Mocha测试框架和项目实例
测试项目已上传github
地址:https://github.com/Hanxueqing...
运行克隆命令,下载到本地
git clone [email protected]:Hanxueqing/Mocha-test.git
一、什么是Mocha
Mocha(发音"摩卡")诞生于2011年,是现在最流行的JavaScript测试框架之一,在浏览器和Node环境都可以使用。所谓"测试框架",就是运行测试的工具。通过它,可以为JavaScript应用添加测试,从而保证代码的质量。
二、Mocha安装和准备
前期准备:安装vue-cli脚手架、安装node、安装Git
(1)先用vue-cli创建一个vue-test项目
vue create vue-test(2)全局安装mocha
npm i mocha -g将mocha安装到本地目录
npm i mocha -D(3)修改package.json中的test路径为我们本地的mocha路径
"test": "./node_modules/mocha/bin/mocha"三、测试框架
1、创建test文件夹
测试脚本都存放在test文件夹中
2、编写测试框架
创建test/demo.js
describe("Demo", function(){
describe("方法 1", function(){
context("情境 1", function(){
before(function(){
console.log("-----测试之前------");
});
after(function(){
console.log("-----测试之后------");
});
beforeEach(function(){
console.log("-------每条测试之前---------");
})
afterEach(function(){
console.log("-------每条测试之后---------");
})
it("测试 1", function(){
})
it("测试 2", function(){
})
})
})
})上面这段代码,就是测试脚本,它可以独立执行。测试脚本里面应该包括一个或多个describe块,每个describe块应该包括一个或多个it块。
describe
describe块称为"测试套件"(test suite),表示一组相关的测试。它是一个函数,第一个参数是测试套件的名称("Demo"),第二个参数是一个实际执行的函数。
it
it块称为"测试用例"(test case),表示一个单独的测试,是测试的最小单位。它也是一个函数,第一个参数是测试用例的名称("测试1"),第二个参数是一个实际执行的函数。
测试用例的钩子
Mocha在describe块之中,提供测试用例的四个钩子:before()、after()、beforeEach()和afterEach()。它们会在指定时间执行。
befor:定义测试之前进行的操作
after:定义测试之后进行的操作
beforeEach:定义每条测试之前进行的操作
afterEach:定义每条测试之后进行的操作
3、进行测试
执行mocha 命令使用全局安装的mocha进行测试或者执行npm test命令使用本地安装的mocha进行测试
四、断言库chai
所谓"断言",就是判断源码的实际执行结果与预期结果是否一致,如果不一致就抛出一个错误。
1、全局安装chai模块
npm i chai -g2、本地安装chai模块
npm i chai -D3、断言风格
断言库有很多种,Mocha并不限制使用哪一种。
assert风格的断言
在test文件夹下新建test_lib文件夹,创建assert.js编写测试脚本。
const chai = require("chai");
//引入断言的风格
const assert = chai.assert;
describe("Demo", function () {
it("使用 assert风格的断言测试", function () {
var value = "hello";
//断言value值的类型为字符串
assert.typeOf(value, "string");
//断言value值等于"hello"
assert.equal(value, "hello");
//断言value值的长度为5
assert.lengthOf(value, 5);
})
})进入test_lib文件夹下,执行mocha assert.js运行测试脚本,因为我们这三个断言都是真的,所以测试通过。
should风格断言
创建should.js编写测试脚本。
const chai = require("chai");
const should = chai.should();
describe("Demo", () => {
it("使用 should风格的断言测试", function () {
var value = "hello";
//value应该存在
value.should.exist
//value的数字类型应该是一个字符串
value.should.be.a("string");
//value值应该等于"hello"
value.should.equal("hello");
//value值不等于"你好"
value.should.not.equal("你好");
//value的长度应该为5
value.should.have.length(5);
})
})我们也可以换成另一种更简洁的写法,使用and连接断言
value.should.exist
.and.be.a("string")
.and.equal("hello")
.and.have.length(5)进入test_lib文件夹下,执行mocha should.js运行测试脚本,因为我们这五个断言都是真的,所以测试通过。
expect风格断言
expect断言的优点是很接近自然语言
创建expect.js编写测试脚本。
const chai = require("chai");
const expect = chai.expect;
describe("Demo", () => {
it("使用 expect风格的断言测试", function () {
var value = "hello";
//value应该存在
expect(value).to.exist;
//value的数字类型应该是一个字符串
expect(value).to.be.a("string");
//value值应该等于"hello"
expect(value).to.equal("hello");
//value值不等于"你好"
expect(value).to.not.equal("你好");
//value的长度应该为5
expect(value).to.have.length(5);
})
})进入test_lib文件夹下,执行mocha expect.js运行测试脚本,因为我们这五个断言都是真的,所以测试通过。
同样我们也可以定义一个数字,使用expect断言来判断数字的区间
var number = 3;
//判断number是否在3~5之间的数
expect(number).to.be.at.most(5);
expect(number).to.be.at.least(3);
//判断number是否在1~3之间的数
expect(number).to.be.within(1, 3);五、编写测试脚本
Mocha的作用是运行测试脚本,首先必须学会写测试脚本。所谓"测试脚本",就是用来测试源码的脚本。
1、测试返回结果是否正确
(1)创建被测试的项目lib/demo-1.js
class Demo {
subtotal(unitPrice, quantity) {
return unitPrice * quantity;
}
}
module.exports = Demo;(2)创建测试脚本test/demo-1.test.js
通常,测试脚本与所要测试的源码脚本同名,但是后缀名为.test.js(表示测试)或者.spec.js(表示规格)。比如,demo-1.js的测试脚本名字就是demo-1.test.js。
//demo-1.test.js
const chai = require("chai");
const expect = chai.expect;
var Demo = require("../lib/demo-1");
var demo = new Demo();
describe("Demo",()=>{
it("单价10块钱的3件商品小计金额应该是30块",function(){
var subtotal = demo.subtotal(10,3);
expect(subtotal).to.equal(30);
})
})2、异步操作测试setTimeout
(1)Mocha默认每个测试用例最多执行2000毫秒,如果到时没有得到结果,就报错。对于涉及异步操作的测试用例,这个时间往往是不够的,需要用-t或--timeout参数指定超时门槛。
进入lib/demo-1.js,编写异步等待方法,规定2秒之后返回结果
waitTwoSecond(data,callback){
setTimeout(function(){
callback(data);
},2000);
}(2)进入test/demo-1.test.js,编写测试脚本
//异步操作测试
//mocha不会等到异步执行结束以后进行测试,而是直接运行得到测试结果
it("一段时间以后返回数据",function(done){
demo.waitTwoSecond("hello",function(data){
expect(data).to.equal("hello")
done(); //只有调用done方法才能等待调用结束以后测试
//mocha默认的等待时间是2秒,上述操作超过两秒,报错
//运行命令mocha demo-1.test.js -t 5000重置等待时间解决
})
})另外,上面的测试用例里面,有一个done函数。it块执行的时候,传入一个done参数,当测试结束的时候,必须显式调用这个函数,告诉Mocha测试结束了。否则,Mocha就无法知道,测试是否结束,会一直等到超时报错。如果把这行删除,则mocha不会等到异步执行结束以后进行测试,而是直接运行得到测试结果,返回的断言结果始终为真。
(3)虽然测试用例中规定2秒返回结果,但是实际运行时间肯定超过2秒,所以,需要用-t或--timeout参数,改变默认的超时设置。
mocha demo-1.test.js -t 5000上面命令将测试的超时时限指定为5000毫秒。
3、测试接口数据https
接口地址https://douban.uieee.com/v2/m...
(1)lib/demo-1.js
引入https模块
var https = require("https");定义fetchData方法
fetchData(api,callback){
var requestUrl = `https://douban.uieee.com/v2/movie/${api}`;
https.get(requestUrl,function(res){
var responseData = ""
res.setEncoding("utf8")
res.on("data",function(chunk){
responseData += chunk
})
res.on("end",function(){
callback(JSON.parse(responseData))
})
})
}(2)test/demo-1.test.js
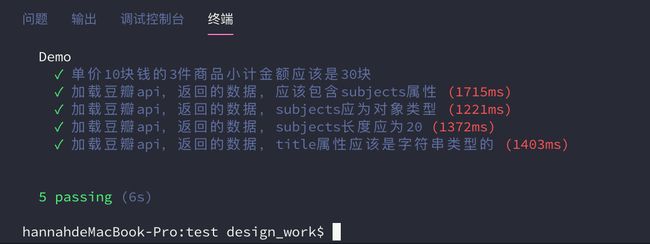
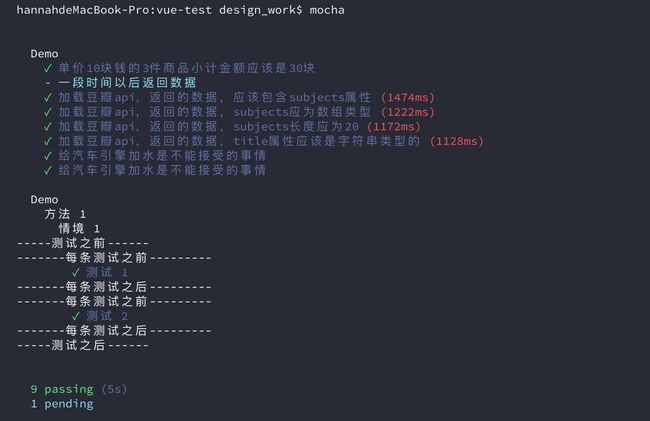
it("加载豆瓣api,返回的数据,应该包含subjects属性",function(done){
demo.fetchData("top250",function(data){
expect(data).to.have.property("subjects");
done();
})
})
it("加载豆瓣api,返回的数据,subjects应为对象类型", function (done) {
demo.fetchData("top250", function (data) {
var subjects = data.subjects;
expect(subjects).to.be.a("array");
done();
})
})
it("加载豆瓣api,返回的数据,subjects长度应为20", function (done) {
demo.fetchData("top250", function (data) {
var subjects = data.subjects;
expect(subjects).to.have.length(20);
done();
})
})
it("加载豆瓣api,返回的数据,title属性应该是字符串类型的", function (done) {
demo.fetchData("top250", function (data) {
var title = data.subjects[0].title
expect(title).to.be.a("string");
expect(title).to.equal("肖申克的救赎")
done();
})
})(3)运行结果
4、测试异常
(1)lib/demo-1.js
engine(fuel){
if(fuel !== "gas"){
throw new Error("not accept")
}
}(2)test/demo-1.test.js
//定义一个异常
it("给汽车引擎加水是不能接受的事情",function(){
expect(function(){
demo.engine("water");
}).to.throw("not accept")
})//另外一种写法
it("给汽车引擎加水是不能接受的事情",function(){
expect(demo.engine.bind(demo,"water")).to.throw("not accept")
})(3)测试结果
六、运行多个测试
1、直接使用mocha命令运行test子目录中的测试脚本
Mocha默认运行test子目录里面的测试脚本。所以,一般都会把测试脚本放在test目录里面,然后执行mocha就不需要参数了。
所以在控制台中输入mocha,只会执行test子目录里的测试脚本demo-1.test.js和demo.js,而test_lib中的assert.js、expect.js、should.js则不会执行。
运行结果:
2、执行test子目录下面所有的测试用例
这时可以看到,test子目录里面的测试脚本执行了。但是,你打开test子目录,会发现下面还有一个test/test_lib子目录,里面还有三个测试脚本assert.js、expect.js、should.js,并没有得到执行。Mocha默认只执行test子目录下面第一层的测试用例,不会执行更下层的用例。
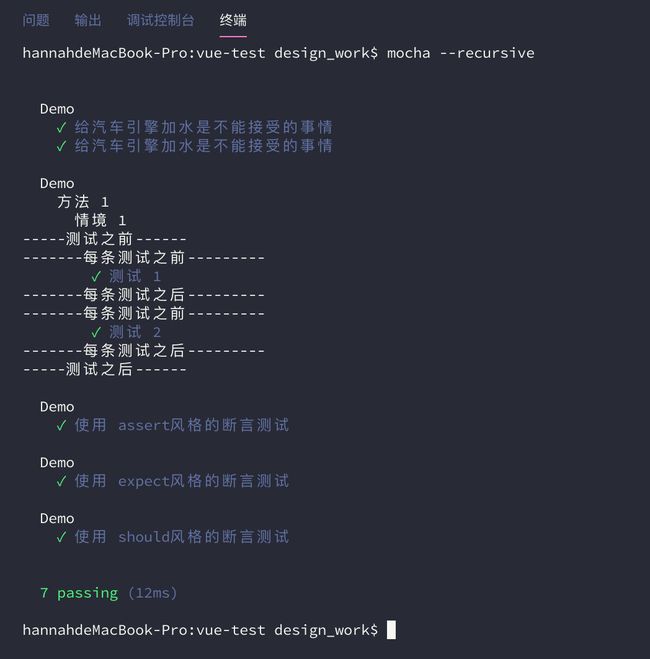
为了改变这种行为,就必须加上--recursive参数,这时test子目录下面所有的测试用例,不管在哪一层,都会执行。
mocha --recursive运行结果:
3、执行多个测试脚本
mocha命令后面紧跟测试脚本的路径和文件名,可以指定多个测试脚本。
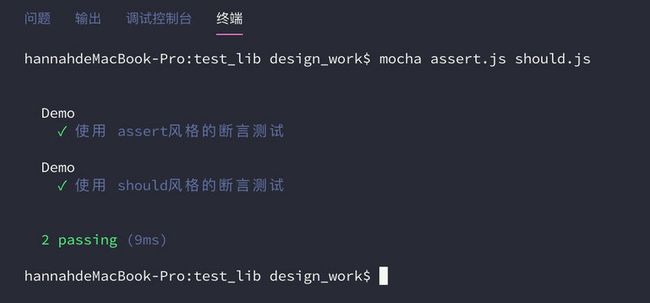
进入tets_lib目录下,运行assert.js和should.js两个测试脚本
mocha assert.js should.js运行结果
七、测试用例管理
1、only表示只运行某个测试套件或测试用例。
大型项目有很多测试用例。有时,我们希望只运行其中的几个,这时可以用only方法。describe块和it块都允许调用only方法,表示只运行某个测试套件或测试用例。
it.only("单价10块钱的3件商品小计金额应该是30块",function(){
var subtotal = demo.subtotal(10,3);
expect(subtotal).to.equal(30);
})运行结果:只运行了添加only方法的测试脚本
2、skip表示跳过指定的测试套件或测试用例。
it.skip("一段时间以后返回数据",function(done){
demo.waitTwoSecond("hello",function(data){
expect(data).to.equal("hello")
done(); //只有调用done方法才能等待调用结束以后测试
//mocha默认的等待时间是2秒,上述操作超过两秒,报错
//运行命令mocha demo-5.js -t 5000重置等待时间解决
})
})运行结果:跳过了添加skip方法的测试脚本
八、ES6测试
1、ES5写法
src/add.js
function add(x, y) {
return x + y;
}
module.exports = add;test/demo-2.test.js
const chai = require("chai");
const expect = chai.expect;
var Add = require("../src/add.js");
describe('加法函数的测试', function () {
it('1 加 1 应该等于 2', function () {
expect(Add(1, 1)).to.be.equal(2);
});
});
运行命令
mocha运行结果
2、ES6写法
test/demo-2.test.js
const chai = require("chai");
const expect = chai.expect;
var Add = require("../src/add.js");
describe('加法函数的测试', function () {
it('1 加 1 应该等于 2', function () {
expect(Add(1, 1)).to.be.equal(2);
});
});
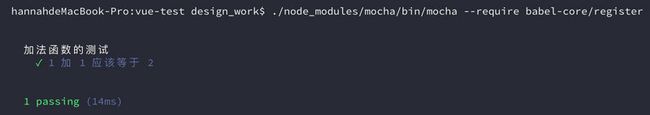
如果测试脚本是用ES6写的,那么运行测试之前,需要先用Babel转码。
(1)安装Babel
npm install babel-core babel-preset-es2015 --save-dev(2)在项目目录下面,新建一个.babelrc文件:
{
"presets": [ "es2015" ]
}运行命令
./node_modules/mocha/bin/mocha --require babel-core/register运行结果
九、测试报告
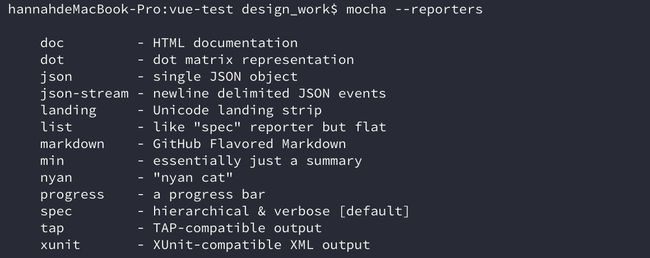
运行 mocha --reporters可以显示所有内置的报告格式。
1、spec格式
--reporter参数用来指定测试报告的格式,默认是spec格式。
mocha
等同于
mocha --reporter spec运行结果:
2、tap格式
mocha --reporter tap运行结果:
3、HTML格式
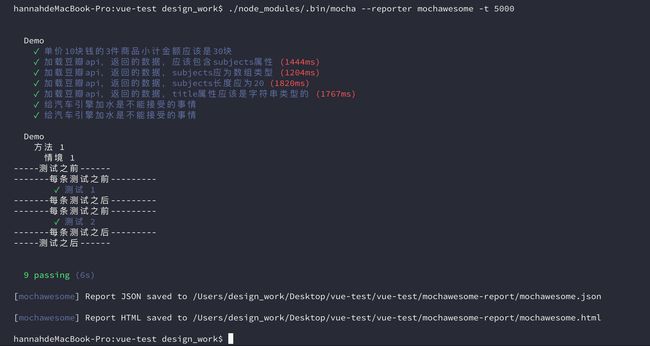
使用mochawesome模块,可以生成漂亮的HTML格式的报告。
(1)安装mochawesome模块
npm install --save-dev mochawesome(2)执行测试命令
./node_modules/.bin/mocha --reporter mochawesome上面代码中,mocha命令使用了项目内安装的版本,而不是全局安装的版本,因为mochawesome模块是安装在项目内的。
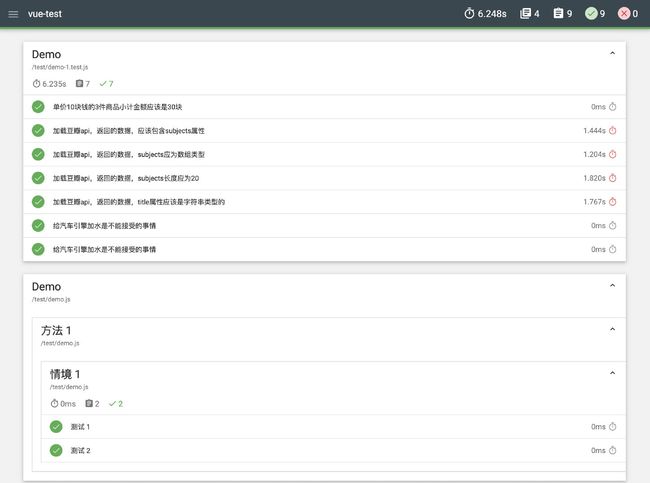
(3)运行结果:
(4)测试结果报告在mochaawesome-reports子目录生成。
(5)在浏览器中浏览html格式的测试报告
十、生成测试文件
Mocha支持从测试用例生成规格文件。
1、Markdown格式
mocha demo-1.test.js --recursive -R markdown > spec.md上面命令根据test目录的demo-1.test.js测试脚本,生成一个规格文件spec.md。-R markdown参数指定规格报告是markdown格式。
2、HTML格式
mocha demo-1.test.js --recursive -R doc > spec.html上面命令根据test目录的demo-1.test.js测试脚本,生成一个规格文件spec.html.
十一、在浏览器中测试
除了在命令行运行,Mocha还可以在浏览器运行。
1、首先,使用mocha init命令在指定目录生成初始化文件。
mocha init vue-test运行上面命令,就会在vue-test目录下生成index.html文件,以及配套的脚本和样式表。
Mocha
2、新建一个源码文件add.js
function add(x, y) {
return x + y;
}
module.exports = add;3、新建一个测试脚本tests.js
var expect = chai.expect;
describe('加法函数的测试', function () {
it('1 加 1 应该等于 2', function () {
expect(add(1, 1)).to.be.equal(2);
});
it('任何数加0等于自身', function () {
expect(add(1, 0)).to.be.equal(1);
expect(add(0, 0)).to.be.equal(0);
});
});4、然后,把这个文件,以及断言库chai.js,加入index.html。
Mocha
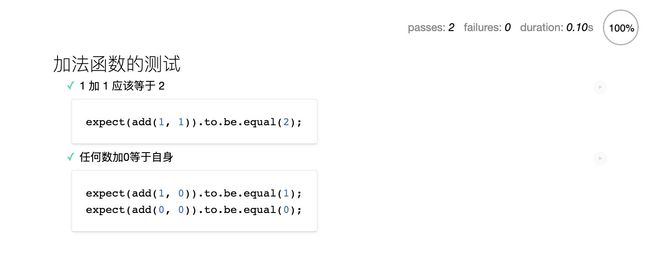
5、现在,在浏览器里面打开index.html,就可以看到测试脚本的运行结果。
参考文档
mocha官网
测试框架 Mocha 实例教程 by 阮一峰
https://juejin.im/entry/5941e...
【前端单元测试入门01】Mocha与chai
https://www.jianshu.com/p/aa5...
vue项目中添加单元测试
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_...
vue官网-单元测试模块