使用Comparable、Comparator接口实现对对象数组、List集合自定义排序
1、实现对象数组排序
(1)方法一,需要排序的对象所属的类实现Comparable接口,复写 comparaTo方法(2)方法二,需要排序的对象所属的类已经完成无法实现Comparable接口,这种情况用实现Comparator接口,需要自定义排序规则类 复写compare方法
2、实现List集合排序,和对象数组是一样的规则,只是最终排序调用的工具类是Collections.sort()方法
直接看代码:
方法一:学生Student类
package cn.com.lcx.model;
public class Student implements Comparable{
private String name;
private int age;
private double score;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Student(String name, int age, double score) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* 重写toString()方法,方便打印对象信息
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", score=" + score
+ "]";
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
/**
* 实现Comparable的compareTo 方法
* 1表示大于,-1表示小于,0表示等于
* 如果if条件和返回值表示一样(即if表达式是大于 返回值且是1)那么就是升序,反之则是降序
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
/**
* 按年龄降序(if条件和返回值相反) 年龄相同 按成绩升序(if条件和返回值相同)
*/
if(this.age> o.age){
return -1;
}else if(this.age< o.age){
return 1;
}else{
if(this.score> o.score){
return 1;
}else if(this.score< o.score){
return -1;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
}
}
package cn.com.lcx.model;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class StudentComparator implements Comparator{
/**
* 实现Comparator的compare 方法
* 1表示大于,-1表示小于,0表示等于
* 如果if条件和返回值表示一样(即if表达式是大于 返回值且是1)那么就是升序,反之则是降序
*/
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
/**
* 按年龄升序(if条件和返回值相同) 年龄相同 按成绩降序(if条件和返回值相反)
*/
if(o1.getAge()> o1.getAge()){
return 1;
}else if(o1.getAge()< o1.getAge()){
return -1;
}else{
if(o1.getScore()> o2.getScore()){
return -1;
}else if(o1.getScore()< o2.getScore()){
return 1;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
}
}
package cn.com.lcx.test;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import cn.com.lcx.model.Student;
import cn.com.lcx.model.StudentComparator;
public class StudentSort {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 1、实现对象数组排序
* (1)方法一,需要排序的对象所属的类实现Comparable接口,复写 comparaTo方法
* (2)方法二,需要排序的对象所属的类已经完成无法实现Comparable接口,
* 这种情况用实现Comparator接口,需要自定义排序规则类 复写compare方法
* 最终排序用Arrays.sort方法
*/
Student[] stuArr = {
new Student("lwx-1", 10, 100),
new Student("lwx-2", 30, 90),
new Student("lwx-3", 30, 95),
new Student("lwx-4", 30, 85),
new Student("lwx-5", 20, 70),
new Student("lwx-6", 40, 60)};
//方法一实现Comparable接口
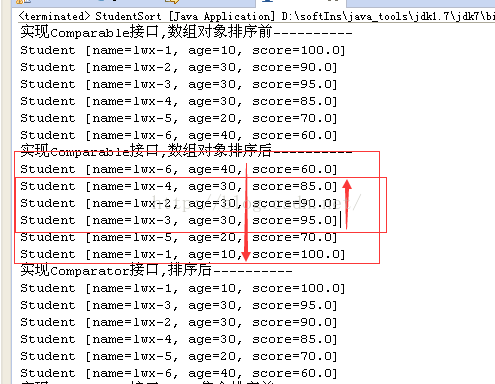
System.out.println("实现Comparable接口,数组对象排序前----------");
printArr(stuArr);
System.out.println("实现Comparable接口,数组对象排序后----------");
Arrays.sort(stuArr);
printArr(stuArr);
//方法二自定义排序规则类实现Comparator接口
System.out.println("实现Comparator接口,数组对象排序后----------");
Arrays.sort(stuArr,new StudentComparator());
printArr(stuArr);
/**
* 2、实现List集合排序,和对象数组是一样的规则,只是最终排序调用的工具类是Collections.sort()方法
*/
Student[] stuArr2 = {
new Student("lwx-4", 30, 85),
new Student("lwx-5", 20, 70),
new Student("lwx-6", 40, 60),
new Student("lwx-1", 10, 100),
new Student("lwx-2", 30, 90),
new Student("lwx-3", 30, 95)};
List stuList = Arrays.asList(stuArr2);
//方法一实现Comparable接口
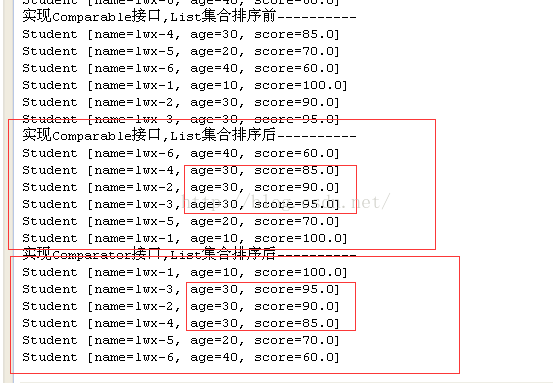
System.out.println("实现Comparable接口,List集合排序前----------");
printList(stuList);
System.out.println("实现Comparable接口,List集合排序后----------");
Collections.sort(stuList);
printList(stuList);
//方法二自定义排序规则类实现Comparator接口
System.out.println("实现Comparator接口,List集合排序后----------");
Collections.sort(stuList,new StudentComparator());
printList(stuList);
}
/**
* 打印对象数组元素
* @param objArr
*/
public static void printArr(Object[] objArr){
for(Object obj: objArr){
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
/**
* 打印List集合中的元素
* @param list
*/
public static void printList(List list){
for(Object obj: list){
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
}
验证结果: