[TOC]
准备工作
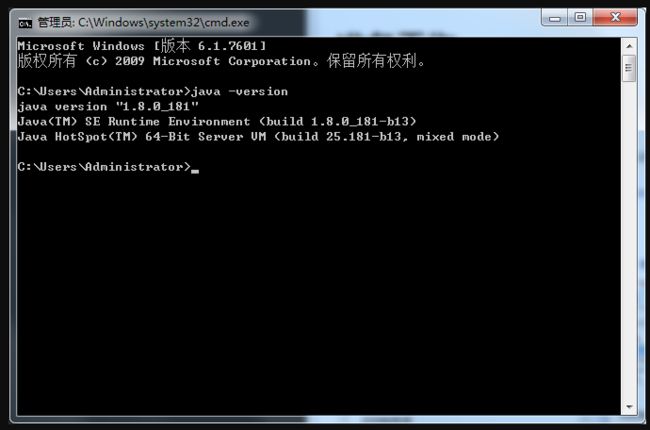
1. 安装Java 1.8 SDK
由于框架以及一些兼容性问题,我们采用大家通用的 JAVA 1.8 sdk。
下载地址: http://www.oracle.com/technet...
2. 安装IntelliJ IDEA
这个就不简述了,大家自由发挥。但是推荐入正版。
3. 安装Maven
下载地址: https://maven.apache.org/down...
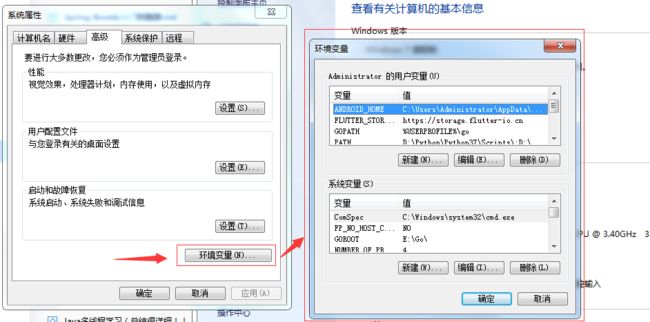
下载之后解压到文件夹,然后与Java sdk一样配置一个环境变量。
验证命令
> mvn -v
Apache Maven 3.5.4 (1edded0938998edf8bf061f1ceb3cfdeccf443fe; 2018-06-18T02:33:1
4+08:00)
Maven home: D:\JAVA_TOOLS\apache-maven-3.5.4\bin\..
Java version: 1.8.0_181, vendor: Oracle Corporation, runtime: E:\Java\jre
Default locale: zh_CN, platform encoding: GBK
OS name: "windows 7", version: "6.1", arch: "amd64", family: "windows"初始化项目
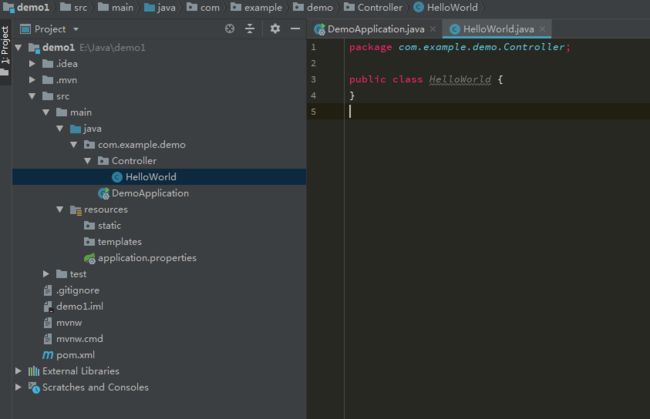
打开IDEA,然后新建项目。在左侧选择Spring Initializr,右侧SDK选择1.8。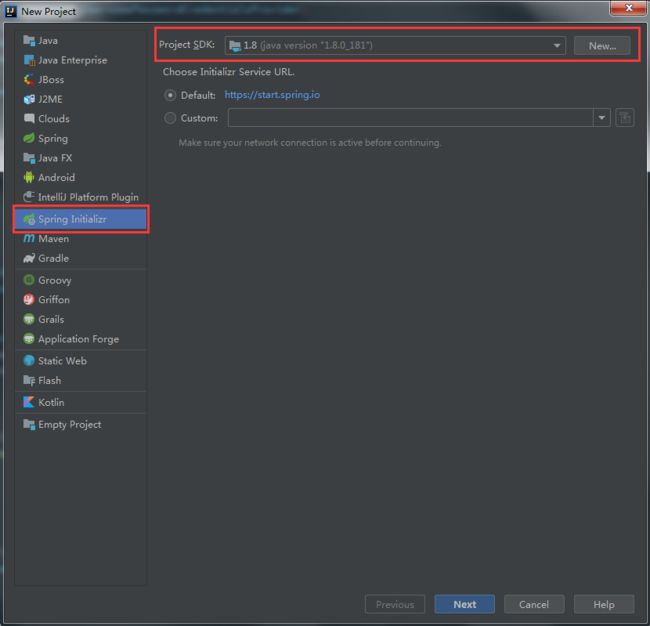
这个界面上,要选择 1. WEB -> WEB 2. SQL -> MyBatis 。 点击Next,配置项目存放地址。点击Finish创建项目,并由IDEA载入项目。
这个时候你可以稍微休息一下,等待Maven初始化载入所需要的包。
创建SQLITE数据库
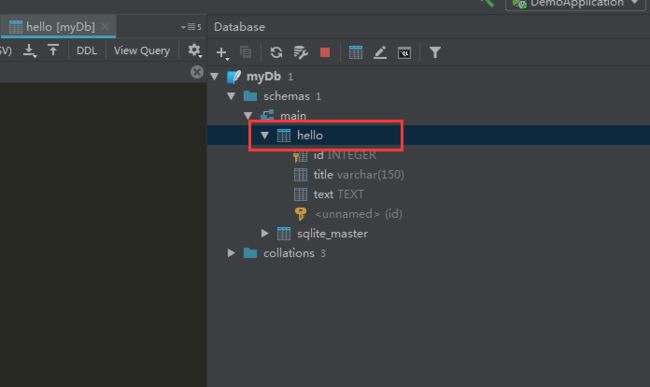
在main目录下方新建一个DB目录,并且在目录上右键点击,新建一个Sqlite数据库。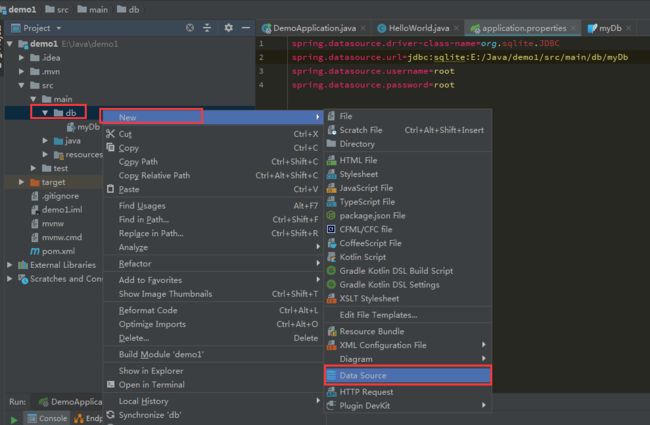
在右侧DataBase中点击数据库,右键Open Console,运行如下脚本,创建一个表:
create table hello
(
id INTEGER primary key,
title varchar(150),
text TEXT
);
配置项目SQLITE
基本配置
Maven配置
打开pom.xml文件,在dependencies节点中增加以下节点
org.xerial
sqlite-jdbc
3.21.0.1
保存之后,稍等一会,IDEA会通过MAVEN拉取指定版本的包。
如果没有成功拉取到包,可以尝试手动拉取。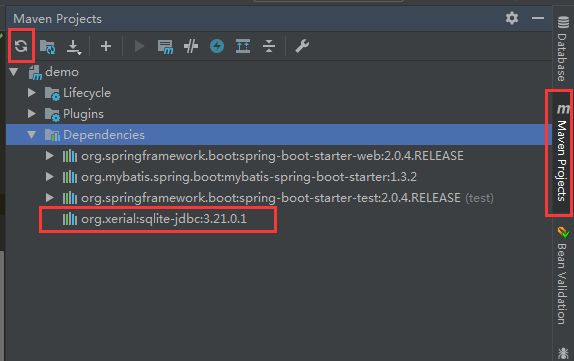
点击刷新,查看dependencies是否多了Sqlite包。
Mybatis配置
创建config目录。新增MyBatisConfig文件,代码如下
package com.example.demo.Config;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.sqlite.SQLiteDataSource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
public class MyBatisConfig {
@Autowired
private DataSourceProperties dataSourceProperties;
@Bean(name="dataSource")
public DataSource dataSource() {
SQLiteDataSource dataSource = new SQLiteDataSource();
dataSource.setUrl(dataSourceProperties.getUrl());
return dataSource;
}
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory() throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource());
return sqlSessionFactoryBean.getObject();
}
}
增加MyBatis的扫描配置文件,新建文件MyBatisMapperScannerConfig,代码如下:
package com.example.demo.Config;
import org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class MyBatisMapperScannerConfig {
@Bean
public MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer() {
MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer = new MapperScannerConfigurer();
mapperScannerConfigurer.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName("sqlSessionFactory");
//com.example.demo.dal.mapper 这个包名是所有的Mapper.java文件所在的路径,该包下面的子包里面的文件同样会扫描到。
//此包名与具体的应用的名称相关
mapperScannerConfigurer.setBasePackage("com.example.demo.Mapper");
return mapperScannerConfigurer;
}
}
项目入口配置
打开DemoApplication文件。增加新的注解
package com.example.demo;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration;
// 下面这一行为新增数据库关联注解
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
@MapperScan("com.example.demo.mapper")
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
编写数据库对象模型
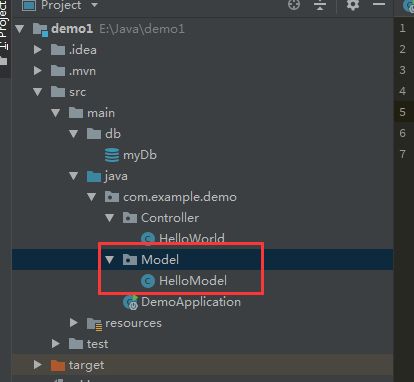
在目录中创建Model目录,并且添加HelloModel类文件。
在文件中输入数据库对象结构。
package com.example.demo.Model;
public class HelloModel {
private long Id;
private String Title;
private String Text;
}
在文件中,点击右键,选择Generate 选择 Getter and Setter自动生成对象的GET,SET。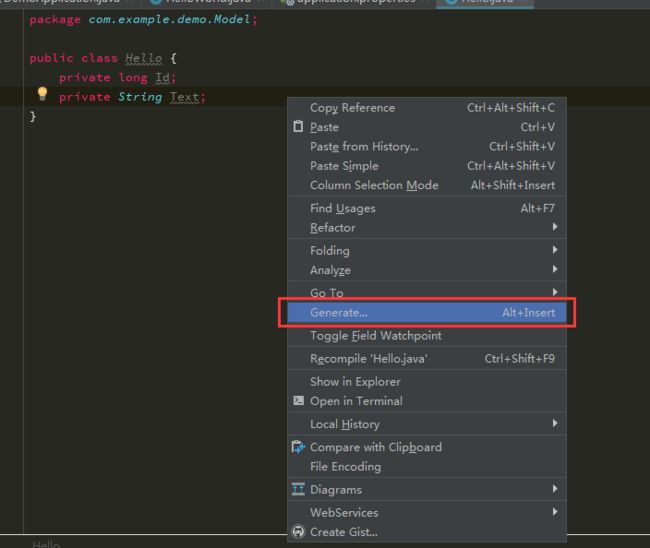
处理完成之后的文件应该是这样的
package com.example.demo.Model;
public class HelloModel {
private long Id;
public long getId() {
return Id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
Id = id;
}
public String getTitle() {
return Title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
Title = title;
}
public String getText() {
return Text;
}
public void setText(String text) {
Text = text;
}
private String Title;
private String Text;
}
与Model同目录创建文件夹Mapper,新建一个HelloMapper类文件,编写以下内容。
package com.example.demo.Mapper;
import com.example.demo.Model.*;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper
@Component
public interface HelloMapper {
// 插入 并查询id 赋给传入的对象
@Insert("INSERT INTO hello(key, value) VALUES(#{key}, #{value})")
@SelectKey(statement = "SELECT seq id FROM sqlite_sequence WHERE (name = 'hello')", before = false, keyProperty = "id", resultType = int.class)
int insert(HelloModel model);
// 根据 ID 查询
@Select("SELECT * FROM hello WHERE id=#{id}")
HelloModel select(int id);
// 查询全部
@Select("SELECT * FROM hello")
List selectAll();
// 更新 value
@Update("UPDATE hello SET value=#{value} WHERE id=#{id}")
int updateValue(HelloModel model);
// 根据 ID 删除
@Delete("DELETE FROM hello WHERE id=#{id}")
int delete(Integer id);
} 同目录创建Service文件夹,新建HelloService类文件。编写以下代码
package com.example.demo.Service;
import com.example.demo.Mapper.HelloMapper;
import com.example.demo.Model.HelloModel;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class HelloService {
private final HelloMapper dao;
@Autowired
public HelloService(HelloMapper dao) {
this.dao = dao;
}
public boolean insert(HelloModel model) {
return dao.insert(model) > 0;
}
public HelloModel select(int id) {
return dao.select(id);
}
public List selectAll() {
return dao.selectAll();
}
public boolean updateValue(HelloModel model) {
return dao.updateValue(model) > 0;
}
public boolean delete(Integer id) {
return dao.delete(id) > 0;
}
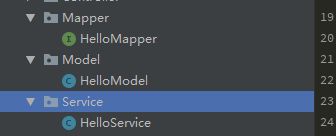
} 整个项目的Mapper,DAL文件架构看起来应该是这个样子的。
为项目指定数据库地址
打开src\main\resources\application.properties文件,配置数据库信息。
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.sqlite.JDBC
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:sqlite:E:/Java/demo1/src/main/db/myDb
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root编写第一个Hello World
package com.example.demo.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
public class HelloWorld {
@RequestMapping("/")
public String Index() {
return "Hello World";
}
}
增加了一个名为Index的方法,并且通过注解设置了如何访问此方法的路径。
打开浏览器,输入http://localhost:8080可以看到第一个控制器显示的内容。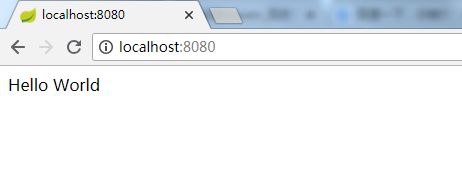
输出数据库内容到浏览器
在Controller/HelloWorld文件中,新建List方法。
package com.example.demo.Controller;
import com.example.demo.Model.HelloModel;
import com.example.demo.Service.HelloService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
public class HelloWorld {
private final HelloService HelloService;
@Autowired
public HelloWorld(HelloService HelloService) {
this.HelloService = HelloService;
}
@RequestMapping("/")
public String Index() {
return "Hello World";
}
@RequestMapping("/list")
public List List() {
return HelloService.selectAll();
}
}
注意我们创建了HelloWorld的DAL层依赖注入。
重新运行整个项目,我们输入http://localhost:8080/list可以看到,服务端将数据库内容组合成了JSON输出给我们了。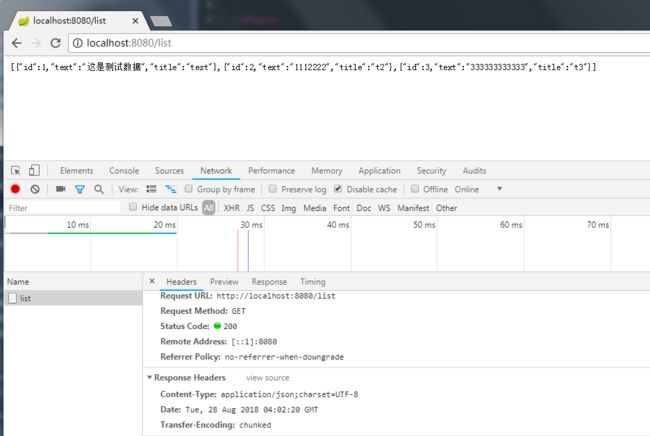
创建请求对象
在model文件夹中新建ReqBody类文件。输入以下内容
package com.example.demo.Model;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty;
public class ReqBody {
/**
* 分支名
*/
private String Name;
public String getName() {
return Name;
}
@JsonProperty(value="Name")
public void setName(String name) {
Name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return Email;
}
@JsonProperty(value="Email")
public void setEmail(String email) {
Email = email;
}
private String Email;
}
注意,关注JsonProperty这个注解,我看很多教程都只是说了,使用@RequestBody就可以将POST对象映射出来,但是,经过多次尝试,发现必须增加这个注解并且指定解析名字。@RequestBody才会正确的解析提交的Application/Json数据格式。
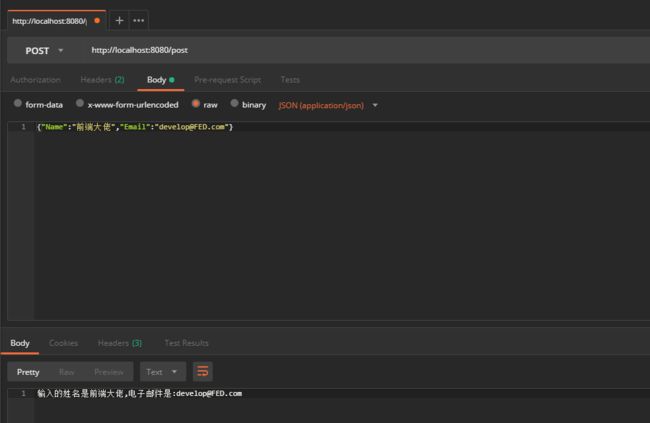
获取Post数据
我们回到HelloWorld这个Controller上。新增一个Post方法,并且指定他的访问路径。
@RequestMapping(value = "/post", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String Post(
@RequestBody ReqBody map
) throws IOException {
return "输入的姓名是" + map.getName() + ",电子邮件是:" + map.getEmail();
}后记
作为有一定的.net开发基础的前端攻城狮,对于写JAVA还是略有不擅长。主要需要知道什么是依赖注入,和控制反转。还有AOP编程。了解这些之后,对于写项目有莫大的帮助。
另外,十分感谢Java开发的朋友帮助解析困惑。@Alex @青龙
参考文章
https://www.jianshu.com/p/418...