grpc源码阅读(go)
grpc源码阅读(go)
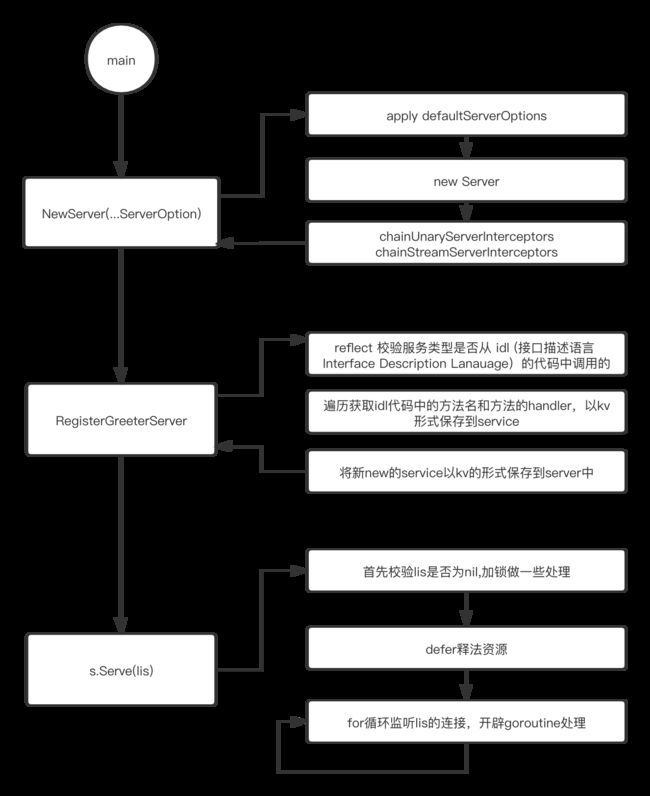
- server
- grpce.NewServer(...ServerOption)
- RegisterGreeterServer
- s.Serve(lis)
- 全部流程
server
- 参考
func main() {
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", port)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to listen: %v", err)
}
s := grpc.NewServer()
pb.RegisterGreeterServer(s, &server{})
if err := s.Serve(lis); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to serve: %v", err)
}
}
此处是grpc下example的例子,主要完成了三件事 new一个server和注册该server,和启动该server
下面将从这两个方面来阐述。
grpce.NewServer(…ServerOption)
// NewServer creates a gRPC server which has no service registered and has not
// started to accept requests yet.
func NewServer(opt ...ServerOption) *Server {
opts := defaultServerOptions
for _, o := range opt {
o.apply(&opts)
}
s := &Server{
lis: make(map[net.Listener]bool),
opts: opts,
conns: make(map[transport.ServerTransport]bool),
m: make(map[string]*service),
quit: grpcsync.NewEvent(),
done: grpcsync.NewEvent(),
czData: new(channelzData),
}
chainUnaryServerInterceptors(s)
chainStreamServerInterceptors(s)
s.cv = sync.NewCond(&s.mu)
if EnableTracing {
_, file, line, _ := runtime.Caller(1)
s.events = trace.NewEventLog("grpc.Server", fmt.Sprintf("%s:%d", file, line))
}
if channelz.IsOn() {
s.channelzID = channelz.RegisterServer(&channelzServer{s}, "")
}
return s
}
此处主要完成以下几件事
(1)获取defaultServerOptions 遍历opts,其中serverOption是一个接口,只有一个方法apply,通过装饰器newFuncServerOption 将各类参数转为*funcServerOption类型(例如WriteBufferSize),其中funcServerOption仅包含一个参数
f func(*serverOptions),执行ServerOption的apply(*serverOptions)方法,也就是执行func (fdo *funcServerOption) apply(do *serverOptions),等于执行方法f。
// A ServerOption sets options such as credentials, codec and keepalive parameters, etc.
type ServerOption interface {
apply(*serverOptions)
}
此处是serverOptions
type serverOptions struct {
creds credentials.TransportCredentials //证书
codec baseCodec //序列化和反序列化
cp Compressor // 压缩接口
dc Decompressor // 解压接口
unaryInt UnaryServerInterceptor //一元拦截器
streamInt StreamServerInterceptor // 流拦截器
chainUnaryInts []UnaryServerInterceptor
chainStreamInts []StreamServerInterceptor
inTapHandle tap.ServerInHandle
statsHandler stats.Handler
maxConcurrentStreams uint32
maxReceiveMessageSize int //最大接收数据
maxSendMessageSize int //最大发送数据
unknownStreamDesc *StreamDesc
keepaliveParams keepalive.ServerParameters // 长连接的server参数
keepalivePolicy keepalive.EnforcementPolicy
initialWindowSize int32 //初始化的windows大小 下限为64k 上限为2^31
initialConnWindowSize int32 //初始化conn大小,一个conn有多个stream,等于上面的值*16,htt2的限制是大于0,默认一个连接有100个流,超过了就被拒绝
writeBufferSize int //写入缓冲大小
readBufferSize int //读入缓冲大小
connectionTimeout time.Duration //连接超时时间 默认120s
maxHeaderListSize *uint32 //最大头部大小
headerTableSize *uint32
}
var defaultServerOptions = serverOptions{
maxReceiveMessageSize: defaultServerMaxReceiveMessageSize,
//1024 * 1024 * 4 默认4m
maxSendMessageSize: defaultServerMaxSendMessageSize,
// math.MaxInt32 其中 MaxInt32 = 1<<31 - 1
connectionTimeout: 120 * time.Second,
writeBufferSize: defaultWriteBufSize, //defaultWriteBufSize = 32 * 1024
readBufferSize: defaultReadBufSize,
//defaultReadBufSize = 32 * 1024
}
type funcServerOption struct {
f func(*serverOptions)
}
func (fdo *funcServerOption) apply(do *serverOptions) {
fdo.f(do)
}
func newFuncServerOption(f func(*serverOptions)) *funcServerOption {
return &funcServerOption{
f: f,
}
}
// WriteBufferSize determines how much data can be batched before doing a write on the wire.
// The corresponding memory allocation for this buffer will be twice the size to keep syscalls low.
// The default value for this buffer is 32KB.
// Zero will disable the write buffer such that each write will be on underlying connection.
// Note: A Send call may not directly translate to a write.
func WriteBufferSize(s int) ServerOption {
return newFuncServerOption(func(o *serverOptions) {
o.writeBufferSize = s
})
}
(2)构建一个server , s := &Server,其中server的参数如下
// Server is a gRPC server to serve RPC requests.
type Server struct {
opts serverOptions // 上面提到的defaultServerOptions
mu sync.Mutex // guards following
lis map[net.Listener]bool
conns map[transport.ServerTransport]bool
serve bool
drain bool
cv *sync.Cond // signaled when connections close for GracefulStop
m map[string]*service // service name -> service info
events trace.EventLog
quit *grpcsync.Event
done *grpcsync.Event
channelzRemoveOnce sync.Once
serveWG sync.WaitGroup // counts active Serve goroutines for GracefulStop
channelzID int64 // channelz unique identification number
czData *channelzData
}
其中grpcsync.Event和channelzData的结构体如下
// Event represents a one-time event that may occur in the future.
type Event struct {
fired int32
c chan struct{}
o sync.Once
}
// channelzData is used to store channelz related data for ClientConn, addrConn and Server.
// These fields cannot be embedded in the original structs (e.g. ClientConn), since to do atomic
// operation on int64 variable on 32-bit machine, user is responsible to enforce memory alignment.
// Here, by grouping those int64 fields inside a struct, we are enforcing the alignment.
type channelzData struct {
callsStarted int64
callsFailed int64
callsSucceeded int64
// lastCallStartedTime stores the timestamp that last call starts. It is of int64 type instead of
// time.Time since it's more costly to atomically update time.Time variable than int64 variable.
lastCallStartedTime int64
}
(3)调用chainUnaryServerInterceptors ,其中UnaryServerInterceptor的类型如下
type UnaryServerInterceptor func(ctx context.Context, req interface{}, info *UnaryServerInfo, handler UnaryHandler) (resp interface{}, err error)
type UnaryHandler func(ctx context.Context, req interface{}) (interface{}, error)
type UnaryServerInfo struct {
// Server is the service implementation the user provides. This is read-only.
Server interface{}
// FullMethod is the full RPC method string, i.e., /package.service/method.
FullMethod string
}
具体的实现代码如下
将opts.chainUnaryInts拿出来,形成责任链,放到opts.unaryInt,具体该责任链的调用过程之后讲解。
// chainUnaryServerInterceptors chains all unary server interceptors into one.
func chainUnaryServerInterceptors(s *Server) {
// Prepend opts.unaryInt to the chaining interceptors if it exists, since unaryInt will
// be executed before any other chained interceptors.
interceptors := s.opts.chainUnaryInts
if s.opts.unaryInt != nil {
interceptors = append([]UnaryServerInterceptor{s.opts.unaryInt}, s.opts.chainUnaryInts...)
}
var chainedInt UnaryServerInterceptor
if len(interceptors) == 0 {
chainedInt = nil
} else if len(interceptors) == 1 {
chainedInt = interceptors[0]
} else {
chainedInt = func(ctx context.Context, req interface{}, info *UnaryServerInfo, handler UnaryHandler) (interface{}, error) {
return interceptors[0](ctx, req, info, getChainUnaryHandler(interceptors, 0, info, handler))
}
}
s.opts.unaryInt = chainedInt
}
// getChainUnaryHandler recursively generate the chained UnaryHandler
func getChainUnaryHandler(interceptors []UnaryServerInterceptor, curr int, info *UnaryServerInfo, finalHandler UnaryHandler) UnaryHandler {
if curr == len(interceptors)-1 {
return finalHandler
}
return func(ctx context.Context, req interface{}) (interface{}, error) {
return interceptors[curr+1](ctx, req, info, getChainUnaryHandler(interceptors, curr+1, info, finalHandler))
}
}
- ps chainStreamServerInterceptors 的执行同理 ,EnableTracing 与 channelz之后分析
RegisterGreeterServer
在newServer获取一个服务后,以下面为例子,将通过pb.RegisterGreeterServer(s, &server{}) 注册一个server,事实上是通过上面获取到的server的注册方法将GreeterServer类型的服务注册进去
type server struct {
pb.UnimplementedGreeterServer
}
func main() {
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", port)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to listen: %v", err)
}
s := grpc.NewServer()
pb.RegisterGreeterServer(s, &server{})
if err := s.Serve(lis); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to serve: %v", err)
}
}
protoc生成的文件
type GreeterServer interface {
// Sends a greeting
SayHello(context.Context, *HelloRequest) (*HelloReply, error)
}
func RegisterGreeterServer(s *grpc.Server, srv GreeterServer) {
s.RegisterService(&_Greeter_serviceDesc, srv)
}
var _Greeter_serviceDesc = grpc.ServiceDesc{
ServiceName: "helloworld.Greeter",
HandlerType: (*GreeterServer)(nil),
Methods: []grpc.MethodDesc{
{
MethodName: "SayHello",
Handler: _Greeter_SayHello_Handler,
},
},
Streams: []grpc.StreamDesc{},
Metadata: "helloworld.proto",
}
注册的过程分为以下几个逻辑
(1)校验。校验注册的服务是否是预期服务
func (s *Server) RegisterService(sd *ServiceDesc, ss interface{}) {
ht := reflect.TypeOf(sd.HandlerType).Elem()
st := reflect.TypeOf(ss)
if !st.Implements(ht) {
grpclog.Fatalf("grpc: Server.RegisterService found the handler of type %v that does not satisfy %v", st, ht)
}
s.register(sd, ss)
}
func (s *Server) register(sd *ServiceDesc, ss interface{}) {
s.mu.Lock()
defer s.mu.Unlock()
s.printf("RegisterService(%q)", sd.ServiceName)
if s.serve {
grpclog.Fatalf("grpc: Server.RegisterService after Server.Serve for %q", sd.ServiceName)
}
if _, ok := s.m[sd.ServiceName]; ok {
grpclog.Fatalf("grpc: Server.RegisterService found duplicate service registration for %q", sd.ServiceName)
}
srv := &service{
server: ss,
md: make(map[string]*MethodDesc),
sd: make(map[string]*StreamDesc),
mdata: sd.Metadata,
}
for i := range sd.Methods {
d := &sd.Methods[i]
srv.md[d.MethodName] = d
}
for i := range sd.Streams {
d := &sd.Streams[i]
srv.sd[d.StreamName] = d
}
s.m[sd.ServiceName] = srv
}
(2) 遍历之后,,将protoc生成的服务中的grpc.MethodDesc获取出来通过k v的形式保存。所有的MethodDesc中都有一个methodHandler 类型为
type methodHandler func(srv interface{}, ctx context.Context, dec func(interface{}) error, interceptor UnaryServerInterceptor) (interface{}, error)
例如_Greeter_SayHello_Handler是这样的
func _Greeter_SayHello_Handler(srv interface{}, ctx context.Context, dec func(interface{}) error, interceptor grpc.UnaryServerInterceptor) (interface{}, error) {
in := new(HelloRequest)
if err := dec(in); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if interceptor == nil {
return srv.(GreeterServer).SayHello(ctx, in)
}
info := &grpc.UnaryServerInfo{
Server: srv,
FullMethod: "/helloworld.Greeter/SayHello",
}
handler := func(ctx context.Context, req interface{}) (interface{}, error) {
return srv.(GreeterServer).SayHello(ctx, req.(*HelloRequest))
}
return interceptor(ctx, in, info, handler)
}
(3) 然后将该服务保存到前面 NewServer获得的server的service中
s.m[sd.ServiceName] = srv
s.Serve(lis)
server(lis)的代码如下
func (s *Server) Serve(lis net.Listener) error {
s.mu.Lock()
s.printf("serving")
s.serve = true
if s.lis == nil {
// Serve called after Stop or GracefulStop.
s.mu.Unlock()
lis.Close()
return ErrServerStopped
}
s.serveWG.Add(1)
defer func() {
s.serveWG.Done()
if s.quit.HasFired() {
// Stop or GracefulStop called; block until done and return nil.
<-s.done.Done()
}
}()
ls := &listenSocket{Listener: lis}
s.lis[ls] = true
if channelz.IsOn() {
ls.channelzID = channelz.RegisterListenSocket(ls, s.channelzID, lis.Addr().String())
}
s.mu.Unlock()
defer func() {
s.mu.Lock()
if s.lis != nil && s.lis[ls] {
ls.Close()
delete(s.lis, ls)
}
s.mu.Unlock()
}()
var tempDelay time.Duration // how long to sleep on accept failure
for {
rawConn, err := lis.Accept()
if err != nil {
if ne, ok := err.(interface {
Temporary() bool
}); ok && ne.Temporary() {
if tempDelay == 0 {
tempDelay = 5 * time.Millisecond
} else {
tempDelay *= 2
}
if max := 1 * time.Second; tempDelay > max {
tempDelay = max
}
s.mu.Lock()
s.printf("Accept error: %v; retrying in %v", err, tempDelay)
s.mu.Unlock()
timer := time.NewTimer(tempDelay)
select {
case <-timer.C:
case <-s.quit.Done():
timer.Stop()
return nil
}
continue
}
s.mu.Lock()
s.printf("done serving; Accept = %v", err)
s.mu.Unlock()
if s.quit.HasFired() {
return nil
}
return err
}
tempDelay = 0
// Start a new goroutine to deal with rawConn so we don't stall this Accept
// loop goroutine.
//
// Make sure we account for the goroutine so GracefulStop doesn't nil out
// s.conns before this conn can be added.
s.serveWG.Add(1)
go func() {
s.handleRawConn(rawConn)
s.serveWG.Done()
}()
}
}
(1) 首先校验lis是否为nil,加锁做一些处理,最后defer释法资源
s.mu.Lock()
s.printf("serving")
s.serve = true
if s.lis == nil {
// Serve called after Stop or GracefulStop. //优雅的停止服务
s.mu.Unlock()
lis.Close()
return ErrServerStopped
}
s.serveWG.Add(1)
defer func() {
s.serveWG.Done()
if s.quit.HasFired() {
// Stop or GracefulStop called; block until done and return nil.
<-s.done.Done()
}
}()
//包装连接对象,并声明为true,代表有效
ls := &listenSocket{Listener: lis}
s.lis[ls] = true
if channelz.IsOn() {
ls.channelzID = channelz.RegisterListenSocket(ls, s.channelzID, lis.Addr().String())
}
s.mu.Unlock()
//清理资源
defer func() {
s.mu.Lock()
if s.lis != nil && s.lis[ls] {
ls.Close()
delete(s.lis, ls)
}
s.mu.Unlock()
}()
// HasFired returns true if Fire has been called.
func (e *Event) HasFired() bool {
return atomic.LoadInt32(&e.fired) == 1
}
(2)通过for循环监听端口,每接收到一条请求,通过一个goroutine去处理
var tempDelay time.Duration // how long to sleep on accept failure
for {
rawConn, err := lis.Accept()
// 如果数据错误的时候则做一些处理
if err != nil {
if ne, ok := err.(interface {
Temporary() bool
}); ok && ne.Temporary() {
if tempDelay == 0 {
tempDelay = 5 * time.Millisecond
} else {
tempDelay *= 2
}
if max := 1 * time.Second; tempDelay > max {
tempDelay = max
}
s.mu.Lock()
s.printf("Accept error: %v; retrying in %v", err, tempDelay)
s.mu.Unlock()
timer := time.NewTimer(tempDelay)
select {
case <-timer.C:
case <-s.quit.Done():
timer.Stop()
return nil
}
continue
}
s.mu.Lock()
s.printf("done serving; Accept = %v", err)
s.mu.Unlock()
if s.quit.HasFired() {
return nil
}
return err
}
tempDelay = 0
// Start a new goroutine to deal with rawConn so we don't stall this Accept
// loop goroutine.
//
// Make sure we account for the goroutine so GracefulStop doesn't nil out
// s.conns before this conn can be added.
// 数据正确的时候,开一条goroutine去处理连接
s.serveWG.Add(1)
go func() {
s.handleRawConn(rawConn)
s.serveWG.Done()
}()
}
全部流程
下一篇介绍goroutine如何处理连接 (即 s.handleRawConn(rawConn))