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
/**
* 工具类
* @author AdminTC
*/
public class MybatisUtil {
private static ThreadLocal threadLocal = new ThreadLocal();
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
/**
* 加载位于src/mybatis.xml配置文件
*/
static{
try {
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis.xml");
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
/**
* 禁止外界通过new方法创建
*/
private MybatisUtil(){}
/**
* 获取SqlSession
*/
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(){
//从当前线程中获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = threadLocal.get();
//如果SqlSession对象为空
if(sqlSession == null){
//在SqlSessionFactory非空的情况下,获取SqlSession对象
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//将SqlSession对象与当前线程绑定在一起
threadLocal.set(sqlSession);
}
//返回SqlSession对象
return sqlSession;
}
/**
* 关闭SqlSession与当前线程分开
*/
public static void closeSqlSession(){
//从当前线程中获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = threadLocal.get();
//如果SqlSession对象非空
if(sqlSession != null){
//关闭SqlSession对象
sqlSession.close();
//分开当前线程与SqlSession对象的关系,目的是让GC尽早回收
threadLocal.remove();
}
}
/**
* 测试
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = MybatisUtil.getSqlSession().getConnection();
System.out.println(conn!=null?"连接成功":"连接失败");
}
}
创建实体与映射关系文件
配置实体与表的映射关系
现在我们已经有了Mybatis的配置文件和表与实体之前的映射文件了,因此我们要将配置文件和映射文件关联起来
在测试类上,我们是可以获取得到连接的
编写DAO
public class StudentDao {
public void add(Student student) throws Exception {
//得到连接对象
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();
sqlSession.insert();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDao();
Student student = new Student(1, "zhongfucheng", 10000D);
studentDao.add(student);
}
}
到现在为止,我们实体与表的映射文件仅仅映射了实体属性与表的字段的关系...
我们在Hibernate中如果想要插入数据什么的,只要调用save()方法就行了。Hibernate是自动化屏蔽掉了数据库的差异,而我们Mybatis是需要自己手动编写SQL代码的...
那么SQL代码是写在哪里的呢???明显地,我们作为一个框架,不可能在程序中写SQL,我们是在实体与表的映射文件中写的!
Mybatis实体与表的映射文件中提供了insert标签【SQL代码片段】供我们使用
//在JDBC中我们通常使用?号作为占位符,而在Mybatis中,我们是使用#{}作为占位符
//parameterType我们指定了传入参数的类型
//#{}实际上就是调用了Student属性的get方法
INSERT INTO ZHONGFUCHENG.STUDENTS (ID, NAME, SAL) VALUES (#{id},#{name},#{sal});
在程序中调用映射文件的SQL代码片段
public void add(Student student) throws Exception {
//得到连接对象
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();
try{
//映射文件的命名空间.SQL片段的ID,就可以调用对应的映射文件中的SQL
sqlSession.insert("StudentID.add", student);
sqlSession.commit();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
throw e;
}finally{
MybatisUtil.closeSqlSession();
}
}
值得注意的是:Mybatis中的事务是默认开启的,因此我们在完成操作以后,需要我们手动去提交事务!
Mybatis工作流程
- 通过Reader对象读取Mybatis映射文件
- 通过SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象创建SqlSessionFactory对象
- 获取当前线程的SQLSession
- 事务默认开启
- 通过SQLSession读取映射文件中的操作编号,从而读取SQL语句
- 提交事务
- 关闭资源
完成CRUD操作
我们在上面中已经简单知道了Mybatis是怎么使用的以及工作流程了,这次我们使用Mybatis来完成CRUD的操作,再次巩固Mybatis的开发步骤以及一些细节
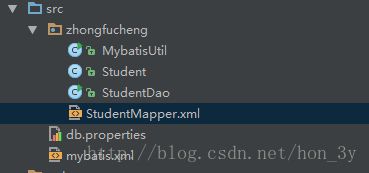
包与类之间的结构
增加学生
配置文件
映射文件
INSERT INTO ZHONGFUCHENG.STUDENTS (ID, NAME, SAL) VALUES (#{id},#{name},#{sal});
插入数据
public class StudentDao {
public void add(Student student) throws Exception {
//得到连接对象
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();
try{
//映射文件的命名空间.SQL片段的ID,就可以调用对应的映射文件中的SQL
sqlSession.insert("StudentID.add", student);
sqlSession.commit();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
throw e;
}finally{
MybatisUtil.closeSqlSession();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDao();
Student student = new Student(3, "zhong3", 10000D);
studentDao.add(student);
}
}
根据ID查询数据
增加select标签
查询出来的结果是一个Student对象,我们调用SelectOne方法
public Student findById(int id) throws Exception {
//得到连接对象
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();
try{
//映射文件的命名空间.SQL片段的ID,就可以调用对应的映射文件中的SQL
return sqlSession.selectOne("StudentID.findById",id);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
throw e;
}finally{
MybatisUtil.closeSqlSession();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDao();
Student student = studentDao.findById(1);
System.out.println(student.getName());
}
查询所有数据
我们查询出来的结果不单单只有一个对象了,因此我们使用的是SelectList这个方法
public List findAll() throws Exception {
//得到连接对象
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();
try{
//映射文件的命名空间.SQL片段的ID,就可以调用对应的映射文件中的SQL
return sqlSession.selectList("StudentID.findAll");
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
throw e;
}finally{
MybatisUtil.closeSqlSession();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDao();
List students = studentDao.findAll();
System.out.println(students.size());
}
根据id删除
DELETE FROM STUDENTS WHERE id=#{id};
调用delete方法删除
public void delete(int id ) throws Exception {
//得到连接对象
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();
try{
//映射文件的命名空间.SQL片段的ID,就可以调用对应的映射文件中的SQL
sqlSession.delete("StudentID.delete", id);
sqlSession.commit();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
throw e;
}finally{
MybatisUtil.closeSqlSession();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDao();
studentDao.delete(1);
}
修改
update students set name=#{name},sal=#{sal} where id=#{id};
查询出对应的对象,对其进行修改
public void update(Student student ) throws Exception {
//得到连接对象
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();
try{
//映射文件的命名空间.SQL片段的ID,就可以调用对应的映射文件中的SQL
sqlSession.update("StudentID.update", student);
sqlSession.commit();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
throw e;
}finally{
MybatisUtil.closeSqlSession();
}
}
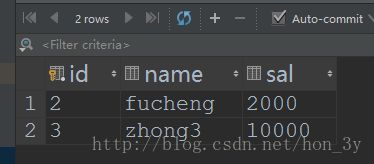
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDao();
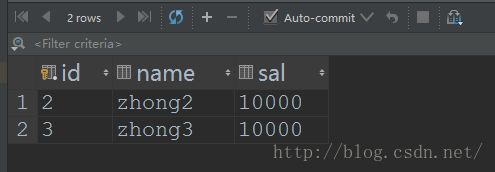
Student student = studentDao.findById(2);
student.setName("fucheng");
student.setSal(2000D);
studentDao.update(student);
}
小细节
Mybatis分页
分页是一个非常实用的技术点,我们也来学习一下使用Mybatis是怎么分页的...
我们的分页是需要多个参数的,并不是像我们之前的例子中只有一个参数。当需要接收多个参数的时候,我们使用Map集合来装载!
public List pagination(int start ,int end) throws Exception {
//得到连接对象
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();
try{
//映射文件的命名空间.SQL片段的ID,就可以调用对应的映射文件中的SQL
/**
* 由于我们的参数超过了两个,而方法中只有一个Object参数收集
* 因此我们使用Map集合来装载我们的参数
*/
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("start", start);
map.put("end", end);
return sqlSession.selectList("StudentID.pagination", map);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
throw e;
}finally{
MybatisUtil.closeSqlSession();
}
}
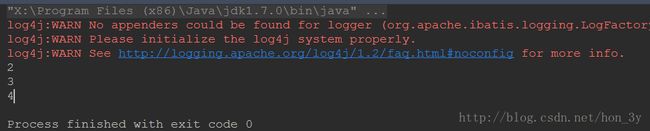
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDao();
List students = studentDao.pagination(0, 3);
for (Student student : students) {
System.out.println(student.getId());
}
}
那么在实体与表映射文件中,我们接收的参数就是map集合
动态SQL
何为动态SQL??回顾一下我们之前写的SSH项目中,有多条件查询的情况,如下图
我们当时刚开始做的时候,是需要在Controller中判断SQL是否已经有条件了,因为SQL语句需要拼接起来....这样干的话,就非常容易出错的。
如下的代码,如果有多个条件的话,那么拼接起来很容易出错!
public String listUI() {
//查询语句
String hql = "FROM Info i ";
List后来,我们觉得这样不好,于是就专门写了一个查询助手类:
package zhongfucheng.core.utils;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created by ozc on 2017/6/7.
*/
public class QueryHelper {
private String fromClause = "";
private String whereClause = "";
private String orderbyClause = "";
private List这样一来的话,我们就不用自己手动拼接了,给我们的查询助手类去拼接就好了。
而如果我们使用Mybatis的话,就可以免去查询助手类了。因为Mybatis内部就有动态SQL的功能【动态SQL就是自动拼接SQL语句】!
动态查询
查询出来小于9000块的人
public List findByCondition(String name,Double sal) throws Exception {
//得到连接对象
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();
try{
//映射文件的命名空间.SQL片段的ID,就可以调用对应的映射文件中的SQL
/**
* 由于我们的参数超过了两个,而方法中只有一个Object参数收集
* 因此我们使用Map集合来装载我们的参数
*/
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name", name);
map.put("sal", sal);
return sqlSession.selectList("StudentID.findByCondition", map);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
throw e;
}finally{
MybatisUtil.closeSqlSession();
}
}
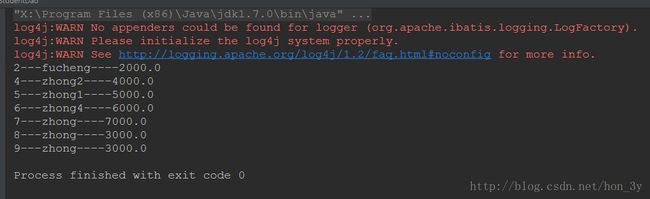
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDao();
List students = studentDao.findByCondition(null,9000D);
for (Student student : students) {
System.out.println(student.getId() + "---" + student.getName() + "----" + student.getSal());
}
}
动态更新
update students
name = #{name},
sal = #{sal},
where id = #{id}
给出三个更新的字段
public void updateByConditions(int id,String name,Double sal) throws Exception {
//得到连接对象
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();
try{
//映射文件的命名空间.SQL片段的ID,就可以调用对应的映射文件中的SQL
/**
* 由于我们的参数超过了两个,而方法中只有一个Object参数收集
* 因此我们使用Map集合来装载我们的参数
*/
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("id", id);
map.put("name", name);
map.put("sal", sal);
sqlSession.update("StudentID.updateByConditions", map);
sqlSession.commit();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
throw e;
}finally{
MybatisUtil.closeSqlSession();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDao();
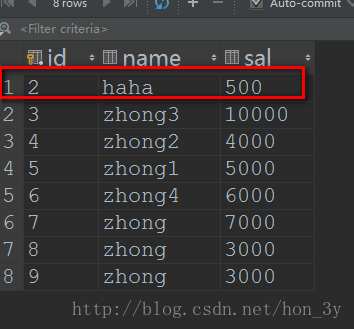
studentDao.updateByConditions(2,"haha",500D);
}
动态删除
以前我们使用JDBC也好,Hibernate也好,想要批量删除的时候,总是使用的是循环删除。而我们现在使用的是Mybatis,SQL语句是自己写的。所以我们可以写下如下的SQL来进行删除
delete from students where id in (?,?,?,?);
而我们的Mybatis又支持动态SQL,所以删除起来就非常方便了!
delete from students where id in
#{ids}
删除编号为2,3,4的记录
public void deleteByConditions(int... ids) throws Exception {
//得到连接对象
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();
try{
//映射文件的命名空间.SQL片段的ID,就可以调用对应的映射文件中的SQL
/**
* 由于我们的参数超过了两个,而方法中只有一个Object参数收集
* 因此我们使用Map集合来装载我们的参数
*/
sqlSession.delete("StudentID.deleteByConditions", ids);
sqlSession.commit();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
throw e;
}finally{
MybatisUtil.closeSqlSession();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDao();
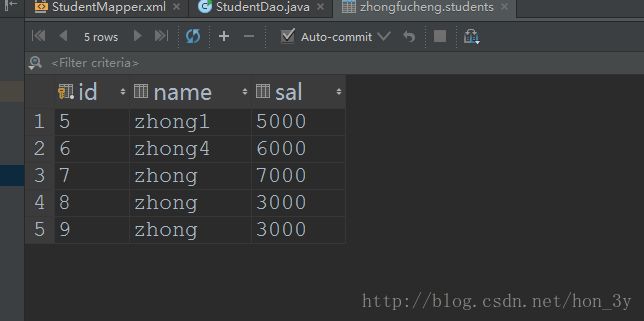
studentDao.deleteByConditions(2,3,4);
}
动态插入
我们要想动态插入的话,就比其他的DML语句稍微复杂一点,因为它有两部分是不确定的,平常的SQL语句是这样的:
insert into student(id,name,sal) values(?,?,?)
SQL代码块是不能像之前那样帮我们自动去除多余的逗号的,因此我们需要使用trim标签来自己手动去除...
编写insertSQL语句的时候,不要忘了写()括号。
id,
name,
sal,
#{id},
#{name},
#{sal},
insert into students (
测试三个不同内容的数据
public void insertByConditions(Student student) throws Exception {
//得到连接对象
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();
try{
//映射文件的命名空间.SQL片段的ID,就可以调用对应的映射文件中的SQL
sqlSession.insert("StudentID.insertByConditions", student);
sqlSession.commit();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
throw e;
}finally{
MybatisUtil.closeSqlSession();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDao();
studentDao.insertByConditions(new Student(55, null, null));//name和sal为空
studentDao.insertByConditions(new Student(66, "haxi", null));//sal为空
studentDao.insertByConditions(new Student(77, null, 3999d));//name为空
}
总结
- Mybatis的准备工作与Hibernate差不多,都需要一个总配置文件、一个映射文件。
- Mybatis的SQLSession工具类使用ThreadLocal来对线程中的Session来进行管理。
- Mybatis的事务默认是开启的,需要我们手动去提交事务。
- Mybatis的SQL语句是需要手写的,在程序中通过映射文件的命名空间.sql语句的id来进行调用!
- 在Mybatis中,增删改查都是需要我们自己写SQL语句的,然后在程序中调用即可了。SQL由于是我们自己写的,于是就相对Hibernate灵活一些。
- 如果需要传入多个参数的话,那么我们一般在映射文件中用Map来接收。
- 由于我们在开发中会经常用到条件查询,在之前,我们是使用查询助手来帮我们完成对SQL的拼接的。而Mybatis的话,我们是自己手写SQL代码的。
- Mybatis也支持一些判断标签,于是我们就可以通过这些标签来完成动态CRUD的操作了。
- 值得注意的是,我们的sql片段代码是需要我们自己手动去分割,号的。
如果文章有错的地方欢迎指正,大家互相交流。习惯在微信看技术文章,想要获取更多的Java资源的同学,可以关注微信公众号:Java3y