Multi-Dimensional Arrays, main Parameters, Casting, void Pointers
2D Arrays
typearray_name[dimension1] [dimension2]
A 2D array is often useful for storing tabular data
Array initialization:
Multi-Dimensional Arrays: 3D Arrays or more
For example:
int table [10] [10] [10];
And:
int four_dimensional_array [5] [5] [5] [5];
Syntax:
typearray_name[dim1] [dim2] [dim3] [dim4] ... [dimN]
char*Arrays
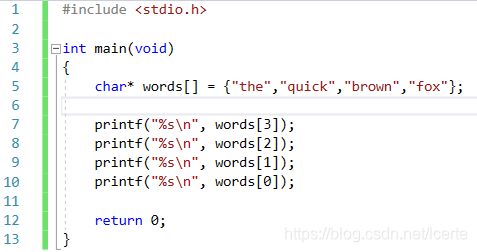
Create an array of C-Strings
This means each element in the array will store the address of a char. And at that location, there may be a C-String
In this case, the elements of array are pointers, so
“the” and “quick” are the value which the element pointer point to.
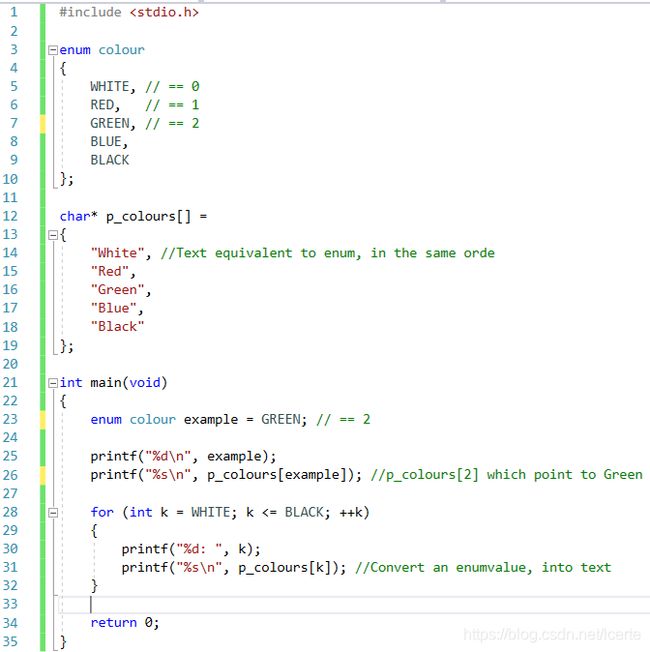
C-String Arrays and Enums
Declare a C-String array alongside an enum.
The Parameters of main
The main function can have parameters
Use as:
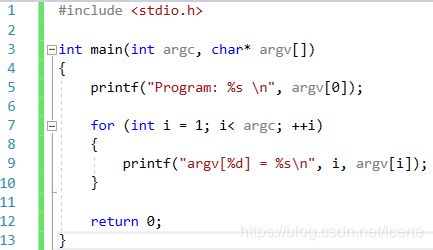
int main (int argc, char* argv [ ]) // this type is fixed !
The first argument, argc,
is the count for the number of command line arguments passed to the program
Translation: 参数的个数,不给main()函数传递参数时默认值为1,即至少有一个参数为该可执行文件的文件名(含目录)
The second argument, argv:
char* argv [] can be re-written as char** argv
So, the argv variable stores the address of, a pointer to a char
Each element in the argv array, is a C- string (a character array)
Translation: 为指针数组,分别指向各个字符串参数的首地址,其中argv[0]存储的是可执行文件的文件名的首地址。其中argv[0]为自身运行目录路径和程序名,argv[1]指向第一个参数、argv[2]指向第二个参数
The program can access these parameters via argv, and argc
Print out the address of this program:
Setting Command Line Arguments in Visual Studio
When our program want to do various actions based upon the arguments passed to the program
Type conversions
It is good practice to use the explicit type cast operator whenever conversion between two types is needed
int x = 3.14f //will become x = 3
Type casting is a way to convert a variable from one data type to another data type
As the variables int the formula are int, so the result will be also int
Using Type Casting
The Cast Operator has higher priority than division:
Putting the type cast in front of a value or a variable to converts the value or variable to the type in the bracket
Void Pointers
A void* is a general-purpose pointer
Use it when we do not know what the type of pointer is
As it can store the address of any type of variable
Notice: The compiler does not know what sort of data the pointer points to!
void* my_ptr= 0;
this pointer my_ptrcannot be dereferenced (which means set *my_ptrcannot to anything)
*my_ptrcannot = … is invalid in this case!
Use void pointer to save the address of different type variables:
If we want to dereference a void* in this case
We must tell the compiler what type of data the pointer is pointing to:
type cast