实用算法课后总结-数据结构链表
希望通晓如何使用算法的开发人员首先要学习如何操作数据。而后,他们根据自己的需要应用算法技术来表示数据。通过算法操作数据主要涉及的是在内存中表示数据的技术。怎样存储、访问数据以及怎样转换数据以便最高效的解决给定问题?大多数问题要求开发人员能够熟练地掌握基本数据结构。
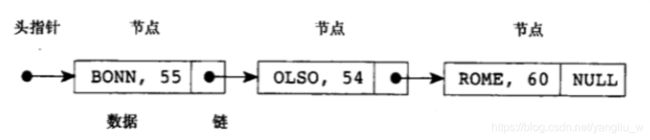
如下图是具有三个节点的链表:
在C语言中,链表的表示如下:
struct Node{
char *city;
int temp;
struct Node *Next;
};
typedef struct Node * Link;
Link Head;
假如需要编写一个程序,从输入文件中读取城市的名称及气温信息。最后按照温度和城市进行排序,并确定中间气温。对于这个问题,使用数组并不是一个好的选择。因为你不知道应该创建多大的数组才合适。或许可以声明一个认为足够大的数组,但是这会浪费内存空间,并且还有输入文件超出预期的风险。一种方案是读两遍输入文件,第一遍确定大小,第二遍再进行数据处理。但是因为磁盘I/O是非常慢的(它几乎是总是程序中最慢的),这样效率非常低,并不可取。一个好的方法是利用链表,它按接收到的数据来存储它们。
下面是一个利用链表,读入输入文件,并按照气温城市进行排序的算法。citytemp.c从数据文件中读取城市和气温,将记录插入到一个链表中(按气温和城市名称的升序进行排序),丢弃重复记录,打印该有序链表,并指出位于中间的条目。数据记录时文本文件中简单的行,它前三个字符表示气温,其后接着最多124个字符表示城市名称。
打印城市和气温的有序链表代码如下:
/*--- citytemp.c--------------------------- Listing 2-1 ---------
* Reads a text file of cities and temperatures in the
* following format: TempCity
* where Temp is a number of three digits or
* a sign and two digits; City is a string of length < 124
* Examples: -10Duluth
* 096Phoenix
* The records are read into a singly linked list by order
* of temperature and city; duplicates are discarded. At EOF,
* the whole list is printed with an indication of the median
* temperature. And then, the list is progressively shortened
* and reprinted showing the median.
* Usage: citytemp filename.ext
*-------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include
#include
#include
/*--- data definitions ---*/
struct Node { /* a node in our linked list */
char *City;
int Temp;
struct Node *Next;
};
typedef struct Node * Link; /* Links are pointers to nodes */
Link Head; /* head of our linked list */
int NodeCount; /* how many nodes in the list */
/*--- functions declarations for linked lists ---*/
int AddNodeAscend ( Link ); /* add a node */
void CreateList ( void ); /* initialize list */
int DeleteNode ( Link ); /* delete a node */
int DuplicateNode ( Link, Link ); /* handle duplicate inserts */
void FreeNode ( Link ); /* free a node's memory */
void ShowNodes ( void ); /* show list of nodes */
int NodeCmp ( Link, Link ); /* compare two nodes */
/*--- function definitions ---*/
int AddNodeAscend ( Link to_add )
{
Link pn, /* local copy of node to be added 指向将被插入的节点*/
prev, /* points to previous node 指向当前被检查节点的前一节点*/
curr; /* points to node being examined 指向当前被检查的节点*/
struct Node dummy;
int i;
/* Make a copy of the input node拷贝插入节点 */
pn = ( Link ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node ));
if ( pn == NULL )
return 0;
memcpy ( pn, to_add, sizeof ( struct Node ));
/* set up a dummy node to simplify logic建立头节点,使逻辑更简单 */
dummy.Next = Head;
prev = &dummy;
curr = Head;
/* insert node pn 插入pn指向的节点*/
for ( ;; prev = curr, curr = curr->Next )
{
if ( curr == NULL )
break; /* reached the end到达链表尾 */
i = NodeCmp ( pn, curr );//比较pn节点与curr节点
if ( i <= 0 )
break; /* pn precedes curr pn节点值小于当前节点curr */
}
if ( curr && i == 0 ) /* we have a duplicate 判断是否重复节点*/
if ( DuplicateNode ( curr, pn ) == 0 )
return ( 1 ); /* bail out if DuplicateNode says to释放重复节点的空间 */
//插入代码
prev->Next = pn;
pn->Next = curr;
Head = dummy.Next;
NodeCount+=1;//yyw
return ( 1 );
}
/*--------------------------------------------------------------
* Handle the duplicate node. In this program,
* we just delete the duplicate.
*-------------------------------------------------------------*/
int DuplicateNode ( Link inlist, Link duplicate )//处理重复节点
{
FreeNode ( duplicate );//调用FreeNode,释放重复节点的空间
return ( 0 );
}
int DeleteNode ( Link to_delete )
{
Link curr, /* the current node指向当前节点 */
prev; /* the previous node 向当前节点的前一节点*/
int i;
/*--- Is there anything in the list? ---判断是不是空表*/
if ( Head == NULL )
return ( 0 );
/*--- If so, step through the list looking for the node ---非空,寻找要删除的节点*/
for ( prev = NULL, curr = Head;
curr != NULL && ( i = NodeCmp ( to_delete, curr )) > 0;
prev = curr, curr = curr->Next )
/* loop around */ ;
/*--- Found a match, so delete it ---找到匹配条件的,删除*/
if ( curr != NULL && i == 0 )//compare之后,若是相同的节点,返回值是0
{
if ( prev )
prev->Next = curr->Next;
else /* deleting Head */
Head = curr->Next;//第一个节点就是匹配待删除的节点
FreeNode ( curr );//释放内存
NodeCount -= 1;//节点数量减1
return ( 1 );
}
return ( 0 );
}
//按温度、城市的规则比较两个节点
int NodeCmp ( Link a, Link b )
{
/* returns 1, 0, -1, depending on whether the data in
* a is greater than, equal, or less than b.
*/
/* if temps are unequal, return based on temp 如果温度不同,按温度排序*/
if ( a->Temp != b->Temp )
return ( a->Temp - b->Temp );
/* else, return based on city's name温度相同,按城市排序 */
return strcmp ( a->City, b->City );
}
//创建空链表(并没有头结点)
void CreateList ( void )
{
Head = NULL;
NodeCount = 0;
}
//释放节点内存
void FreeNode ( Link n )
{
free ( n->City );
free ( n );
}
//展示节点群
void ShowNodes( void )
{
Link pn;
int count, median;
// /* count the nodes */
// for ( count = 0, pn = Head; pn; pn = pn->Next )
// count += 1;
// /* compute the median node */
// median = count / 2 + 1;
///* compute the median node */
median = NodeCount/2+1;//yyw
/* step through the list printing cities and
* temperatures. Announce the median temperature.
遍历链表城市与温度,并指出中点
*/
if ( NodeCount ) /* only print if there's a node且仅当存在节点才展示 */
{
/* initialize the needed variables */
count = 0; /* count of nodes we've printed计算打印的节点 */
for ( pn = Head; pn; pn = pn->Next )
{
printf ( "%-20s: %3d", pn->City, pn->Temp );
count += 1;
if ( count == median )
printf ( " --Median--" );
printf ( "\n" );
}
}
else
printf ( "Empty list\n" );
}
/*--- main line ---*/
int main ( int argc, char *argv[] )
{
FILE *fin; /* file we'll be reading from */
char buffer[128]; /* where we'll read the file into */
struct Node n; /* the node we add each time */
if ( argc != 2 )
{
fprintf ( stderr, "Usage: citytemp filename.ext\n" );
exit ( EXIT_FAILURE );
}
fin = fopen ( argv[1], "rt" );
if ( fin == NULL )
{
fprintf ( stderr, "Cannot open/find %s\n", argv[2] );
exit ( EXIT_FAILURE );
}
/* Create and initialize the linked list to empty创建并初始化链表*/
CreateList();
/*--- main loop ---*/
while ( ! feof ( fin ))//循环直到文件流末EOF
{
/* read a record consisting of a line of text */
if ( fgets ( buffer, 127, fin ) == NULL )//从文件指针fin中读取127-1个字符,
//存到以buff为起始地址的空间里,直到读完一行,如果成功则返回s的指针,否则返回NULL。
break;
/* get rid of the trailing carriage return 行末字符为结束符*/
buffer [ strlen ( buffer ) - 1 ] = '\0';
/* copy the city name to the node to be added 复制从buff+3开始的字符串*/
n.City = strdup ( buffer + 3 );
/* mark off the temperature and convert to int置行上第4个字符为结束符 */
buffer[3] = '\0';
n.Temp = atoi ( buffer );//把行上前3个数字字符转换成整型数
/* add the node to the list 设置好n节点后,插入链表*/
if ( AddNodeAscend ( &n ) == 0 )
{
fprintf ( stderr, "Error adding node. Aborting\n" );
exit ( EXIT_FAILURE );
}
}
ShowNodes();
/* Now, delete something */
printf( "\n" );
DeleteNode ( Head );
ShowNodes();
//从第一个节点开始,依次删除一个节点并展示节点群
while (Head && Head->Next)
{
printf ( "\n" );
DeleteNode ( Head->Next );
ShowNodes();
}
printf ( "\n" );
DeleteNode ( Head );
ShowNodes();
fclose ( fin );//关闭流
return ( EXIT_SUCCESS );
} 涉及的一些函数:
(1)void *memcpy(void *dest, const void *src, int n)
从源src所指的内存地址的起始位置开始拷贝n个字节到目标dest所指的内存地址的起始位置中.函数返回一个指向dest的指针。
(2)char *fgets(char *s, int n, FILE *stream)
参数: *s: 字符型指针,指向将存储到的数据地址 n: 整型数据,将从流中读取 n - 1 个字符 *stream: 指针数据,欲读取的流。从文件指针stream中读取n-1个字符,存到以s为起始地址的空间里,直到读完一行,如果成功则返回s的指针,否则返回NULL。
(3)int atoi(const char *nptr)
把字符串转换成整型数,参数nptr字符串,如果第一个非空格字符不存在或者不是数字也不是正负号则返回零,否则开始做类型转换,之后检测到非数字(包括结束符 \0) 字符时停止转换,返回整型数。
(4)extern char *strdup(char *s)
复制字符串s,strdup()在内部调用了malloc()为变量分配内存,当程序结束后,必须用free()释放相应的内存空间,否则会造成内存泄漏
(5)extern int strcmp(const char *s1,const char * s2)
比较字符串s1和s2,一般形式:strcmp(字符串1,字符串2)。当s1
用于该程序的一个实例数据文件如下:
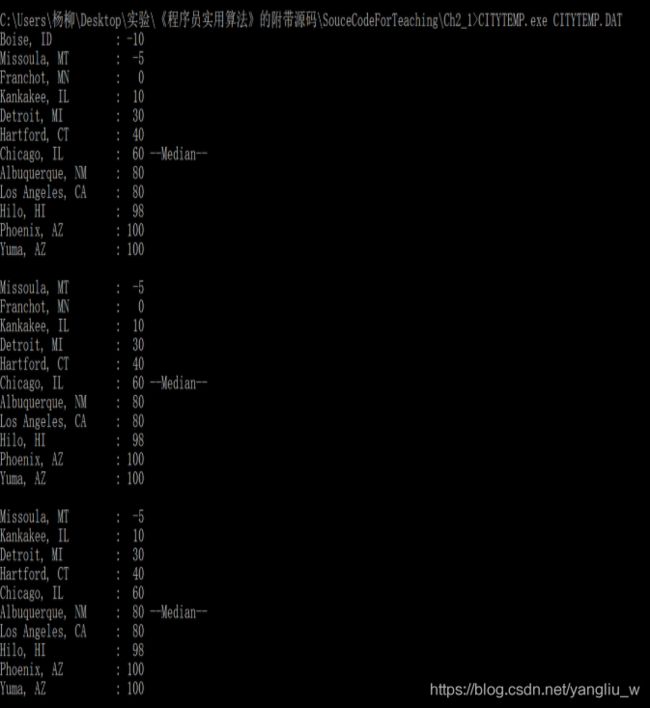
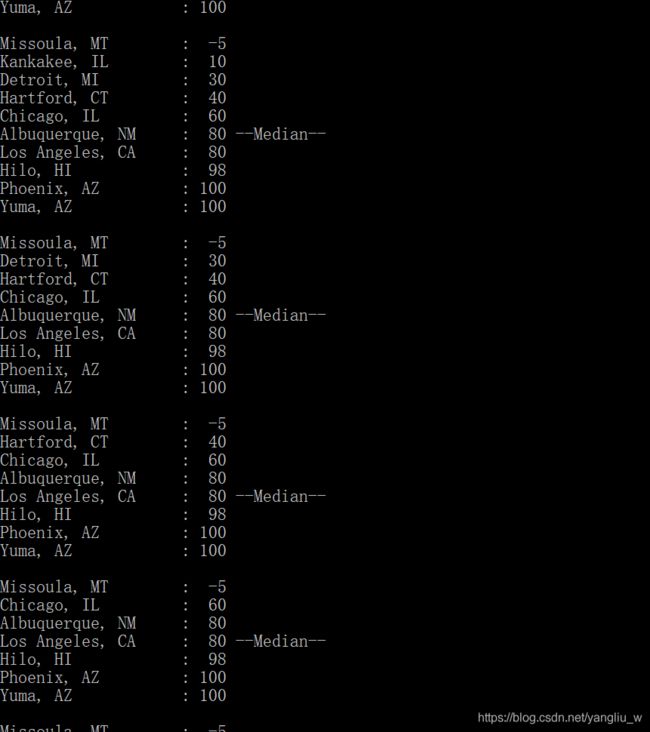
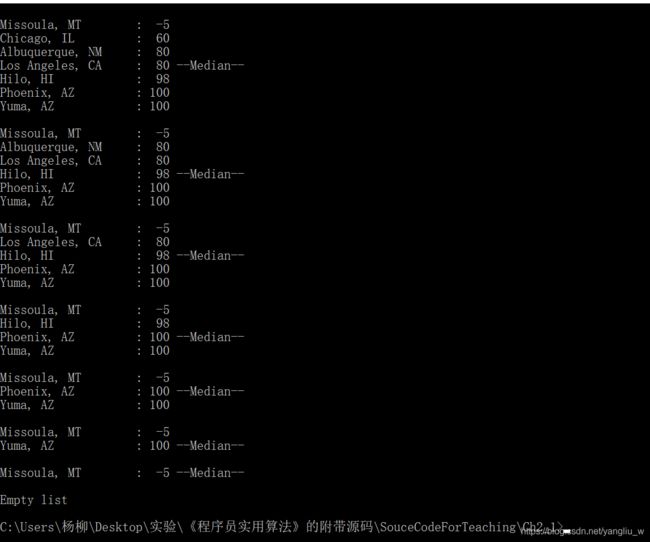
算法运行截图:
该程序显示了如何创建以及遍历链表、按顺序添加节点,以及比较两个节点。还包括函数DeleteNode()删除一个节点,删除节点需要遍历一个链表,直到找到删除的节点为止。程序通过free()函数把当前节点占用的内存返回给系统。