使用OpenCV做Blob检测
1 What is a Blob ?
A Blob is a group of connected pixels in an image that share some common property ( E.g grayscale value ). In the image above, the dark connected regions are blobs, and the goal of blob detection is to identify and mark these regions.
2 SimpleBlobDetector Example
OpenCV provides a convenient way to detect blobs and filter them based on different characteristics. Let’s start with the simplest example
2.1 Python Code
# Standard imports
import cv2
import numpy as np;
# Read image
im = cv2.imread("blob.jpg", cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
# Set up the detector with default parameters.
detector = cv2.SimpleBlobDetector()
# Detect blobs.
keypoints = detector.detect(im)
# Draw detected blobs as red circles.
# cv2.DRAW_MATCHES_FLAGS_DRAW_RICH_KEYPOINTS ensures the size of the circle corresponds to the size of blob
im_with_keypoints = cv2.drawKeypoints(im, keypoints, np.array([]), (0,0,255), cv2.DRAW_MATCHES_FLAGS_DRAW_RICH_KEYPOINTS)
# Show keypoints
cv2.imshow("Keypoints", im_with_keypoints)
cv2.waitKey(0)
2.2 C++ Code
using namespace cv;
// Read image
Mat im = imread( "blob.jpg", IMREAD_GRAYSCALE );
// Set up the detector with default parameters.
SimpleBlobDetector detector;
// Detect blobs.
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints;
detector.detect( im, keypoints);
// Draw detected blobs as red circles.
// DrawMatchesFlags::DRAW_RICH_KEYPOINTS flag ensures the size of the circle corresponds to the size of blob
Mat im_with_keypoints;
drawKeypoints( im, keypoints, im_with_keypoints, Scalar(0,0,255), DrawMatchesFlags::DRAW_RICH_KEYPOINTS );
// Show blobs
imshow("keypoints", im_with_keypoints );
waitKey(0);
3 How does Blob detection work ?
SimpleBlobDetector, as the name implies, is based on a rather simple algorithm described below. The algorithm is controlled by parameters ( shown in bold below ) and has the following steps. Scroll down to know how the parameters are set.
3.1 Thresholding
Convert the source images to several binary images by thresholding the source image with thresholds starting at minThreshold. These thresholds are incremented by thresholdStep until maxThreshold. So the first threshold is minThreshold, the second is minThreshold + thresholdStep, the third is minThreshold + 2 x thresholdStep, and so on.
3.2Grouping
In each binary image, connected white pixels are grouped together. Let’s call these binary blobs.
3.3Merging
The centers of the binary blobs in the binary images are computed, and blobs located closer than minDistBetweenBlobs are merged.
3.4 Center & Radius Calculation
The centers and radii of the new merged blobs are computed and returned.
4 Filtering Blobs by Color, Size and Shape
The parameters for SimpleBlobDetector can be set to filter the type of blobs we want.
- By Color :
[ Note : This feature appears to be broken. I checked the code, and it appears to have a logical error ] First you need to set filterByColor = 1. Set blobColor = 0 to select darker blobs, and blobColor = 255 for lighter blobs.
- By Size :
You can filter the blobs based on size by setting the parameters filterByArea = 1, and appropriate values for minArea and maxArea. E.g. setting minArea = 100 will filter out all the blobs that have less then 100 pixels.
- By Shape :
Now shape has three different parameters.
- Circularity : This just measures how close to a circle the blob is.
E.g. a regular hexagon has higher circularity than say a square. To
filter by circularity, set filterByCircularity = 1. Then set
appropriate values for minCircularity and maxCircularity.
Circularity is defined as
frac{4piArea}/{perimeter * perimeter}
This means that a circle has a circularity of 1, circularity of a square is 0.785, and so on. - Convexity : A picture is worth a thousand words. Convexity is
defined as the (Area of the Blob / Area of it’s convex hull). Now,
Convex Hull of a shape is the tightest convex shape that completely
encloses the shape. To filter by convexity, set filterByConvexity =
1, followed by setting 0 ≤ minConvexity ≤ 1 and maxConvexity ( ≤ 1)
Concave versus Convex Shape

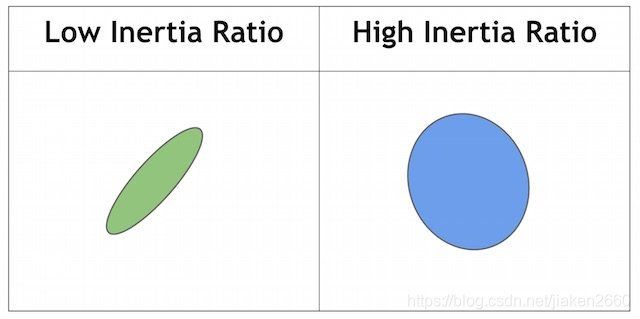
- Inertia Ratio : Don’t let this scare you. Mathematicians often use
confusing words to describe something very simple. All you have to
know is that this measures how elongated a shape is. E.g. for a
circle, this value is 1, for an ellipse it is between 0 and 1, and
for a line it is 0. To filter by inertia ratio, set filterByInertia
= 1, and set 0 ≤ minInertiaRatio ≤ 1 and maxInertiaRatio (≤ 1 ) appropriately.
5 How to set SimpleBlobDetector params ?
Setting parameters for SimpleBlobDetector is easy. Here is an example
5.1 Python Code
# Setup SimpleBlobDetector parameters.
params = cv2.SimpleBlobDetector_Params()
# Change thresholds
params.minThreshold = 10;
params.maxThreshold = 200;
# Filter by Area.
params.filterByArea = True
params.minArea = 1500
# Filter by Circularity
params.filterByCircularity = True
params.minCircularity = 0.1
# Filter by Convexity
params.filterByConvexity = True
params.minConvexity = 0.87
# Filter by Inertia
params.filterByInertia = True
params.minInertiaRatio = 0.01
# Create a detector with the parameters
ver = (cv2.__version__).split('.')
if int(ver[0]) < 3 :
detector = cv2.SimpleBlobDetector(params)
else :
detector = cv2.SimpleBlobDetector_create(params)
5.2 C++ Code
Setting of params for SimpleBlobDetector in OpenCV 2 is slightly different from OpenCV 3. In the code below we use the macro CV_MAJOR_VERSION to detect the version of OpenCV. In OpenCV 3, the SimpleBlobDetector::create method is used to create a smart pointer. The usage is shown in the code below.
// Setup SimpleBlobDetector parameters.
SimpleBlobDetector::Params params;
// Change thresholds
params.minThreshold = 10;
params.maxThreshold = 200;
// Filter by Area.
params.filterByArea = true;
params.minArea = 1500;
// Filter by Circularity
params.filterByCircularity = true;
params.minCircularity = 0.1;
// Filter by Convexity
params.filterByConvexity = true;
params.minConvexity = 0.87;
// Filter by Inertia
params.filterByInertia = true;
params.minInertiaRatio = 0.01;
#if CV_MAJOR_VERSION < 3 // If you are using OpenCV 2
// Set up detector with params
SimpleBlobDetector detector(params);
// You can use the detector this way
// detector.detect( im, keypoints);
#else
// Set up detector with params
Ptr<SimpleBlobDetector> detector = SimpleBlobDetector::create(params);
// SimpleBlobDetector::create creates a smart pointer.
// So you need to use arrow ( ->) instead of dot ( . )
// detector->detect( im, keypoints);
#endif
