第一部分 模型简介
隐马尔可夫模型是马尔可夫链的一种,它的状态不能直接观察到,但能通过观测向量序列观察到,每个观测向量都是通过某些概率密度分布表现为各种状态,每一个观测向量是由一个具有相应概率密度分布的状态序列产生。所以,隐马尔可夫模型是一个双重随机过程 ----具有一定状态数的隐马尔可夫链和显示随机函数集。自20 世纪80年代以来,HMM被应用于语音识别,取得重大成功。到了90年代,HMM还被引入计算机文字识别和移动通信核心技术“多用户的检测”。HMM在生物信息科学、故障诊断等领域也开始得到应用。
1.隐马尔可夫模型(HMM)可以用一个五元组来描述,包括2个状态集合和3个概率矩阵:
(1)隐含状态S集合
这些状态之间满足马尔可夫性质,是马尔可夫模型中实际所隐含的状态。这些状态通常无法通过直接观测而得到。(例如S1、S2、S3等等)
(2)可观测符号O集合
在模型中与隐含状态相关联,可通过直接观测而得到。(例如O1、O2、O3等等,可观测状态的数目不一定要和隐含状态的数目一致。)
(3)初始状态概率矩阵 π
表示隐含状态在初始时刻t=1的概率矩阵,(例如t=1 时,P(S1)=p1、P(S2)=P2、P(S3)=p3,则初始状态概率矩阵 π=[ p1 p2 p3 ].
(4)隐含状态转移概率矩阵 A。
描述了HMM模型中各个状态之间的转移概率。其中Aij = P( Sj | Si ),1≤i,,j≤N。表示在 t 时刻、状态为 Si 的条件下,在 t+1 时刻状态是 Sj 的概率。
(5)观测状态转移概率矩阵 B (英文名为Confusion Matrix,直译为混淆矩阵不太易于从字面理解)。
令N代表隐含状态数目,M代表可观测状态数目,则:Bij = P( Oi | Sj ), 1≤i≤M,1≤j≤N.表示在 t 时刻、隐含状态是 Sj 条件下,观察状态为 Oi 的概率。
总结:一般的,可以用λ=(A,B,π)三元组来简洁的表示一个隐马尔可夫模型。隐马尔可夫模型实际上是标准马尔可夫模型的扩展,添加了可观测状态集合和这些状态与隐含状态之间的概率关系。
第二部分 基本问题
1. 评估问题。
给定观测序列 O=O1O2O3…Ot和模型参数λ=(A,B,π),怎样有效计算某一观测序列的概率,进而可对该HMM做出相关评估。例如,已有一些模型参数各异的HMM,给定观测序列O=O1O2O3…Ot,我们想知道哪个HMM模型最可能生成该观测序列。通常我们利用forward 算法分别计算每个HMM产生给定观测序列O的概率,然后从中选出最优的HMM模型。
这类评估的问题的一个经典例子是语音识别。在描述语言识别的隐马尔科夫模型中,每个单词生成一个对应的HMM,每个观测序列由一个单词的语音构成,单词的识别是通过评估进而选出最有可能产生观测序列所代表的读音的HMM而实现的。
2.解码问题
给定观测序列 O=O1O2O3…Ot 和模型参数λ=(A,B,π),怎样寻找某种意义上最优的隐状态序列。在这类问题中,我们感兴趣的是马尔科夫模型中隐含状态,这些状态不能直接观测但却更具有价值,通常利用Viterbi算法来寻找。
这类问题的一个实际例子是中文分词,即把一个句子如何划分其构成才合适。例如,句子“发展中国家”是划分成“发展-中-国家”,还是“发展-中国-家”。这个问题可以用隐马尔科夫模型来解决。句子的分词方法可以看成是隐含状态,而句子则可以看成是给定的可观测状态,从而通过建HMM来寻找出最可能正确的分词方法。
3. 学习问题。
即HMM的模型参数λ=(A,B,π)未知,如何调整这些参数以使观测序列O=O1O2O3…Ot的概率尽可能的大。通常使用Baum- Welch算法以及Reversed Viterbi算法解决。
怎样调整模型参数λ=(A,B,π),使观测序列 O=O1O2O3…Ot的概率最大?
4.针对每个问题,人们提出了相应的算法:
(1)评估问题: 前向算法
(2)解码问题: Viterbi算法
(3)学习问题: Baum-Welch算法(向前向后算法)
第三部分 实验结果
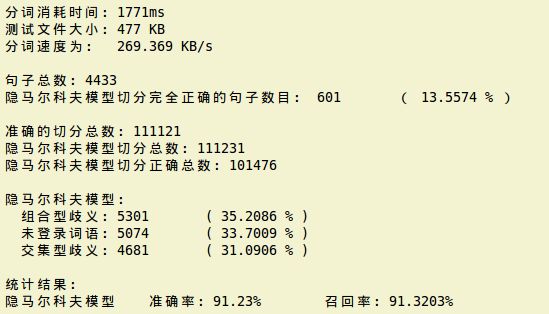
对于二阶马尔科夫过程来说,由于训练语料的规模所限,符号发射矩阵会存在数据稀疏的问题,因此要在程序中进行数据平滑处理。实验选取了两种方式进行数据平滑,其一是Good-Turing(古德-图灵)平滑方法,其二为加一平滑方式。
语料来源:《人民日报》1998年一月语料。
下面是运用Good-Turing(古德-图灵)平滑方法处理数据,最终获得的结果为:
下面是运用加一平滑方法(词频都加一)处理数据,最终获得的结果为:

从上面的结果中看出,加一平滑方法结果更好一些。
第四部分 源代码
(1)文件名:util.h。下面好几个文件都要用到该文件,如将测试文件中的/去掉。
#include
using namespace std;
/*
* 函数功能:将字符串中的所有特定子串置换为新的字符串
* 函数输入:str 需要进行操作的字符串
* old_str 旧的字符串
* new_str 新的字符串
* 函数输出:置换完毕的字符串
*/
string& replace_all(string &str, string old_str, string new_str){
while(1){
string::size_type pos(0);
if((pos = str.find(old_str)) != string::npos){
str.replace(pos, old_str.length(), new_str);
}else{
break;
}
}
return str;
}
(2)文件名:prehmm.cpp。对文件进行预处理工作,函数的功能请参见代码中的注释。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
(3)文件名:db.h。将汉字和编码的映射文件内存,构造为map,供其他程序使用。
#include
#include
#include
(4)文件名:matrix.cpp。用最大似然估计的方法建立HMM的模型参数。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "db.h"
using namespace std;
const int N = 4; //隐藏状态的数目
const int M = 5236; //汉字的个数
const double VALUE = 1.0; //平滑算法增加的值
//定义字典对象
DB db("db.txt");
/*
* 模型训练,将频数转换为频率(加1平滑)
*/
void turingAdd(const int count[], double prob[], int len){
double sum = 0.0;
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i){
sum += count[i];
}
if(sum == 0.0){
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i){
prob[i] = 0.0;
}
}else{
sum = sum + VALUE * len;
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i){
prob[i] = -log((count[i] + VALUE) / sum);//取对数
}
}
}
/*
* 模型训练,将发射频数转换为频率(古德-图灵平滑)
*/
void turingGood(const int count[], double prob[], int len){
map > freq_map; //key为词频,value为该词频对应的汉字列表
map >::iterator iter; //迭代器
int sum = 0; //词频总和
//初始化freq_map
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
int freq = count[i]; //词频
sum += freq;
iter = freq_map.find(freq);
if(iter != freq_map.end()){
//该词频已经存在,把当前词加入相应的list
freq_map[freq].push_back(i);
}else{
//该词频不存在,建立对应的汉字list
list lst;
lst.push_back(i);
freq_map[freq] = lst;
}
}
//若sum=0,则结果初始化为0.0即可
if(sum == 0){
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
prob[i] = 0.0;
}
return;
}
//数据平滑处理
iter = freq_map.begin();
while(iter != freq_map.end()){
double pr; //频率
int freq = iter -> first;
int freqsize = iter -> second.size();
if(++iter != freq_map.end()){
int freq_2 = iter -> first;
if(freq_2 = freq + 1){
int freqsize_2 = iter -> second.size();
pr = ((1.0 + freq) * freqsize_2) / (sum * freqsize);
}else{
pr = 1.0 * freq / sum;
}
}else{
pr = 1.0 * freq / sum;
}
//计算结果
list lst = (--iter) -> second;
list::iterator iter_in = lst.begin();
while(iter_in != lst.end()){
int index = *iter_in;
prob[index] = pr;
++iter_in;
}
//准备下次迭代
++iter;
}
//概率归一化
double total = 0.0;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
total += prob[i];
}
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
prob[i] = -log((double)prob[i] / total);//取对数
}
}
/*
* 主函数,生成HMM模型的参数
* 状态转移概率矩阵、初始状态概率矩阵、符号发射概率矩阵
*/
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
if(argc < 2){
cout << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " bmes_file !" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
ifstream fin(argv[1]);
if(!fin){
cerr << "Open input file " << argv[1] << "filed !" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
int Pi[N] = {0}; //初始状态出现的次数
int A[N][N] = {0}; //状态转移的次数
int B[N][M] = {0}; //符号发射次数
//抽取文件中的状态和观察值
string line = ""; //存放每一行的内容
int line_num = 0; //句子编号
while(getline(fin, line)){
line_num++;
char state; //状态
string cchar = ""; //一个汉字
int i, j, k;
string::size_type pos = 0; //当前处理位置
if((pos = line.find("/", pos + 1)) != string::npos){
//抽取句子的第一个状态
state = line.at(pos + 1);
i = db.getStateIndex(state);
Pi[i]++;
//抽取句子的第一个观察值
cchar = line.substr(pos - 2, 2);
k = db.getObservIndex(cchar);
B[i][k]++;
while((pos = line.find("/", pos + 1)) != string::npos){
//抽取句子的其他状态
state = line.at(pos + 1);
j = db.getStateIndex(state);
//Pi[j]++;
A[i][j]++;
//抽取句子的其他观察值
cchar = line.substr(pos - 2, 2);
k = db.getObservIndex(cchar);
B[j][k]++;
//准备下次迭代
i = j;
}
}
}
fin.close();
//打开输出流
ofstream fout_1("Pi.mat"); //初始概率矩阵
ofstream fout_2("A.mat"); //状态转移矩阵
ofstream fout_3("B.mat"); //发射概率矩阵
if(!(fout_1 && fout_2 && fout_3)){
cerr << "Create Matrix file failed !" << endl;
return 1;
}
fout_1 << setprecision(8);
fout_2 << setprecision(8);
fout_3 << setprecision(8);
//初始状态矩阵写入文件
double arr_pi[N] = {0.0};
//turingGood(Pi, arr_pi, N);
turingAdd(Pi, arr_pi, N);
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
fout_1 << arr_pi[i] << "\t";
}
fout_1 << endl;
//状态转移矩阵写入文件
double arr_a[N] = {0.0};
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
//turingGood(A[i], arr_a, N);
turingAdd(A[i], arr_a, N);
for(int j = 0; j < N; j++){
fout_2 << arr_a[j] << "\t";
}
fout_2 << endl;
}
//发射概率矩阵写入文件
double arr_b[M] = {0.0};
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
//turingGood(B[i], arr_b, M);
turingAdd(B[i], arr_b, M);
for(int j = 0; j < M; j++){
fout_3 << arr_b[j] << "\t";
}
fout_3 << endl;
}
fout_1.close();
fout_2.close();
fout_3.close();
return 0;
}
(5)文件名:hmm.h。将存储在文件中的HMM的模型参数读取到内存中,构造为一个HMM对象,供其他程序使用。
#include
#include
#include
#include
const int N = 4;
const int M = 5236;
//定义HMM模型
class HMM{
public:
int n; //状态数目
int m; //可能的观察符号数目
double A[N][N]; //状态转移概率矩阵
double B[N][M]; //符号发射概率矩阵
double Pi[N]; //初始状态概率
HMM();
HMM(string f1, string f2, string f3);
};
//无参构造函数
HMM::HMM(){
}
//有参构造函数
HMM::HMM(string f1, string f2, string f3){
ifstream fin_1(f1.c_str());
ifstream fin_2(f2.c_str());
ifstream fin_3(f3.c_str());
if(!(fin_1 && fin_2 && fin_3)){
exit(-1);
}
string line = "";
string word = "";
//读取Pi
getline(fin_1, line);
istringstream strstm_1(line);
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
strstm_1 >> word;
Pi[i] = atof(word.c_str());
}
//读取A
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
getline(fin_2, line);
istringstream strstm_2(line);
for(int j = 0; j < N; j++){
strstm_2 >> word;
A[i][j] = atof(word.c_str());
}
}
//读取B
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
getline(fin_3, line);
istringstream strstm_3(line);
for(int j = 0; j < M; j++){
strstm_3 >> word;
B[i][j] = atof(word.c_str());
}
}
fin_1.close();
fin_2.close();
fin_3.close();
}
(6)文件名:viterbi.cpp。维特比算法,用于分词。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "hmm.h"
#include "db.h"
using namespace std;
HMM hmm("Pi.mat", "A.mat", "B.mat"); //初始化HMM模型
DB db("db.txt"); //初始化字典
/*
* Viterbi算法进行分词
*/
string viterbi(string str_in){
string str_out = "";
if(str_in.size() == 0){
return str_out;
}
//分配矩阵空间
int row = str_in.size() / 2; //输入句子中的汉字个数
double **delta = new double *[row];
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++){
delta[i] = new double[N]();
}
int **path = new int *[row];
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++){
path[i] = new int[N]();
}
//中间变量
string cchar = ""; //存放汉字
int max_path = -1;
double val = 0.0;
double max_val = 0.0;
//初始化矩阵,给delta和path矩阵的第一行赋初值
cchar = str_in.substr(0, 2);
int cchar_num = db.getObservIndex(cchar);
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
delta[0][i] = hmm.Pi[i] + hmm.B[i][cchar_num]; //对数
path[0][i] = -1;
}
//给delta和path的后续行赋值(对数)
for(int t = 1; t < row; t++){
cchar = str_in.substr(2*t, 2);
cchar_num = db.getObservIndex(cchar);
for(int j = 0; j < N; j++){
max_val = 100000.0;
//max_path = -1;
max_path = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
val = delta[t-1][i] + hmm.A[i][j];
if(val < max_val){
max_val = val;
max_path = i;
}
}
delta[t][j] = max_val + hmm.B[j][cchar_num];
path[t][j] = max_path;
}
}
//找delta矩阵最后一行的最大值
max_val = 100000.0;
//max_path = -1;
max_path = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
if(delta[row-1][i] < max_val){
max_val = delta[row-1][i];
max_path = i;
}
}
//从max_path出发,回溯得到最可能的路径
stack path_st;
path_st.push(max_path);
for(int i = row - 1; i > 0; i--){
max_path = path[i][max_path];
path_st.push(max_path);
}
//释放二维数组
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++){
delete []delta[i];
delete []path[i];
}
delete []delta;
delete []path;
//根据标记好的状态序列分词
int pos = 0;
int index = -1;
while(!path_st.empty()){
index = path_st.top();
path_st.pop();
str_out.insert(str_out.size(), str_in, pos, 2);
if(index == 2 || index == 3){
//状态为E或S
str_out.append("/");
}
pos += 2;
}
}
(7)文件名:main.cpp。主函数,调用维特比算法进行分词工作,并对分词结果进行比对,统计后输出结果。
#include
#include
#include
#include

