HDLbits代码答案(2.4 Procedures & 2.5 More Verilog Features)持更
2. Verilog Language
2.3 Procedures
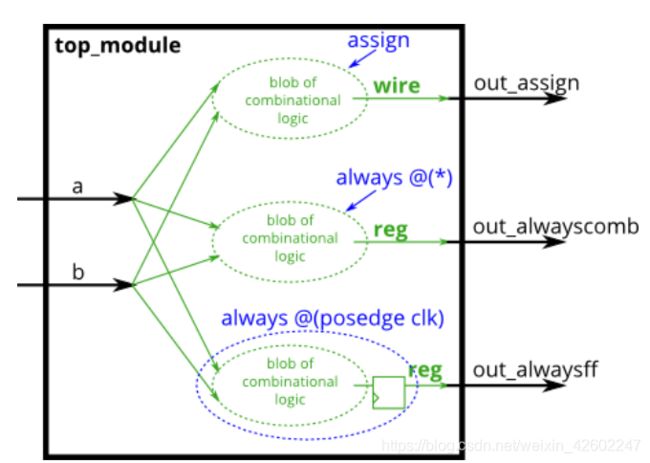
Procedures include always, initial, task, and function blocks. Procedures allow sequential statements (which cannot be used outside of a procedure) to be used to describe the behaviour of a circuit.
过程包括always、initial、task和function块。过程允许使用连续赋值语句(不能在过程之外使用)来描述电路行为。
-
Combinational: always @(*)防止list遗漏,(In SystemVerilog, use always_comb.)
-
Clocked: always @(posedge clk)
-
assign左边必须是net类型(例如wire);
-
always块左边必须是变量类型(例如reg)。
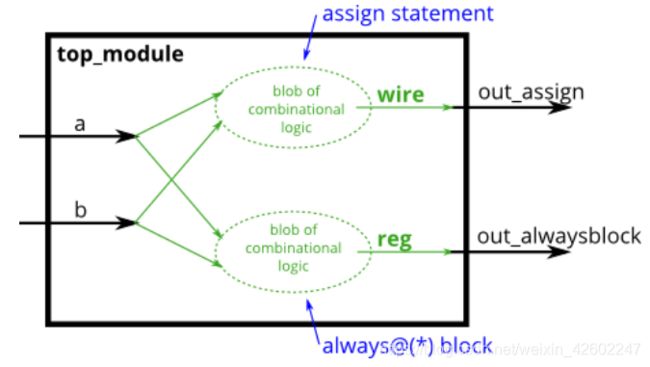
过程块内的语法和过程外的并不相同,过程块有更丰富的语句集(例如if-then, case)。
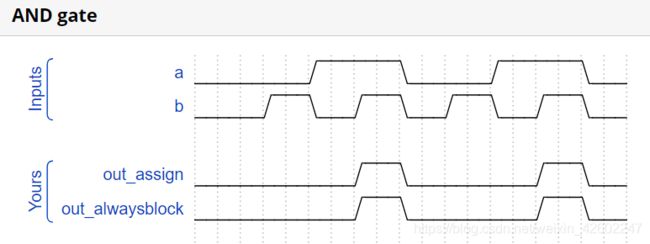
- Always blocks (combinational) //用两种方式表达AND门
// synthesis verilog_input_version verilog_2001
module top_module(
input a,
input b,
output wire out_assign,
output reg out_alwaysblock
);
assign out_assign = a & b;
always @(*) begin
out_alwaysblock = a & b;
end
endmodule
波形:
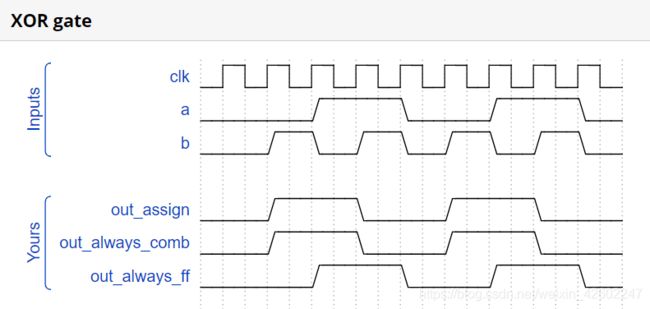
2. Always blocks (clocked) //3种方式表达XOR
阻塞与非阻塞赋值
- In a combinational always block, use blocking assignments. (=)
- In a clocked always block, use non-blocking assignments. (<=)
// synthesis verilog_input_version verilog_2001
module top_module(
input clk,
input a,
input b,
output wire out_assign,
output reg out_always_comb,
output reg out_always_ff );
assign out_assign = a ^ b;
always @(*) out_always_comb = a ^ b;
always @(posedge clk)
out_always_ff <= a ^ b;
endmodule
3. If statement //2-1mux
If条件语句通常用于创造Mux,Mux可以用always@(*),或者三目运算符来写,不过always@()的方式往往容易犯一些隐藏的错误。

module top_module(
input a,
input b,
input sel_b1,
input sel_b2,
output wire out_assign,
output reg out_always );
assign out_assign = (sel_b1 & sel_b2)? b:a;
always @(*) begin
if (sel_b1 & sel_b2) begin
out_always = b;
end
else begin
out_always = a;
end
end
endmodule
波形:

4. If statement latches// 避免锁存器
- 在任何条件下,组合电路必须为所有输出分配值。这意味着需要一个默认值。如果不指定默认值或者所有情况,Verilog默认在其他情况下保证输出不变,从而产生latch。
module top_module (
input cpu_overheated,
output reg shut_off_computer,
input arrived,
input gas_tank_empty,
output reg keep_driving ); //
always @(*) begin
if (cpu_overheated)
shut_off_computer = 1;
else
shut_off_computer = 0;
end
always @(*) begin
if (~arrived)
keep_driving = ~gas_tank_empty;
else
keep_driving = 0;
end
endmodule
波形:

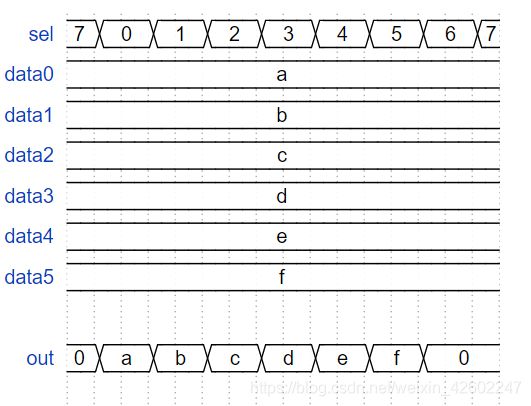
5. Case statement // case语句实现6-1mux
- 每个case只执行一条语句。如果需要多个语句,使用begin…end。
- case-endcase,一定要写default情况
// synthesis verilog_input_version verilog_2001
module top_module (
input [2:0] sel,
input [3:0] data0,
input [3:0] data1,
input [3:0] data2,
input [3:0] data3,
input [3:0] data4,
input [3:0] data5,
output reg [3:0] out );//
always@(*) begin // This is a combinational circuit
case(sel)
0: out = data0;
1: out = data1;
2: out = data2;
3: out = data3;
4: out = data4;
5: out = data5;
default : out = 4'b0;
endcase
end
endmodule
- Priority encoder //优先编码器
// synthesis verilog_input_version verilog_2001
module top_module (
input [3:0] in,
output reg [1:0] pos );
always @(*) begin
case (in)
4'b0000: pos = 2'd0;
4'b0001: pos = 2'd0;
4'b0010: pos = 2'd1;
4'b0011: pos = 2'd0;
4'b0100: pos = 2'd2;
4'b0101: pos = 2'd0;
4'b0110: pos = 2'd1;
4'b0111: pos = 2'd0;
4'b1000: pos = 2'd3;
4'b1001: pos = 2'd0;
4'b1010: pos = 2'd1;
4'b1011: pos = 2'd0;
4'b1100: pos = 2'd2;
4'b1101: pos = 2'd0;
4'b1110: pos = 2'd1;
4'b1111: pos = 2'd0;
default: pos = 2'bx;
endcase
end
endmodule
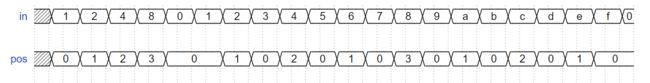
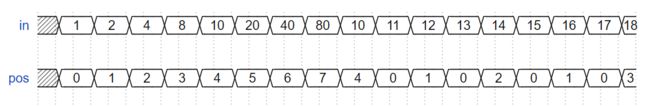
- Priority encoder with casez //casez的使用
- z表示当前位无论是1还是0,case是顺序检查,先判决到的结果优先
- casez和casex都属于case的变体,且不可综合(因为有未知电路)
module top_module (
input [7:0] in,
output reg [2:0] pos );
always @(*) begin
casez (in)
8'bzzzzzzz1: pos = 0;
8'bzzzzzz1z: pos = 1;
8'bzzzzz1zz: pos = 2;
8'bzzzz1zzz: pos = 3;
8'bzzz1zzzz: pos = 4;
8'bzz1zzzzz: pos = 5;
8'bz1zzzzzz: pos = 6;
8'b1zzzzzzz: pos = 7;
default: pos = 0;
endcase
end
endmodule
波形:这一段波形in = 10 的时候, pos应该是1。
8. Avoiding latches //使用default

module top_module (
input [15:0] scancode,
output reg left,
output reg down,
output reg right,
output reg up );
always @(*) begin
up = 1'b0; down = 1'b0; left = 1'b0; right = 1'b0;
//此处先进行置零操作,如果移到default中置0的话,会出现连续高波形状态
case(scancode)
16'he06b: left = 1;
16'he072: down = 1;
16'he074: right = 1;
16'he075: up = 1;
default: ; //default发现没事,就出去了
endcase
end
endmodule
2.4 More Verilog Features
- Conditional ternary operator //三目运算符
((sel[1:0] == 2’h0) ? a : (sel[1:0] == 2’h1) ? b : c ) // A 3-to-1 mux
module top_module (
input [7:0] a, b, c, d,
output [7:0] min);//
wire [7:0] mid1,mid2;
assign mid1 = (a < b) ? a : b;
assign mid2 = (c < d) ? c : d;
assign min = (mid1 < mid2) ? mid1 : mid2;
//此处不可以写成一串三目的对比,冒泡排序是软件思维
endmodule

2. Reduction operators //创建奇偶校验
- & a[3:0] // AND: a[3]&a[2]&a[1]&a[0]. Equivalent to (a[3:0] == 4’hf)
- | b[3:0] // OR: b[3]|b[2]|b[1]|b[0]. Equivalent to (b[3:0] != 4’h0)
- ^ c[2:0] // XOR: c[2]^ c[1] ^c[0]
module top_module (
input [7:0] in,
output parity);
assign parity = ^ in[7:0];
endmodule
- Reduction: Even wider gates
module top_module(
input [99:0] in,
output out_and,
output out_or,
output out_xor
);
assign out_and = & in[99:0];
assign out_or = | in[99:0];
assign out_xor = ^ in[99:0];
endmodule
- Combinational for-loop: Vector reversal 2 //反转长序列矩阵,用always或generate-for
module top_module(
input [99:0] in,
output [99:0] out
);
always @(*) begin
for (integer i=0;i<100;i=i+1) //这里integer和;都不能忘
out[i] = in [99-i];
end
//法二,用generate
/*
genvar i; //定义变量i
generate for(i=0;i<100;i=i+1)
begin:GO //begin-end和名称(GO)都不可以省
assign out[i] =in[99-i];
end
endgenerate
*/
endmodule
generate用法链接:https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_25326461/article/details/52384968
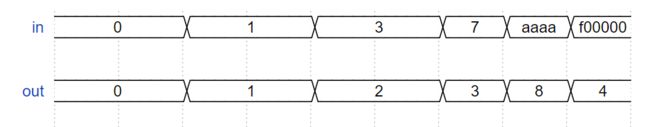
- Combinational for-loop: 255-bit population count //计数器,一定要赋0初值
module top_module(
input [254:0] in,
output [7:0] out );
always@(*) begin
out = 0; //一定要给out赋初值,不然都是z态
for(integer i=0;i<255;i=i+1 ) begin
if(in[i])
out = out + 1'b1;
else
out = out + 1'b0;
end
end
endmodule
6. Generate for-loop: 100-bit binary adder 2 //100位波纹进位加法器
module top_module(
input [99:0] a, b,
input cin,
output [99:0] cout,
output [99:0] sum );
always@(*) begin
{cout[0],sum[0]} = a[0] + b[0] + cin;
for(integer i=1;i<100;i=i+1)
{cout[i],sum[i]} = a[i] + b[i] +cout[i-1];
end
endmodule
- Generate for-loop: 100-digit BCD adder //100个BCD加法器串联
- always里不可以调用子模块,多么痛的领悟
module top_module(
input [399:0] a, b,
input cin,
output cout,
output [399:0] sum );
wire [400:0]cout_mid;
bcd_fadd fa_0(.a(a[3:0]), .b(b[3:0]), .cin(cin), .cout(cout_mid[4]), .sum(sum[3:0]));
assign cout = cout_mid[400];
generate
genvar i;
for (i=4;i<400;i=i+4)
begin:GO
bcd_fadd fa_i(.a(a[i+3:i]), .b(b[i+3:i]), .cin(cout_mid[i]), .cout(cout_mid[i+4]), .sum(sum[i+3:i]));
end
endgenerate
endmodule