zore copy 零拷贝
1.使用场景
如果应用程序不进行数据处理,只是将数据从本地文件发送到socket可以使用零拷贝,提高效率。
2.使用条件
java ,unix,linux
3. 使用方法
使用transferTo代替read send函数
4.对比
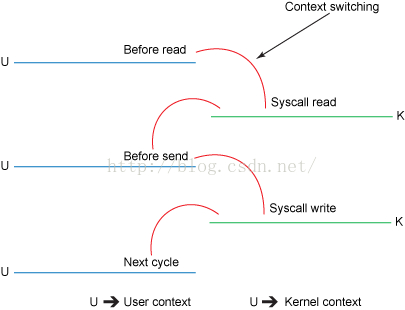
4.1 传统方法
File.read(fileDesc, buf, len);
Socket.send(socket, buf, len);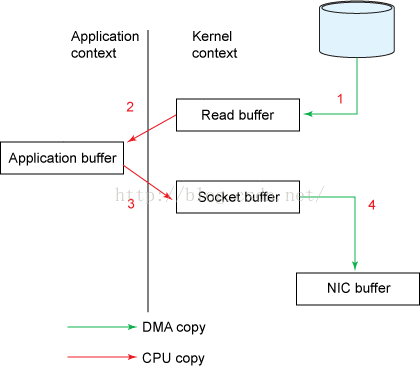
如上图所示,需要4次内存拷贝,4次上下文切换(context switch).
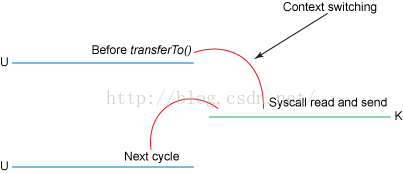
4.2 零拷贝方法
使用函数:
public void transferTo(long position, long count, WritableByteChannel target);其系统调用:
#include
ssize_t sendfile(int out_fd, int in_fd, off_t *offset, size_t count); 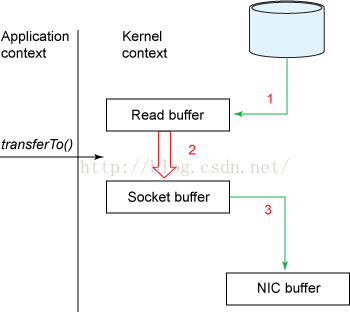
直接在内核中有read buffer拷贝到socket buffer,不经过application buffer中转。拷贝步骤由4个减为3个。
如果底层网卡支持gather operations(linux 2.4及以上修改了套接字缓冲区描述符以适应此要求)。这种模式下没有数据被复制到套接字缓冲区中。 相反,只有具有关于数据的位置和长度的信息的描述符被附加到套接字缓冲器。 DMA引擎将数据直接从内核缓冲区传递到协议引擎,从而消除剩余的最终CPU拷贝。如下图:
具体代码如下:
//TraditionalClient.java
package sendfile;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
public class TraditionalClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int port = 2000;
String server = "localhost";
Socket socket = null;
String lineToBeSent;
DataOutputStream output = null;
FileInputStream inputStream = null;
int ERROR = 1;
// connect to server
try {
socket = new Socket(server, port);
System.out.println("Connected with server " +
socket.getInetAddress() +
":" + socket.getPort());
}
catch (UnknownHostException e) {
System.out.println(e);
System.exit(ERROR);
}
catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
System.exit(ERROR);
}
try {
String fname = "sendfile/NetworkInterfaces.c";
inputStream = new FileInputStream(fname);
output = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
byte[] b = new byte[4096];
long read = 0, total = 0;
while((read = inputStream.read(b))>=0) {
total = total + read;
output.write(b);
}
System.out.println("bytes send--"+total+" and totaltime--"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
try {
output.close();
socket.close();
inputStream.close();
}
catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
//TraditionalServer.java
package sendfile;
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class TraditionalServer {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int port = 2000;
ServerSocket server_socket;
DataInputStream input;
try {
server_socket = new ServerSocket(port);
System.out.println("Server waiting for client on port " +
server_socket.getLocalPort());
// server infinite loop
while(true) {
Socket socket = server_socket.accept();
System.out.println("New connection accepted " +
socket.getInetAddress() +
":" + socket.getPort());
input = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
// print received data
try {
byte[] byteArray = new byte[4096];
while(true) {
int nread = input.read(byteArray , 0, 4096);
if (0==nread)
break;
}
}
catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
// connection closed by client
try {
socket.close();
System.out.println("Connection closed by client");
}
catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
//TransferToClien.java
package sendfile;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.SocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class TransferToClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
TransferToClient sfc = new TransferToClient();
sfc.testSendfile();
}
public void testSendfile() throws IOException {
String host = "localhost";
int port = 9026;
SocketAddress sad = new InetSocketAddress(host, port);
SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.connect(sad);
sc.configureBlocking(true);
String fname = "sendfile/NetworkInterfaces.c";
long fsize = 183678375L, sendzise = 4094;
// FileProposerExample.stuffFile(fname, fsize);
FileChannel fc = new FileInputStream(fname).getChannel();
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
long nsent = 0, curnset = 0;
curnset = fc.transferTo(0, fsize, sc);
System.out.println("total bytes transferred--"+curnset+" and time taken in MS--"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
//fc.close();
}
}
//TansferToServer.java
package sendfile;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class TransferToServer {
ServerSocketChannel listener = null;
protected void mySetup()
{
InetSocketAddress listenAddr = new InetSocketAddress(9026);
try {
listener = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ServerSocket ss = listener.socket();
ss.setReuseAddress(true);
ss.bind(listenAddr);
System.out.println("Listening on port : "+ listenAddr.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Failed to bind, is port : "+ listenAddr.toString()
+ " already in use ? Error Msg : "+e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
TransferToServer dns = new TransferToServer();
dns.mySetup();
dns.readData();
}
private void readData() {
ByteBuffer dst = ByteBuffer.allocate(4096);
try {
while(true) {
SocketChannel conn = listener.accept();
System.out.println("Accepted : "+conn);
conn.configureBlocking(true);
int nread = 0;
while (nread != -1) {
try {
nread = conn.read(dst);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
nread = -1;
}
dst.rewind();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}