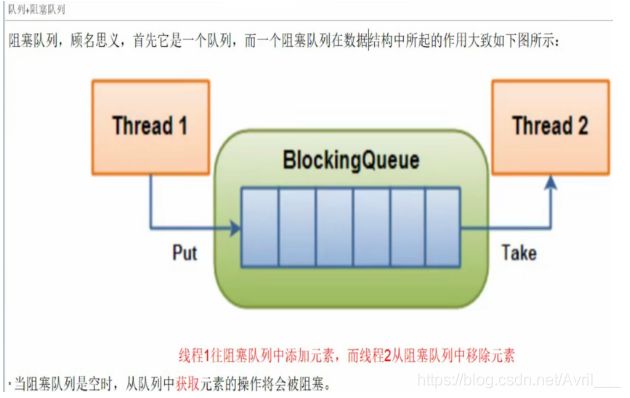
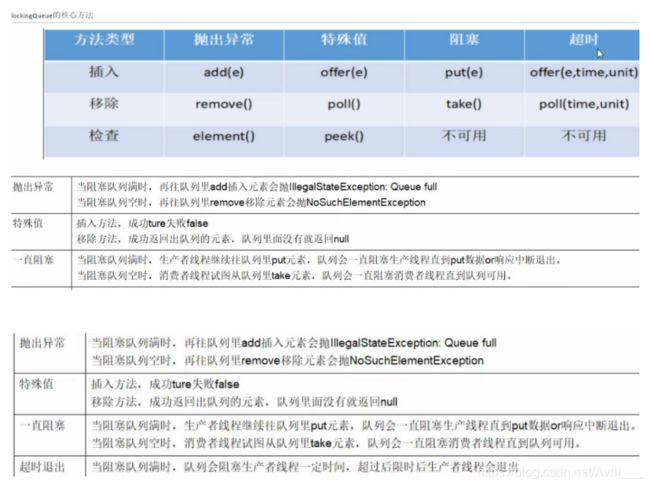
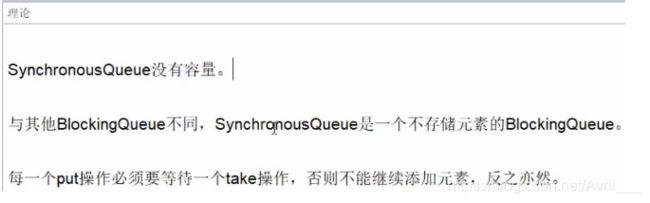
常用的阻塞队列用法以及原理
理论:

阻塞队列举例:
火锅店欢迎阻塞
去银行排队不得不阻塞
架构
继承关系
collection—>queue->七个阻塞队列接口

三个红色是重点一个粉色需注意,最后一个注意拼写(deque)
虽然有界但是是21亿的长度,接近无界(21亿)
synchronousQueue是生产一个,没消费不会再生产,故为不储存(贝克汉姆球鞋)
异常用法
element()是检查队头元素是谁
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
public class BlockingQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<Object> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
System.out.println(queue.add("1"));
System.out.println(queue.add("2"));
System.out.println(queue.add("3"));
//System.out.println(queue.add("6"));
System.out.println(queue.element());
System.out.println(queue.remove());
System.out.println(queue.remove());
System.out.println(queue.remove());
//System.out.println(queue.remove());
}
}
特殊值用法(也就是布尔值)
peek()是查看队列顶端元素
offer添加超过队长返回false
pull拿值无值返回null
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class BlockingQueueDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<Object> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
try {
System.out.println(queue.offer(1,1, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(queue.offer(2,1, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(queue.offer(3,1, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(queue.offer(4,1, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println(queue.peek());
System.out.println();
try {
System.out.println(queue.poll(1,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(queue.poll(1,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(queue.poll(1,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(queue.poll(1,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
阻塞
不够加入或者取不到值就一直阻塞线程
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class BlockingQueueDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<Object> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
try {
queue.put(1);
queue.put(2);
queue.put(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
System.out.println(queue.take());
System.out.println(queue.take());
System.out.println(queue.take());
//System.out.println(queue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
超时
队列超了等几秒,如果还超就返回false
队列取不到值了就等几秒,如果还取不到值就返回null
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class BlockingQueueDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<Object> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
try {
System.out.println(queue.offer(1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(queue.offer(1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(queue.offer(1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(queue.offer(1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
System.out.println(queue.poll(2,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(queue.poll(2,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(queue.poll(2,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(queue.poll(2,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
钱多事少离家近,别人加班你加薪
import java.sql.Time;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class SynchronousQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<Object> queue = new SynchronousQueue<>();
new Thread(()->{
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"put1");
queue.put(1);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"put2");
queue.put(2);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"put3");
queue.put(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"AAA").start();
new Thread(()->{
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"get1");
System.out.println(queue.take());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"get2");
System.out.println(queue.take());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"get3");
System.out.println(queue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"BBB").start();
}
}
同步队列不存储元素,第一个put完必须等take过后才打印,put2,而不是直接打印
只能有一个在队列里面
生产者消费者模式
高内聚低耦合的情况下线程操纵资源类
判断干活唤醒通知
while严防多线程并发状态下的虚假唤醒
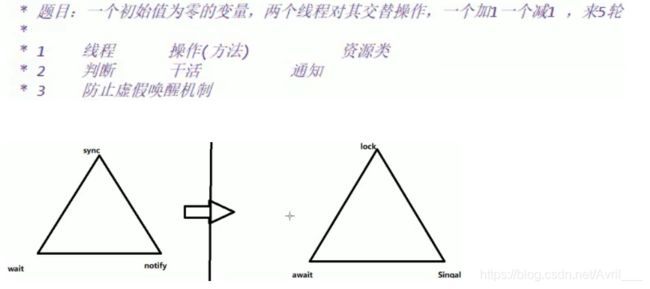
多线程判断要用while防止虚假唤醒
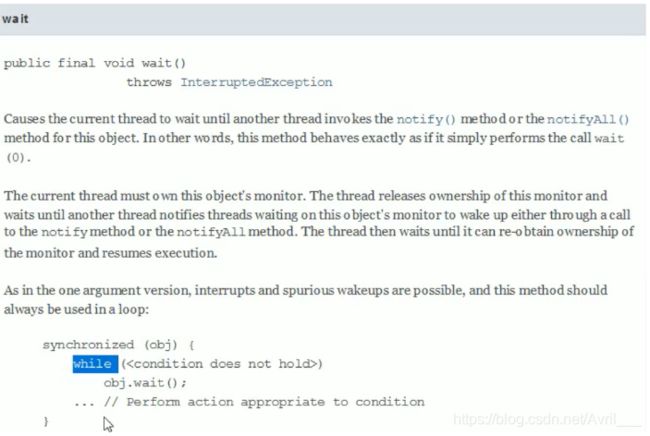
传统版的生产者消费者模式代码
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
class shareDate {
private int number = 0;
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
public void increment() {
lock.lock();
try {
//判断
while (number != 0) {
//不能生产
condition.await();
}
//生产
number++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程 \t" +number+ "生产");
//唤醒
condition.signalAll();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void decrement() {
lock.lock();
try {
//判断
while (number == 0) {
//不能消费
condition.await();
}
//消费
number--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程 \t" +number+ "消费");
//唤醒
condition.signalAll();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public class ProductConsumerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
shareDate shareDate = new shareDate();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 1; i <= 5 ; i++) {
shareDate.increment();
}
},"AAA").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 1; i <= 5 ; i++) {
shareDate.decrement();
}
},"BBB").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 1; i <= 5 ; i++) {
shareDate.increment();
}
},"CCC").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 1; i <= 5 ; i++) {
shareDate.decrement();
}
},"DDD").start();
}
}
sync和lock的区别

sync两次退出,第一次正常退出第二次异常退出
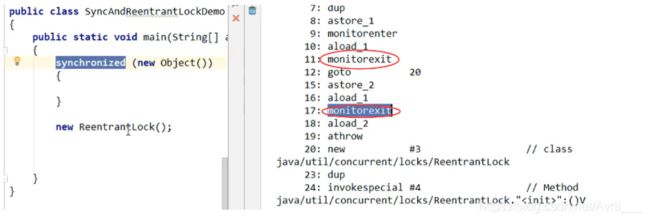
之前敲过

代码
package juc;
import sun.awt.windows.ThemeReader;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
class ShareResource{
private int flag = 1;
private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();
private Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition();
private Condition condition3 = lock.newCondition();
//ctrl+alt+t是try catch
public void print5(int totalLoop){
lock.lock();
try {
//1.判断
while (flag != 1){
condition1.await();
}
//干活
for (int i = 1;i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println("线程名字:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t次数:"+i+"\t轮数:"+totalLoop);
}
//唤醒+通知
flag = 2;
condition2.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void print10(int totalLoop){
lock.lock();
try {
//1.判断
while (flag != 2){
condition2.await();
}
//干活
for (int i = 1;i <= 10; i++) {
System.out.println("线程名字:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t次数:"+i+"\t轮数:"+totalLoop);
}
//唤醒+通知
flag = 3;
condition3.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void print15(int totalLoop){
lock.lock();
try {
//1.判断
while (flag != 3){
condition3.await();
}
//干活
for (int i = 1;i <= 15; i++) {
System.out.println("线程名字:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t次数:"+i+"\t轮数:"+totalLoop);
}
//唤醒+通知
flag = 1;
condition1.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public class ConditionLockDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareResource sr = new ShareResource();
new Thread(()->{
for(int i = 1 ; i<=10 ; i++){
sr.print5(i);
}
},"A").start();
new Thread(()->{
for(int i = 1 ; i<=10 ; i++){
sr.print10(i);
}
},"B").start();
new Thread(()->{
for(int i = 1 ; i<=10 ; i++){
sr.print15(i);
}
},"C").start();
}
}
代码编写时应注意:
通顺,适配,通用
传借口不允许传具体的类
写往抽象写,查往仔细落地查
永远传参传接口
阻塞队列版的生产者消费者模式代码
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
class ProductConsumer {
private volatile boolean FLAG = true;
private AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger();
private BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = null;
public ProductConsumer(BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue) {
this.blockingQueue = blockingQueue;
}
public void increment() throws Exception {
String date = null;
boolean retValue;
while (FLAG) {
date = atomicInteger.incrementAndGet() + "";
retValue = blockingQueue.offer(date, 2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (retValue) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + date + "生产一个蛋糕");
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + date + "生产一个失败");
}
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"boss暂停不生产了");
}
public void decrement() throws Exception {
String result = null;
while (FLAG) {
result = blockingQueue.poll(2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if(null == result || result.equalsIgnoreCase("")){
FLAG = false;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"超过两秒没有取出蛋糕暂停");
return;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"消费蛋糕成功");
}
}
public void stop(){
this.FLAG = false;
}
}
public class ProductConsumerBlockingQueue {
public static void main(String[] args){
ProductConsumer productConsumer = new ProductConsumer(new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10));
new Thread(()->{
try {
System.out.println("生产线程启动");
for (int i = 1; i <= 5 ; i++) {
productConsumer.increment();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"prod").start();
new Thread(()->{
try {
System.out.println("消费线程启动");
for (int i = 1; i <= 5 ; i++) {
productConsumer.decrement();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"consumer").start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("boss叫停");
productConsumer.stop();
}
}