java中的SPI介绍及使用
目录
- SPI介绍
- mysql驱动的实现
- Driver原理解析
SPI介绍
SPI(Service Provider Interface)即服务提供接口,JDK内置的一种服务提供发现机制,是Java提供的一套用来被第三方实现或者扩展的API,它可以用来启用框架扩展和替换组件。
Java SPI的具体约定如下:
当服务的提供者实现了服务接口后,在classpath下的META-INF/services/目录里同时创建一个以服务接口命名的文件。该文件里就是实现该服务接口的具体实现类。
而当外部程序装配这个模块的时候,就能通过该jar包META-INF/services/里的配置文件找到具体的实现类名,并装载实例化,完成模块的注入。
mysql驱动的实现
我们以jdk提供的Driver为例,java提供了SPI类Driver供数据库驱动厂商如mysql、oracle等实现
public interface Driver {
Connection connect(String url, java.util.Properties info)
throws SQLException;
boolean acceptsURL(String url) throws SQLException;
DriverPropertyInfo[] getPropertyInfo(String url, java.util.Properties info)
throws SQLException;
int getMajorVersion();
int getMinorVersion();
boolean jdbcCompliant();
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException;
}
我们在pom.xml中引入mysql的驱动包
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.19</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
查看其中实现了Driver的实现类
public class Driver extends NonRegisteringDriver implements java.sql.Driver {
//
// Register ourselves with the DriverManager
//
static {
try {
java.sql.DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
} catch (SQLException E) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");
}
}
/**
* Construct a new driver and register it with DriverManager
*
* @throws SQLException
* if a database error occurs.
*/
public Driver() throws SQLException {
// Required for Class.forName().newInstance()
}
}
public class NonRegisteringDriver implements java.sql.Driver {
@Override
public java.sql.Connection connect(String url, Properties info) throws SQLException {
try {
if (!ConnectionUrl.acceptsUrl(url)) {
/*
* According to JDBC spec:
* The driver should return "null" if it realizes it is the wrong kind of driver to connect to the given URL. This will be common, as when the
* JDBC driver manager is asked to connect to a given URL it passes the URL to each loaded driver in turn.
*/
return null;
}
ConnectionUrl conStr = ConnectionUrl.getConnectionUrlInstance(url, info);
switch (conStr.getType()) {
case SINGLE_CONNECTION:
return com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl.getInstance(conStr.getMainHost());
case FAILOVER_CONNECTION:
case FAILOVER_DNS_SRV_CONNECTION:
return FailoverConnectionProxy.createProxyInstance(conStr);
case LOADBALANCE_CONNECTION:
case LOADBALANCE_DNS_SRV_CONNECTION:
return LoadBalancedConnectionProxy.createProxyInstance(conStr);
case REPLICATION_CONNECTION:
case REPLICATION_DNS_SRV_CONNECTION:
return ReplicationConnectionProxy.createProxyInstance(conStr);
default:
return null;
}
} catch (UnsupportedConnectionStringException e) {
// when Connector/J can't handle this connection string the Driver must return null
return null;
} catch (CJException ex) {
throw ExceptionFactory.createException(UnableToConnectException.class,
Messages.getString("NonRegisteringDriver.17", new Object[] { ex.toString() }), ex);
}
}
......
}
Driver通过NonRegisteringDriver间接实现了java的Driver接口,并且classpath下指定了对应的实现类路径
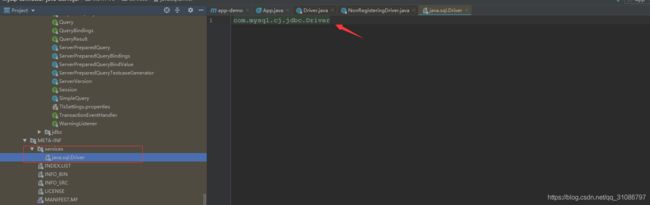
我们在当前项目测试下实现java中Driver的SPI实现类有哪些
public static void main( String[] args )
{
ServiceLoader<Driver> serviceLoader=ServiceLoader.load(Driver.class);
for(Driver dbd:serviceLoader){
System.out.println(dbd.toString());
}
}
输出
D:\java\jdk1.8\jdk1.8.0_161\bin\java.exe "-javaagent:D:\java\idea\IntelliJ IDEA
com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver@34c45dca
Driver原理解析
1、我们先了解一下我们最初连接数据库的操作
- Class.forName(“com.mysql.jdbc.Driver”)注册mysql驱动
- 使用connection = DriverManager.getConnection(“jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test”, “root”, “123456”)连接数据库
其中DriverManager是jdk提供的,Driver被实例化时会注册当前驱动到DriverManager中,然后我们就可以在DriverManager连接数据库,这就是jdk1.6之前我们需要连接数据库必须要做的实例化操作
public class Driver extends NonRegisteringDriver implements java.sql.Driver {
public Driver() throws SQLException {
}
static {
try {
//new一个Driver对象,并将它注册到DriverManage中
DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
} catch (SQLException var1) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");
}
}
}
2、jdk1.6之后提供了SPI接口类ServiceLoader,同时DriverManager也增加了对此的支持
public class DriverManager {
// List of registered JDBC drivers
private final static CopyOnWriteArrayList<DriverInfo> registeredDrivers = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
private static volatile int loginTimeout = 0;
private static volatile java.io.PrintWriter logWriter = null;
private static volatile java.io.PrintStream logStream = null;
// Used in println() to synchronize logWriter
private final static Object logSync = new Object();
/* Prevent the DriverManager class from being instantiated. */
private DriverManager(){}
/**
* Load the initial JDBC drivers by checking the System property
* jdbc.properties and then use the {@code ServiceLoader} mechanism
*/
static {
loadInitialDrivers();
println("JDBC DriverManager initialized");
}
......
}
核心方法loadInitialDrivers,在静态块执行
private static void loadInitialDrivers() {
String drivers;
try {
// 核心代码 1、从环境变量读取数据库驱动类
drivers = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<String>() {
public String run() {
return System.getProperty("jdbc.drivers");
}
});
} catch (Exception ex) {
drivers = null;
}
// If the driver is packaged as a Service Provider, load it.
// Get all the drivers through the classloader
// exposed as a java.sql.Driver.class service.
// ServiceLoader.load() replaces the sun.misc.Providers()
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {
public Void run() {
ServiceLoader<Driver> loadedDrivers = ServiceLoader.load(Driver.class);
Iterator<Driver> driversIterator = loadedDrivers.iterator();
/* Load these drivers, so that they can be instantiated.
* It may be the case that the driver class may not be there
* i.e. there may be a packaged driver with the service class
* as implementation of java.sql.Driver but the actual class
* may be missing. In that case a java.util.ServiceConfigurationError
* will be thrown at runtime by the VM trying to locate
* and load the service.
*
* Adding a try catch block to catch those runtime errors
* if driver not available in classpath but it's
* packaged as service and that service is there in classpath.
*/
try{
while(driversIterator.hasNext()) {
// 核心代码 2、SPI方式读取META-INF/services下面java.sql.Driver文件中的驱动
driversIterator.next();
}
} catch(Throwable t) {
// Do nothing
}
return null;
}
});
println("DriverManager.initialize: jdbc.drivers = " + drivers);
if (drivers == null || drivers.equals("")) {
return;
}
String[] driversList = drivers.split(":");
println("number of Drivers:" + driversList.length);
for (String aDriver : driversList) {
try {
println("DriverManager.Initialize: loading " + aDriver);
// 核心代码 3、实例化环境变量读取的驱动类
Class.forName(aDriver, true,
ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());
} catch (Exception ex) {
println("DriverManager.Initialize: load failed: " + ex);
}
}
}
由上代码可得,jdk1.6之后Driver驱动类注册到DriverManager的方式有以下几种
1、配置环境变量jdbc.drivers指定驱动类路径
2、SPI方式在classpath下的META-INF/services下面创建文件java.sql.Driver中指定驱动类的路径(目前最新版使用,即只需要引入驱动的jar包就可以了)
3、手动调用Class.forName(xxx)
个人理解:
SPI是服务提供者如java提供给第三方用来实现某些特定功能的约定,如Driver接口,提供给不同的数据库厂商实现的默认约定
优点:可插拔式,解耦,应用程序可以根据实际业务情况启用框架扩展或替换框架组件
缺点:需要提前去了解SPI的机制