注解初始化控件(XUtils方式)
新博客地址
注解初始化控件(XUtils方式)
DEMO链接地址
在第一次潭州教育的公开课上接触了这个框架的讲解,我动手研究了一下,结果一出手就停不下来,先后被我碰上了(Glow公司的技术博客——动态Android编程 )、从几个大牛的博客(学到了github pages + Jekyll 免费制作博客网站)
我发现不写博客,很多东西就会忘记(代码如何上传到jcenter我已经忘记了)
Just Do it!真的会有意想不到的收获!
1. IOC概念介绍
http://www.cnblogs.com/qqlin/archive/2012/10/09/2707075.html我是从这边文章学习的IOC概念的,写的浅显易懂
- 控件反转(IOC):创建何种对象的控制权,转移到第三方
- 依赖注入(DI):是由IOC容器在运行期间,动态地将某种依赖关系注入到对象之中。
- IOC与DI之间的关系:DI是一种IOC的具体思想,(编译运行期,动态注入依赖关系);使用配置文件实现依赖关系的配置也是一种IOC思想(依赖拖拽)。
- 约定优于配置 这个是什么鬼??
- 依赖注入/依赖查找/依赖拖拽
- 依赖拖拽是通过对注入对象的集中配置实现的
- 依赖查找是在业务组件代码中进行的(EJB和Apache Avalon )
- XUtils的实现方式XUtils实际上是通过 注解 + 反射 + 动态代理实现的。
layout文件注入:
- 使用:
@ContentViewInject(R.layout.activity_main)
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity- 注解:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)// 使用对象:类
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)// 生命范围:运行期
public @interface ContentViewInject {
int value();// 存放布局id
}- 注入代码:
private static void injectLayout(Activity context) {
try {
// UIClz
Class uiClass = context.getClass();
// 类上的注解
ContentViewInject annotation = uiClass.getAnnotation(ContentViewInject.class);
if (annotation != null) {
// 注解中的layout id值
int value = annotation.value();
// 通过反射使用activity中的setContentView方法进行 布局设置
// 局限性:这个方法仅仅适用于activity
Method setContentView = uiClass.getMethod("setContentView", int.class);
setContentView.invoke(context, value);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}控件注入:
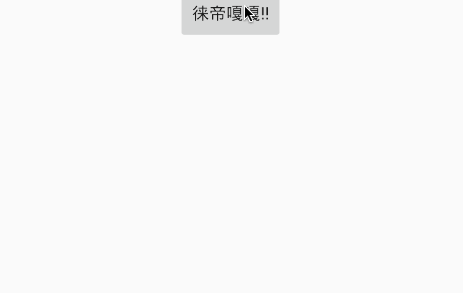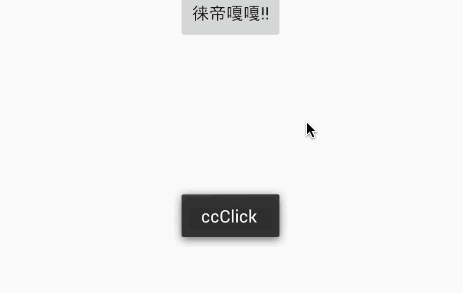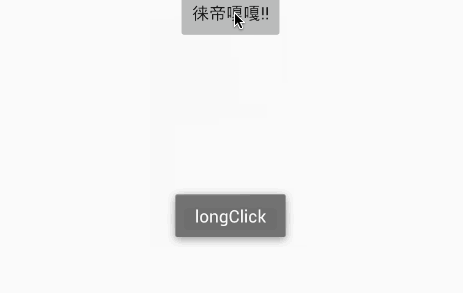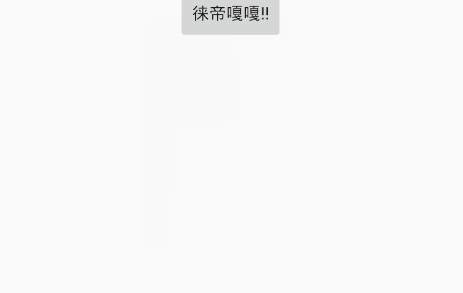
- 使用:
@ViewInject(R.id.textView)
TextView textView;
......
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
TurInject.bind(this);
textView.setText("徕帝嘎嘎");
}- 注解:
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ViewInject {
int value();
}- 注入:
private static void injectViews(Context context) {
try {
Class uiClass = context.getClass();
// 获取成员变量
Field[] fields = uiClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
ViewInject annotation = field.getAnnotation(ViewInject.class);
if (annotation != null) {
int value = annotation.value();
Method findViewById = uiClass.getMethod("findViewById", int.class);
Object invoke = findViewById.invoke(context, value);
// 设置允许访问
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(context, invoke);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}事件注入
- 使用代码:
@ClickEvent(value = {R.id.textView}, type = View.OnClickListener.class)
public void ccClick(View view) {
Toast.makeText(getBaseContext(), "ccClick", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
@ClickEvent(value = {R.id.textView}, type = View.OnLongClickListener.class)
public void longClick(View view) {
Toast.makeText(getBaseContext(), "longClick", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}- 注解
public static void injectMethod(final Context context) {
try {
Class uiClass = context.getClass();
// 获取所有的方法
Method[] methods = uiClass.getMethods();
for (final Method method : methods) {
ClickEvent annotation = method.getAnnotation(ClickEvent.class);
// 塞选含有ClickEvent注解的方法
if (annotation != null) {
int[] values = annotation.value();
Class type = annotation.type();
// 拿到控件
for (int viewId : values) {
// 初始化控件
Method findViewById = uiClass.getMethod("findViewById", int.class);
// view
final Object viewObj = findViewById.invoke(context, viewId);
Class viewClass = viewObj.getClass();
// setOnClickListener/setOnLongClickListener等等
String viewSetMethodName = "set" + type.getSimpleName();
Method viewMethod = viewClass.getMethod(viewSetMethodName, type);
// 动态代理就是针对 任意 一个对象的接口方法的 管理/拦截/AOP
ViewEventInvocationHandler viewEventInvocationHandler = new ViewEventInvocationHandler(context, method);
// type.getClassLoader : 类加载器 new Class[]{type} : type为接口类
Object eventInterfaceInstance = Proxy.newProxyInstance(type.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{type}, viewEventInvocationHandler);
// 动态代理 OnClickListener 中的
// 执行了setOnClickListener这个方法,那么在响应这个参数OnClickListener接口中的,onclick方法的时候会响应InvocationHandler中的invoke方法
viewMethod.invoke(viewObj, eventInterfaceInstance);
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static class ViewEventInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private Context context;
private Method contentMethod;
public ViewEventInvocationHandler(Context context, Method contentMethod) {
this.context = context;
this.contentMethod = contentMethod;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// method 为OnClickListener 中的 onClick
// 系统调用参数接口中的 onClick方法的时候,会响应这个方法
// 响应这个方法的时候我们需要响应(activity中被ClickEvent标记过的方法)
// contentMethod 为activity中被 ClickEvent标记过的方法
contentMethod.invoke(context, args);
return true;
}
}知乎——代理、动态代理
- 主要用来做方法的增强,让你可以在不修改源码的情况下,增强一些方法,在方法执行前后做任何你想做的事情(甚至根本不去执行这个方法),因为在InvocationHandler的invoke方法中,你可以直接获取正在调用方法对应的Method对象,具体应用的话,比如可以添加调用日志,做事务控制等。
- 还有一个有趣的作用是可以用作远程调用
- 在某些情况下,一个客户不想或者不能直接引用另一个对象,而代理对象可以在客户端和目标对象之间起到中介的作用。
- 为其他对象提供一种代理以控制对这个对象的访问
动态代理的缺憾:Proxy已经设计得非常优美,但是还是有一点点小小的遗憾之处,那就是它始终无法摆脱仅支持interface代理的桎梏
到这里呢,XUtils的布局注入、控件注入、事件注入就全部介绍完了!