代码地址:https://pan.baidu.com/s/18dyR6GDcsbsF5CDd3tJ85g 密码:q7je
SSM:spring + spring mvc + mybatis
可以先看看我之前写的spring mvc怎么搭以及怎么使用Mybatis-Generator自动生成Dao、Model层相关代码,再看这篇,传送门:
IntelliJ IDEA搭建最简单的Spring MVC项目
IntelliJ IDEA下Spring MVC数据库配置与增删改查开发
使用Mybatis-Generator自动生成Dao、Model层相关代码
与之相关的就不再写了。
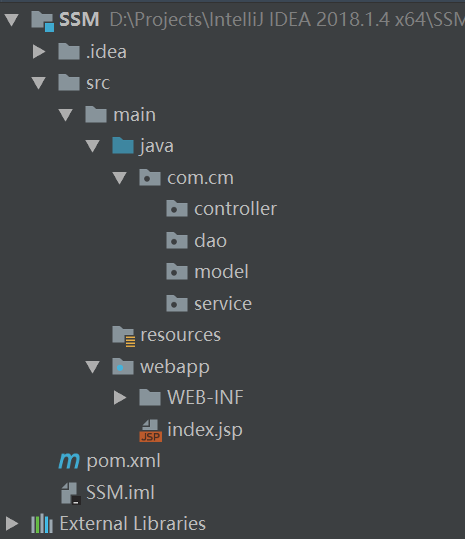
1 新建工程,并完善目录结构与前面两篇文章一样
目录结构多了个service,用以放业务逻辑。
2 添加依赖包
pom.xml中依赖包加入:
UTF-8
1.7
1.7
5.0.5.RELEASE
junit
junit
4.11
test
mysql
mysql-connector-java
5.1.37
runtime
c3p0
c3p0
0.9.1.2
org.mybatis
mybatis
3.3.0
org.mybatis
mybatis-spring
1.2.3
taglibs
standard
1.1.2
jstl
jstl
1.2
com.google.code.gson
gson
2.8.2
javax.servlet
javax.servlet-api
3.1.0
org.springframework
spring-core
4.1.7.RELEASE
org.springframework
spring-beans
4.1.7.RELEASE
org.springframework
spring-context
4.1.7.RELEASE
org.springframework
spring-jdbc
4.1.7.RELEASE
org.springframework
spring-tx
4.1.7.RELEASE
org.springframework
spring-web
4.1.7.RELEASE
org.springframework
spring-webmvc
4.1.7.RELEASE
org.springframework
spring-test
4.1.7.RELEASE
3 添加各种配置文件
数据源
在resources下面新建jdbc.properties文件。
这个文件用以配置jdbc数据源以及数据连接池的各种参数,单独放到文件便于修改。
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/cmtable?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
#最大连接数
maxPoolSize=20
#最小连接数
minPoolSize=10
#连接超时时间
checkoutTimeout=60000
#失败重连次数
acquireRetryAttempts=3
mybatis-config.xml
在resources下面新建mybatis-config.xml,作为MyBatis的全局配置文件。
这个作为MyBatis的全局配置文件,还有很多参数可以设置,这里不细讲。
扫描 sql 配置⽂件:mapper 需要的 xml ⽂件
在resources文件夹下面新建mapper目录,用以放置那些对应的xml文件。
applicationContext.xml Spring全局配置文件
在resources下面新建applicationContext.xml
mvc-dispatcher.xml
在resources下面新建mvc-dispatcher.xml,与前面文章类似。
web.xml
与前面文章一模一样。
Archetype Created Web Application
contextConfigLocation
classpath:applicationContext.xml
encodingFilter
org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter
encoding
UTF-8
encodingFilter
/*
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
SpringMVC
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
contextConfigLocation
classpath:mvc-dispatcher.xml
1
SpringMVC
/
好了,所有的配置文件都弄完了!
4 开发
建表。
使用之前文章里面说的方法自动生成Model和Dao以及对应的xml代码。
看看生成的代码,UserModel.java与前面类似,跳过。
其他的只是能参考,在这个基础上改,毕竟生成的有的接口不符合我们的想法。
package com.cm.dao;
import com.cm.model.UserModel;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserDao {
List getAllUsers();
UserModel getUser(String id);
boolean addUser(UserModel userModel);
boolean updateUser(String id, String name);
boolean deleteUser(String id);
}
MyBatis有个好处就是我们不用自己写实现,只需要配置对应的xml为其提供sql语句就行,在resources下的mapper文件夹下面新建UserDao.xml。模仿我们生成的xml进行修改。
insert ignore into user (name, age) values (#{id}, #{name})
update user set name=#{name} where id=#{id}
delete from user where id=#{id}
其实就是一堆sql语句,namespace表示对应的类。id对应方法名,#{name}表示传入的参数。parameterType为入参类型,可以省略。
service层
在service中新建UserService,放置业务逻辑代码。可以这么理解,Dao颗粒度比较小,基本操作,但是service颗粒度比较大,放业务逻辑操作。
package com.cm.service;
import com.cm.dao.UserDao;
import com.cm.model.UserModel;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.List;
@Service
@Transactional
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
public List getAllUsers(){
return userDao.getAllUsers();
}
public UserModel getUser(String id) {
return userDao.getUser(id);
}
boolean addUser(UserModel userModel) {
return userDao.addUser(userModel);
}
boolean updateUser(String id, String name) {
return userDao.updateUser(id, name);
}
boolean deleteUser(String id) {
return userDao.deleteUser(id);
}
}
学习阶段就不写太大的业务逻辑了。
说几个:
(1) @Service 标记为service,这样就能被Spring扫描到。
(2)@Transactional,我们前面配置文件开启了事务处理。业务逻辑需要进行事务处理。
标注在类前:标示类中所有方法都进行事务处理
标注在接口、实现类的方法前:标示方法进行事务处理
(3)@Autowired这个前面文章讲过了,自动注入。
Controller 层
在controller下面新建UserController.java。内容就不全写了,以两个为例。其他类似。
package com.cm.controller;
import com.cm.model.UserModel;
import com.cm.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import java.util.List;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
public UserController(UserService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
@RequestMapping(value="getAllUsers",method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public List getAllUsers() {
List userModels = userService.getAllUsers();
return userModels;
}
@RequestMapping(value="getUser",method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public UserModel getUser(String id) {
UserModel userModel = userService.getUser(id);
return userModel;
}
}
5 测试
配置Tomcat,方法前面说过了。表中插入一些数据。用浏览器或者postman访问。
http://localhost:8080/user/getAllUsers 结果如下:
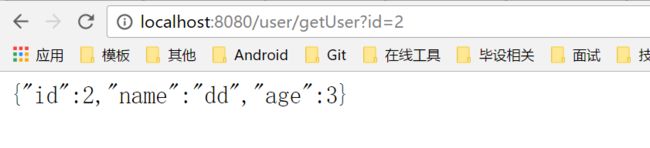
http://localhost:8080/user/getUser?id=2 结果如下:
6 打包
点击左下角,在弹出的地方点击右边的Maven Projects,然后展开Lifecycle,双击package。然后就能在webapp下面看见war包,把war包放到tomcat下面的webapp里面,启动tomcat就能访问。注意这样访问要加上artifactid,示例:http://localhost:8080/SSM/user/getAllUsers
【SSM框架从零开始】系列文章链接:
IntelliJ IDEA搭建最简单的Spring MVC项目
IntelliJ IDEA下Spring MVC数据库配置与增删改查开发
使用Mybatis-Generator自动生成Dao、Model层相关代码
IntelliJ IDEA搭建SSM框架