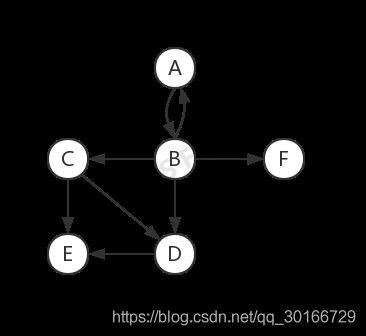
图论入门
相关定义

图 由顶点和边组成的结构
顶点 图中的元素节点,如上图中的A,B,C等
边(弧) 顶点之间的关系连线,如果边是有向(或者点对有序的),则图也会被叫做有向图。
边的表示(A, B),同时也说明A,B邻接
度 顶点邻接的顶点数目
图的存储方式
1.邻接矩阵
对于上边的有向图,可以通过邻接矩阵的方式来表示:
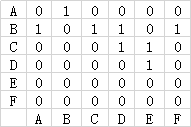
当图中顶点的度比较低时,我们说图是稀疏的,对应的矩阵也被称为稀疏矩阵
2.邻接表
当图是稀疏的时候,可以通过邻接表来表示:
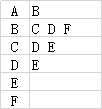
对于每一个顶点,使用一个表来存放所有邻接的顶点
3. 图形结构的搜索
| 起点 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 终点 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
对应的邻接矩阵为:
/*
0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0
0 1 0 0
0 0 0 1
*/
3.1 深度优先搜索 DFS
从某个顶点A开始,遍历节点A的邻接顶点,在遍历过程中,递归调用深度优先搜索。
计算起点到终点的最短路径:
public class DepthFirstSearch {
private static class Point {
int x;
int y;
Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Point point = (Point) o;
return x == point.x &&
y == point.y;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(x, y);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Point{" +
"x=" + x +
", y=" + y +
'}';
}
}
// 表示5行4列
static int m = 5, n = 4;
// 用于保存顶点是否邻接
private static int[][] values = new int[m][n];
/// 用于标记顶点是否已经遍历
private static boolean[][] marks = new boolean[m][n];
// 表示方向,每次都会有上、下、左、右四个方向的节点
private static int[][] direction = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
private static Point targetPoint = new Point(3, 2);
private static LinkedList<Point> stack = new LinkedList<>();
private static Point[] minLoad;
private static int minStep = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
values[i][j] = scanner.nextInt();
}
}
search(0, 0, 0);
System.out.println("最短路径为" + minStep);
System.out.println("最短路径为" + Arrays.toString(minLoad));
}
private static void search(int sourceX, int sourceY, int step) {
Point sourcePoint = new Point(sourceX, sourceY);
stack.push(sourcePoint);
if (sourcePoint.equals(targetPoint) && step < minStep) {
minStep = step;
minLoad = stack.toArray(new Point[]{});
return;
}
for (int[] tem : direction) {
int newX = sourcePoint.x + tem[0];
int newY = sourcePoint.y + tem[1];
// 判断顶点是否存在
if (newX >= m || newX < 0 || newY >= n || newY < 0) {
continue;
}
// 如果顶点不邻接
if (values[newX][newY] == 1) {
continue;
}
/// 如果顶点已遍历
if (marks[newX][newY]) {
continue;
}
// 避免重复查找
marks[newX][newY] = true;
search(newX, newY, step + 1);
// 撤销查找标记
marks[newX][newY] = false;
stack.pop();
}
}
}
3.2 广度优先搜索 WFS
从某个顶点A开始,先遍历距离顶点A距离为1的顶点,再遍历距离顶点A距离为2的顶点(就是距离 与A的距离为1的顶点 为1的顶点),直到遍历完所有顶点。
对与前边表中所示的图,如果要判断从起点是否可以抵达终点
public class BreadthFirstSearch {
private static class Point {
int x;
int y;
Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Point point = (Point) o;
return x == point.x &&
y == point.y;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(x, y);
}
}
// 表示5行4列
static int m = 5, n = 4;
// 用于保存顶点是否邻接
private static int[][] values = new int[m][n];
/// 用于标记顶点是否已经遍历
private static boolean[][] marks = new boolean[m][n];
// 表示方向,每次都会有上、下、左、右四个方向的节点
private static int[][] direction = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
public static void search(int sourceX, int sourceY, int targetX, int targetY) {
Point sourcePoint = new Point(sourceX, sourceY);
Point targetPoint = new Point(targetX, targetY);
// 初始化一个队列
Queue<Point> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(m * n);
queue.offer(sourcePoint);
marks[sourcePoint.x][sourcePoint.y] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Point point = queue.poll();
if (point.equals(targetPoint)) {
System.out.println("找到目标顶点");
return;
}
// 将邻接的顶点添加到队列中
for (int[] tem : direction) {
int newX = point.x + tem[0];
int newY = point.y + tem[1];
// 判断顶点是否存在
if (newX >= m || newX < 0 || newY >= n || newY < 0) {
continue;
}
// 如果顶点不邻接
if (values[newX][newY] == 1) {
continue;
}
/// 如果顶点已遍历
if (marks[newX][newY]) {
continue;
}
Point newPoint = new Point(newX, newY);
queue.offer(newPoint);
}
}
System.out.println("没有找到目标节点");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
values[i][j] = scanner.nextInt();
}
}
search(0, 0, 3, 2);
}
}