属性动画的基本使用
Android中动画大概可以分为补间动画,帧动画,属性动画三种
(一)补间动画Animation分以下4种:
1.TranslateAnimation 平移动画 x,y方向上的平移 对应xml标签
2.ScaleAnimation 缩放动画 x,y方向上的缩放 对应xml标签
3.RotateAnimation 旋转动画 对应xml标签
4.AlphaAnimation 透明度动画 对应xml标签
创建的xml动画文件放在res/anim文件夹下
(二)帧动画是通过顺序播放一组图片实现的
系统使用AnimationDrawable类来定义帧动画也可以通过xml来实现,对应使用标签中包含标签来实现
(三)属性动画是api11新加入的,api11以下的需要使用NineOldAndroid.jar来做兼容,属性动画的实现原理是通过修改对象的属性值来实现的,可作用于任何对象。补间动画中的四种动画效果,也可以通过属性动画来实现。
下面主要介绍一下属性动画的使用,属性动画中主要用到以下几个类:
1)ObjectAnimator 该类继承于ValueAnimator 对应xml标签
2)ValueAnimator 值动画 对应xml标签
3)AnimatorSet 属性动画集合 对应xml标签
4)PropertyValueHolder
5)TypeEvaluator 估值器 控制属性值的变化
6)Interpolator 插值器 控制属性值变化的速度,加速减速匀速等变化
当然属性动画也可以通过xml来定义,xml文件要放在res/animator的目录下,相关定义标签。通常情况下,我们都是通过代码方式来实现属性动画的。
一.ValueAnimator
通过以下方法创建
ValueAnimator.ofFloat(“对象属性”,“属性值1…属性值n”);
ValueAnimator.ofArgb(“对象属性”,“属性值1…属性值n”);
ValueAnimator.ofInt(“对象属性”,“属性值1…属性值n”);
…
常用方法有以下几种
setDuration(500);//设置动画时长 时间单位为ms
setRepeatCount(ValueAnimator.INFINITE);//设置循环次数 INFINITE表示循环执行动画
setRepeatMode(ValueAnimator.RESTART);//设置重复模式 RESTART重新开始/REVERSE反转
setStartDelay(200);//延迟执行动画 时间单位为ms
setEvaluator(new FloatEvaluator());//设置动画的估值器
setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator());//设置动画的插值器
addUpdateListener(AnimatorUpdateListener listener);//添加监听值改变的监听器
addListener(AnimatorListener listener)//添加动画监听 当前动画执行状态 onAnimationStart / onAnimationEnd / onAnimationCancel
getAnimatedFraction()//在监听中可以通过该方法来获取当前动画执行进度
getAnimatedValue()//在监听中可以通过该方法来获取当前动画执行的值
cancel()//取消当前动画
isRunning()
isStarted()
start()
二.ObjectAnimator
ObjectAnimator继承自ValueAnimator
ObjectAnimator对象可以使用以下方法来创建
ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(“作用对象类”,“对象属性”,“属性值1…属性值n”);
ObjectAnimator.ofArgb(“作用对象类”,“对象属性”,“属性值1…属性值n”);
ObjectAnimator.ofInt(“作用对象类”,“对象属性”,“属性值1…属性值n”);
…
先看一下View中自带的实现属性动画的方法
//将ImageView水平向左平移500
iv.setTranslationX(500);
//将ImageView垂直向下平移500
iv.setTranslationY(500);
//将ImageView水平方向上缩放为原来的1.5倍
iv.setScaleX(1.5f);
//将ImageView垂直方向上缩放为原来的1.5倍
iv.setScaleY(1.5f);
//将ImageView水平方向上旋转30度
iv.setRotationX(30);
//将ImageView垂直方向上旋转30度
iv.setRotationY(30);
//将ImageView的透明度设置为100
iv.setAlpha(100);
//改变ImageView的背景色
iv.setBackgroundColor(Color.RED);
以上代码都是View的一些属性方法
这里我们也可以通过ObjectAnimator来对ImageView的属性进行改变,可实现相关动画效果
//实现水平方向上平移 向左500 设置一个值的时候,默认初始值为0
ObjectAnimator translateXAnim=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(iv,//作用的对象
"translationX", //改变对象相关的属性
500f);//这里是一个泛型数组,可以有多个值 表示改变对象属性的值
translateXAnim.setDuration(500);//设置动画时长
translateXAnim.start();
//实现垂直方向上的平移 向下500
ObjectAnimator translateYAnim=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(iv,//作用的对象
"translationY", //改变对象相关的属性
500f);//这里是一个泛型数组,可以有多个值 表示改变对象属性的值
translateYAnim.setDuration(500);
translateYAnim.start();
//实现水平方向上的缩放 为原来的1.5倍
ObjectAnimator scaleXAnim=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(iv,//作用的对象
"scaleX", //改变对象相关的属性
1.5f);//这里是一个泛型数组,可以有多个值 表示改变对象属性的值
scaleXAnim.setDuration(500);
scaleXAnim.start();
//实现垂直方向上的缩放 为原来的1.5倍
ObjectAnimator scaleYAnim=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(iv,//作用的对象
"scaleY", //改变对象相关的属性
1.5f);//这里是一个泛型数组,可以有多个值 表示改变对象属性的值
scaleYAnim.setDuration(500);
scaleYAnim.start();
//实现水平方向上的旋转
ObjectAnimator rotateXAnim=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(iv,//作用的对象
"rotationX", //改变对象相关的属性
30f);//这里是一个泛型数组,可以有多个值 表示改变对象属性的值
rotateXAnim.setDuration(500);
rotateXAnim.start();
//实现垂直方向上的旋转
ObjectAnimator rotateYAnim=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(iv,//作用的对象
"rotationY", //改变对象相关的属性
30f);//这里是一个泛型数组,可以有多个值 表示改变对象属性的值
rotateYAnim.setDuration(500);
rotateYAnim.start();
为什么通过以上方法就可以实现对ImageView的动画效果呢,主要是通过改变View的属性值来实现,这个就涉及到属性动画的实现原理了,后面我们会通过对属性动画的源码分析来它的具体实现
多个动画同时执行可通过PropertyValuesHolder来实现,也可以通过下面的AnimatorSet来实现
PropertyValuesHolder holder1 = PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat("alpha", 1f,0.5f);
PropertyValuesHolder holder2 = PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat("scaleX", 1f,0.5f);
PropertyValuesHolder holder3 = PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat("scaleY", 1f,0.5f);
ObjectAnimator animator = ObjectAnimator.ofPropertyValuesHolder(iv, holder1,holder2,holder3);
animator.setDuration(200);
animator.start();
三.AnimatorSet
AnimatorSet表示一个动画集合控制多个动画一起播放,主要通过以下方法来实现:
play(Animator anim)
playSequentially(Animator… items) //表示按照顺序播放动画
playSequentially(List items)
playTogether(Animator… items) //一起播放所有动画
playTogether(Collection items)
play()方法可以和AnimatorSet.Builder中的方法一起使用来控制动画播放顺序
with(Animator anim)
before(Animator anim)
after(Animator anim)
after(long delay)
下面我们来实现多个动画同时执行
ObjectAnimator animator1 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(iv, "translationX", 0f,100f);
animator1.setRepeatCount(3);
ObjectAnimator animator2 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(iv, "alpha", 0f,1f);
animator2.setStartDelay(startDelay)//设置延迟执行
ObjectAnimator animator3 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(iv, "scaleX", 0f,2f);
AnimatorSet animatorSet = new AnimatorSet();
animatorSet.setDuration(500);
animatorSet.play(animator3).with(animator2).after(animator1);//animator1在前面
animatorSet.play(animator3).with(animator2).before(animator1);//animator1在后面
animatorSet.playTogether(animator1,animator2,animator3);
animatorSet.playSequentially(animator1,animator2,animator3);
animatorSet.start();
四.TypeEvaluator
Android系统给我们提供了一些常用的估值器,TypeEvaluator有以下子类可供使用
IntEvaluator
FloatEvaluator
ArgbEvaluator
IntArrayEvaluator
FloatArrayEvaluator
RectEvaluator
PointFEvaluator
我们也可以根据自己的需求来自定义估值器,TypeEvaluator的源码如下,TypeEvaluator只是一个接口,定义了一个计算值的方法evaluate
ublic interface TypeEvaluator<T> {
/**
* This function returns the result of linearly interpolating the start and end values, with
* fraction representing the proportion between the start and end values. The
* calculation is a simple parametric calculation: result = x0 + t * (x1 - x0),
* where x0 is startValue, x1 is endValue,
* and t is fraction.
*
* @param fraction The fraction from the starting to the ending values 这个是一个进度值百分比
* @param startValue The start value.开始值
* @param endValue The end value.结束值
* @return A linear interpolation between the start and end values, given the
* fraction parameter.
*/
public T evaluate(float fraction, T startValue, T endValue);
}
自定义估值器需要实现TypeEvaluator接口,并实现evaluate方法,主要代码实现逻辑是在evaluate方法中根据当前进度值对要返回的值进行动态改变,例如系统提供的FloatEvaluator类
public class FloatEvaluator implements TypeEvaluator<Number> {
public Float evaluate(float fraction, Number startValue, Number endValue) {
//对传入的值根据进度百分比进行计算后返回
float startFloat = startValue.floatValue();
return startFloat + fraction * (endValue.floatValue() - startFloat);
}
}
五.Interpolator
Android系统给我们提供了一些常用的插值器,供我们日常使用
Interpolator继承自TimeInterpolator,BaseInterpolator和LookupTableInterpolator都继承自Interpolator
BaseInterpolator主要有以下子类
AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator
AnticipateInterpolator
PathInterpolator
BounceInterpolator
OvershootInterpolator
AnticipateOvershootInterpolator
LinearInterpolator
AccelerateInterpolator
DecelerateInterpolator
CycleInterpolator
LookupTableInterpolator主要有以下子类
FastOutSlowInInterpolator
FastOutLinearInInterpolator
LinearOutSlowInInterpolator
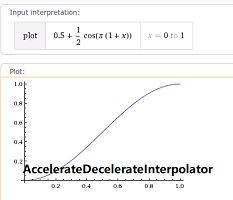

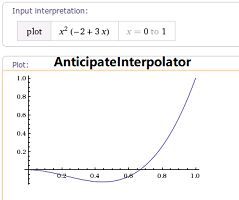
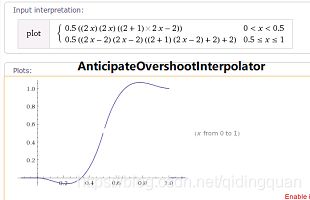
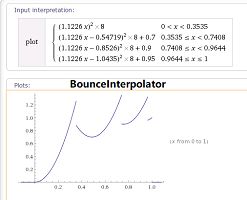
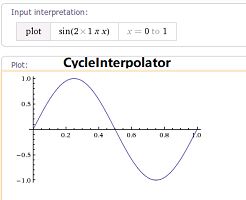
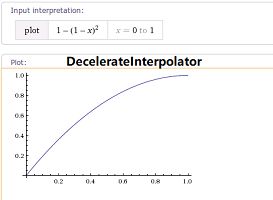
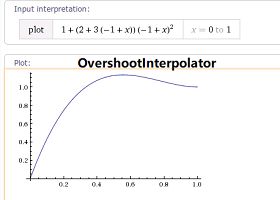
我们也可以自定义插值器对当前动画的进行速度进行动态改变,这里需要实现TimeInterpolator 接口来实现自定义类
TimeInterpolator的源码如下
public interface TimeInterpolator {
/**
* Maps a value representing the elapsed fraction of an animation to a value that represents
* the interpolated fraction. This interpolated value is then multiplied by the change in
* value of an animation to derive the animated value at the current elapsed animation time.
*
* @param input A value between 0 and 1.0 indicating our current point
* in the animation where 0 represents the start and 1.0 represents
* the end
* @return The interpolation value. This value can be more than 1.0 for
* interpolators which overshoot their targets, or less than 0 for
* interpolators that undershoot their targets.
*/
float getInterpolation(float input);
}
AccelerateInterpolator的源码实现,代码的主要实现逻辑在getInterpolation方法中
BaseInterpolator extends Interpolator
Interpolator extends TimeInterpolator
public class AccelerateInterpolator extends BaseInterpolator implements NativeInterpolatorFactory {
private final float mFactor;
private final double mDoubleFactor;
public AccelerateInterpolator() {
mFactor = 1.0f;
mDoubleFactor = 2.0;
}
/**
* Constructor
*
* @param factor Degree to which the animation should be eased. Seting
* factor to 1.0f produces a y=x^2 parabola. Increasing factor above
* 1.0f exaggerates the ease-in effect (i.e., it starts even
* slower and ends evens faster)
*/
public AccelerateInterpolator(float factor) {
mFactor = factor;
mDoubleFactor = 2 * mFactor;
}
public AccelerateInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context.getResources(), context.getTheme(), attrs);
}
/** @hide */
public AccelerateInterpolator(Resources res, Theme theme, AttributeSet attrs) {
TypedArray a;
if (theme != null) {
a = theme.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.AccelerateInterpolator, 0, 0);
} else {
a = res.obtainAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.AccelerateInterpolator);
}
mFactor = a.getFloat(R.styleable.AccelerateInterpolator_factor, 1.0f);
mDoubleFactor = 2 * mFactor;
setChangingConfiguration(a.getChangingConfigurations());
a.recycle();
}
//主要实现方法
public float getInterpolation(float input) {
if (mFactor == 1.0f) {
return input * input;
} else {
return (float)Math.pow(input, mDoubleFactor);
}
}
/** @hide */
@Override
public long createNativeInterpolator() {
return NativeInterpolatorFactoryHelper.createAccelerateInterpolator(mFactor);
}
}
六.实现今日头条点赞效果

实现原理
1.在点击按钮的时候,不断的向布局中添加不同的ImageView
2.自定义TypeEvaluator重写evaluate方法,对坐标值进行二阶贝塞尔曲线计算,并返回计算后的坐标值
3.然后使用ValueAnimator添加AnimatorUpdateListener监听来获取当前点的坐标值
4.在动画改变的过程中对ImageView的x,y值进行处理,同时改变它的透明度和大小缩放
实现代码如下:
public class AnimatorActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener {
private static final String TAG = "AnimatorActivity";
//表情资源
private static final int[] faces = {
R.mipmap.face1, R.mipmap.face2, R.mipmap.face3, R.mipmap.face4,
R.mipmap.face5, R.mipmap.face6, R.mipmap.face7, R.mipmap.face8,
R.mipmap.face9, R.mipmap.face10, R.mipmap.face11, R.mipmap.face12,
R.mipmap.face13, R.mipmap.face14, R.mipmap.face15, R.mipmap.face16,
R.mipmap.face17, R.mipmap.face18, R.mipmap.face19, R.mipmap.face20,
};
private Stack<ImageView> cacheViews;//用于缓存ImageView 重复使用
private Random random;
private int screenWidth;
private int screenHeight;
private List<PointF> points;
private PointF pointF;
private PointF leftTopP;
private PointF midTopP;
private PointF rightTopP;
private PointF leftBottomP;
private PointF midBottomP;
private PointF rightBottomP;
private RelativeLayout content;
private CheckBox checkbox;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_animator);
checkbox = findViewById(R.id.checkbox);
checkbox.setOnCheckedChangeListener(this);
content = findViewById(R.id.content);
cacheViews = new Stack<>();
screenWidth = getScreenSize()[0];
screenHeight = getScreenSize()[1];
points = new ArrayList<>();
random = new Random();
//初始化点赞起始点得坐标值 为手机屏幕中央
pointF = new PointF(screenWidth / 2, screenHeight / 2);
//初始化点赞表情移动轨迹结束点6个 分别为左上,中上,右上,左底,中底,右底
leftTopP = new PointF(0, 0);
midTopP = new PointF(screenWidth / 2, 0);
rightTopP = new PointF(screenWidth, 0);
leftBottomP = new PointF(0, screenHeight / 2);
midBottomP = new PointF(screenWidth / 2, screenHeight);
rightBottomP = new PointF(screenWidth, screenHeight);
points.add(leftTopP);
points.add(midTopP);
points.add(rightTopP);
points.add(leftBottomP);
points.add(midBottomP);
points.add(rightBottomP);
}
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(CompoundButton buttonView, boolean isChecked) {
ImageView imageView = addFaceView();
startAnim(imageView);
}
/**
* 每点击一次生成一个View 执行平移和缩放和淡出动画
*/
private ImageView addFaceView() {
//生成一个随机数来获取图片资源
int index = random.nextInt(faces.length - 1);
Log.e(TAG, "addFaceView: index=" + index);
ImageView imageView;
//先从缓存中取控件
if (!cacheViews.empty()) {
imageView = cacheViews.pop();
} else {
imageView = new ImageView(this);
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams params = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
params.addRule(RelativeLayout.CENTER_IN_PARENT);
imageView.setLayoutParams(params);
}
imageView.setImageResource(faces[index]);
//当前结束点只有6 个,而图片有20个 这里需要转换一下index避免数组越界
imageView.setTag(index >= points.size() ? index / (faces.length / points.size() + 1) : index);
content.addView(imageView);
return imageView;
}
private void startAnim(final ImageView view) {
int index = (int) view.getTag();
//这里动态生成二阶贝塞尔曲线路径控制点的坐标
PointF controlP = new PointF();
if (index < index / 2) {
//控制点x坐标不变 y坐标屏幕上半部分使用结束点y坐标加上屏幕四分之一
controlP.x = points.get(index).x;
controlP.y = points.get(index).y + screenHeight / 4;
} else {
//控制点x坐标不变 y坐标屏幕上半部分使用结束点y坐标减去屏幕四分之一
controlP.x = points.get(index).x;
controlP.y = points.get(index).y - screenHeight / 4;
}
//这里将控制点坐标传入估值器
FaceEvaluator faceEvaluator = new FaceEvaluator(controlP);
//在值动画中传入 动画执行的开始点坐标和结束点坐标 开始点坐标不变都是屏幕中心 结束点则随机生成
ValueAnimator valueAnimator = ValueAnimator.ofObject(faceEvaluator, pointF, points.get(index));
valueAnimator.setInterpolator(new AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator());
valueAnimator.setDuration(2000);
valueAnimator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
PointF pointF = (PointF) animation.getAnimatedValue();
//移动路径动画
view.setX(pointF.x);
view.setY(pointF.y);
//透明度动画
view.setAlpha(1-animation.getAnimatedFraction()/2);
//缩放动画
view.setScaleX(0.9f+(animation.getAnimatedFraction()/2));
view.setScaleY(0.9f+(animation.getAnimatedFraction()/2));
}
});
valueAnimator.addListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
//动画执行完成后将view缓存起来,方便下次使用
content.removeView(view);
cacheViews.push(view);
}
});
valueAnimator.start();
}
private static class FaceEvaluator implements TypeEvaluator<PointF> {
//控制点坐标
private PointF controlPoint;
public FaceEvaluator(PointF controlPoint) {
this.controlPoint = controlPoint;
}
@Override
public PointF evaluate(float fraction, PointF startValue, PointF endValue) {
//(1 - t)^2 P0 + 2 t (1 - t) P1 + t^2 P2
//使用二阶贝塞尔曲线来改变值得走势
PointF point = new PointF();
point.x = (float) (Math.sqrt(1 - fraction) * startValue.x + 2 * fraction * (1 - fraction) * controlPoint.x + Math.sqrt(fraction) * endValue.x);
point.y = (float) (Math.sqrt(1 - fraction) * startValue.y + 2 * fraction * (1 - fraction) * controlPoint.y + Math.sqrt(fraction) * endValue.y);
// point.x=startValue.x+(endValue.x-startValue.x)*fraction;
// point.y=startValue.y+(endValue.y-startValue.y)*fraction;
return point;
}
}
/**
* 获取屏幕得宽高
*
* @return 宽高的数组
*/
private int[] getScreenSize() {
int[] screenSize = new int[2];
DisplayMetrics metrics = new DisplayMetrics();
getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(metrics);
screenSize[0] = metrics.widthPixels;
screenSize[1] = metrics.heightPixels;
return screenSize;
}
}
XML布局文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".AnimatorActivity">
<CheckBox
android:id="@+id/checkbox"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:button="@drawable/agree_selector"/>
</RelativeLayout>