Java 线程与进程(1):基础知识及用法(问答形式)
1 Java 中有几种新起线程的方式?run和start的区别?
方式一:自定义线程继承Thread
方式二:实现Runnable接口
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 方式一
NewThread1 newThread1 = new NewThread1();
newThread1.start();
// 方式二
NewThread2 newThread2 = new NewThread2();
new Thread(newThread2).start();
}
public static class NewThread1 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
System.out.println("new thread by extends Thread");
}
}
public static class NewThread2 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("new thread by implements Runnable");
}
}
run是函数调用 和线程没有任何关系;
start会走底层,走系统层 最终调度到 run函数,这才是线程。
2 怎么让Java线程安全停止工作?
stop()还是interrupt()的选择:
- stop() : 暴力方式,不要用(过时), 如下载一部分终止危险,且线程机制中有来不及释放的碎片
- interrupt():协作方式,可以安全停止(以下有Thread和Runnable两种方式的中断处理代码)
public class EndThread {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
myThread.start();
MyRunnable myRunnable = new MyRunnable();
Thread runableThread = new Thread(myRunnable);
Thread.sleep(1000);
runableThread.interrupt();
myThread.interrupt();// 发出中断信号 但不会自己使线程停止 需线程中通过isInterrupted()做判断处理
}
public static class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
while (!isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println(name + " ==== is run state" + isInterrupted());
}
}
}
public static class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
// 获取当前线程的中断信息状态
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println(name + " ==== is run state" + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
}
}
}
}
3 多线程中的并行和并发的理解
并行:类比几个车道就可以有几辆车并行行驶
并发:和时间有关系,计算吞吐量,类比车流量
4 线程常用的方法和线程状态(图),各个方法使用场景及流程
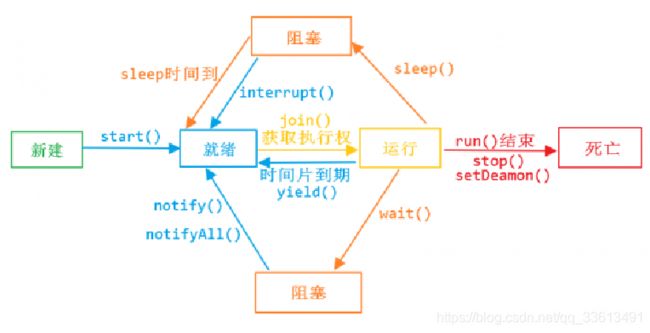
4.1 sleep与wait的区别
sleep 是休眠,等休眠时间一过,才有执行权的资格(无条件可以休眠)
wait 是等待,需要人家来唤醒,唤醒后,才有执行权的资格(某些原因与条件需要等待一下)
注意:只是又有资格了,并不代表马上就会被执行,什么时候又执行起来,取决于操作系统调度
另外,sleep在 catch异常时会被 InterruptedException e 清除中断标记
4.2 如何控制线程的顺序——join控制
public class JoinThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
JoinThread joinThreadA = new JoinThread("A");
JoinThread joinThreadB = new JoinThread("B");
joinThreadA.start();
//放弃当前线程的执行,并返回对应的线程的执行, joinThreadA执行完了,main线程才有执行的机会
joinThreadA.join();
joinThreadB.start();
}
public static class JoinThread extends Thread{
public JoinThread(String name){
super(name);
}
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
System.out.println(this.getName() + ":" + i);
}
}
}
}
4.3 如何让出当前线程执行权—yield(几乎不用)
用法与上面的 join 一样,只不过执行效果是等其他线程执行完了最后才执行设置 yield 的线程。
4.4 关于守护线程----场景?:
// 主线程执行完毕后守护线程也跟着一起结束
public class DaemonThread {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(getName() + "---" + i);
}
}
};
t.setDaemon(true); // 设置了守护线程
t.start(); // 谁调用的 main, main管了我 我就守护main
// 主线程,是为了 等 Thread t 10秒钟
Thread.sleep(10000);
// 走到这里,代表主线程结束,主线程结束不管t线程有没有结束都必须结束,因为t线程是守护线程,守护了main
}
}
5 对锁的使用和区分(类锁/对象锁/显示锁)—死锁
5.1 类锁------隐式锁
public class GPSEngine {
private static GPSEngine gpsEngine;
public GPSEngine getGpsEngine(){
if (gpsEngine == null){
gpsEngine = new GPSEngine();
}
return gpsEngine;
}
// 持有GPSEngine.class的类锁
public static synchronized GPSEngine getGpsEngine1(){
if (gpsEngine == null){
// 其他任何线程不能进来,效率低
gpsEngine = new GPSEngine();
}
return gpsEngine;
}
// 标准单例模式------DCL
public static synchronized GPSEngine getInstance(){
if (gpsEngine == null){
// 持有类锁
synchronized (GPSEngine.class){
if (gpsEngine == null){
gpsEngine = new GPSEngine();
}
}
}
return gpsEngine;
}
}
5.2 对象锁------隐式锁
public class SynTest {
private long count =0;
private Object obj = new Object(); // 作为一个锁 对象锁obj
public long getCount() {
return count;
}
public void setCount(long count) {
this.count = count;
}
public void incCount(){
synchronized (obj){ // 使用一把锁------对象锁
count++;
}
}
// synchronized == 类锁
public synchronized void incCount2(){
count++;
}
// this == 类锁
public void incCount3(){
synchronized (this){
count++;
}
}
// 线程
private static class Count extends Thread{
private SynTest simplOper;
public Count(SynTest simplOper) {
this.simplOper = simplOper;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){
simplOper.incCount(); // count = count+10000
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
SynTest simplOper = new SynTest();
// 启动两个线程
Count count1 = new Count(simplOper);
Count count2 = new Count(simplOper);
count1.start();
count2.start();
Thread.sleep(50);
System.out.println(simplOper.count);//20000
}
}
5.3 显示锁 Lock/ReentrantLock
// 声明一个显示锁之可重入锁 new 可重入锁------ 非公平锁
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void incr(){
// 使用 显示锁 的规范
lock.lock();
try{
count++;
} finally { // 打死都要执行 最后一定会执行
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 可重入锁 意思就是递归调用自己,锁可以释放出来
// synchronized == 天生就是 可重入锁
// 如果是非重入锁 ,就会自己把自己锁死
public synchronized void incr2(){
count++;
incr2();
}
6 生产者消费者案例(产生问题—解决方案)
6.1 初始版代码
public class CommunicationDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建资源对象
Res res = new Res();
// 创建生产者任务
ProduceRunnable produceRunnable = new ProduceRunnable(res);
// 创建消费者任务
ConsumeRunnable consumeRunnable = new ConsumeRunnable(res);
// 启动生产者任务
new Thread(produceRunnable).start();
// 启动消费者任务
new Thread(consumeRunnable).start();
}
}
// 生产者任务
class ProduceRunnable implements Runnable {
private Res res;
ProduceRunnable(Res res) {
this.res = res;
}
@Override
public void run() {//执行线程任务
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
res.put("面包");
}
}
}
// 消费者任务
class ConsumeRunnable implements Runnable {
private Res res;
ConsumeRunnable(Res res) {
this.res = res;
}
@Override
public void run() {//执行线程任务
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
res.out();
}
}
}
class Res {
private String name;
private int id;
public void put(String name) { // 生产一个面包
id += 1;
this.name = name + " 商品编号:" + id;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "生产者 生产了:" + this.name);
}
public void out() {// 消费
id -= 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 消费者 消费了:" + this.name);
}
}
6.2 内置锁解决安全问题------先全部生产再消费
// 对操作共享数据的地方加入同步锁的方式来解决安全问题
public synchronized void put(String name) {
id += 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "生产者 生产了:" + this.id);
}
public synchronized void out() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 消费者 消费了:" + this.id);
id -= 1;
}
6.3 实现生产一个消费一个------ wait/notify等待唤醒机制
class Res2 {
private String name;
private int id;
private boolean flag; // 定义标记 默认第一次为false
public synchronized void put(String name) { // 生产一个面包
if (!flag) {
id += 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "生产者 生产了:" + this.id);
flag = true;// 修改标记
//唤醒 wait(); 冻结的线程,如果没有就是空唤醒,Java是支持的
notify(); // 注意:⚠️ wait(); notify(); 这些必须要有同步锁包裹着
//当前自己线程 冻结,释放CPU执行资格,释放CPU执行权,CPU就会去执行其他线程了
try {
wait(); // 生产好一个,休息下
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public synchronized void out() {// 消费
// 消费之前判断标记
if (flag) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 消费者 消费了:" + this.id);
flag = false;//修改标记
notify();
try {
wait(); // 消费完休息下
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
7 ThreadLocal——隔离线程(待完善)
设置的值只对当前设置的线程有用,类似于副本,不会全局修改,Handler中有用到
ThreadLocalMap: 性能最高
8 并发基础补充知识点(待完善)
8.1 线程的生命周期
8.2 第三种创建方式的实质
8.3 死锁的条件及解决方案
8.4 活锁
9 CAS(Compare And Swap)
9.1 CAS含义及原理
原子操作:全部完成或全部未做,不可再分,如synchronized
含义:比较并交换
原理:循环指令直到成功
9.2 悲观锁和乐观锁
悲观锁:上下文切换 一次切换3-5ms 效率低
乐观锁:一次指令0.6ns
9.3 CAS问题
ABA问题:期间被换了但保持原样(本质已变)——加个版本戳解决
开销问题
只能保证一个共享变量的原子操作
9.4 原子操作类的使用(凡是以Atomic开头的)
更新基本类型类
更新数组类
更新引用类型
10 队列和阻塞队列
10.1 含义
队列:先进先出
阻塞队列:BlockingQueue接口
10.2 常见阻塞队列
有界
ArrayBlockingQueue:
LinkedBlockingQueue:
无界
PriorityBlockingQueue:
DelayBlockingQueue:
LinkedTranceferQueue:
其他
SychrononsQueue:不存储元素的阻塞队列
LinkedBlockingDeque:
11 线程池
11.1 什么是线程池?为什么要用线程池?
缩短任务的总执行时间
11.2 ThreadPoolExcutor 线程池
各个参数的含义:
corePoolSize:核心线程数
maxnumPoolSize:最大线程数
keepAliveTime:空闲线程存活时间
unit:存活时间单位
workQueue:阻塞队列
threadFactory:
handler:拒绝策略,四种
| 拒绝策略名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| DiscardOldestPolicy | 排在最前面最老的的丢弃 |
| CallerRunsPolicy | 你行你来做,谁往线程池提交任务谁来做 |
| DiscardPolicy | 最新提交的任务直接丢弃 |
| AbortPolicy | 抛出异常,默认策略 |
流程:
核心线程==》阻塞队列==》最大线程数==》拒绝策略
提交任务
submit
关闭线程池
shutdown:中断未在执行的线程
shutdownNow:尝试关闭所有线程,但不一定会成功
11.3 合理配置线程池
任务特性
CPU密集型:CPU在不断计算的——配置线程数不能超过CPU核心数
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()
IO密集型:与网络进行通讯,有读写磁盘操作的——机器CPU核心数*2
混合型: