在上篇文章中看过了使用Parrallel.For、Parael.Foreach在效率上给我们带来的提高。本文就来如何终止循环、线程局部变量 进行说明。
Thread-Local Variables
首先我们来看下线程局部变量,是的我们也许一直在想我们如何去定义一个线程局部变量呢。先看段顺序执行的代码:
[TestMethod()]
public void NormalSequenceTest()
{
int[] nums = Enumerable.Range(0, 1000000).ToArray();
long total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length;i++ )
{
total += nums[i];
}
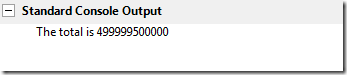
Console.WriteLine("The total is {0}", total);
}执行结果:
我们再来看这段代码:
[TestMethod()]
public void NormalParallelTest()
{
int[] nums = Enumerable.Range(0, 1000000).ToArray();
long total = 0;
Parallel.For(0,nums.Length,i=>
{
total += nums[i];
});
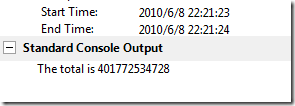
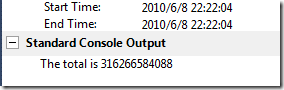
Console.WriteLine("The total is {0}", total);
}执行结果:
再运行下:
也许我们会感到很奇怪为什么会这样呢,其实我们想想就可以明白了,total变量是公共的,而我们的程序是多个线程的加,而多个线程之间是不能把数据共享的。其实我们需要的是在每个线程中计算出一个和值,然后再进行累加。我们来看看线程局部变量:
[TestMethod()]
public void ThreadLocalTest()
{
int[] nums = Enumerable.Range(0, 1000000).ToArray();
long total = 0;
Parallel.For(0, nums.Length, () => 0, (j, loop, subtotal) =>
{
subtotal += nums[j];
return subtotal;
},
(x) => Interlocked.Add(ref total, x)
);
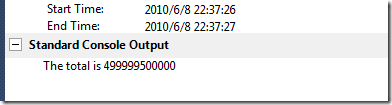
Console.WriteLine("The total is {0}", total);
} 我们再看下执行结果:
下面说下泛型方法Parallel.For
public static ParallelLoopResult For(int fromInclusive, int toExclusive, Func localInit, Func body, Action localFinally); TLocal:线程变量的类型;第一个、第二个参数就不必多说了,就是其实值跟结束值。
localInit:每个线程的线程局部变量初始值的设置;
body:每次循环执行的方法,其中方法的最后一个参数就是线程局部变量;
localFinally:每个线程之后执行的方法。
相信这样解释后就能明白了为什么需要线程局部变量了,也明白如何使用线程局部变量了。我们再看看在Parallel.Foreach
[TestMethod()]
public void ForeachThreadLocalTest()
{
int[] nums = Enumerable.Range(0, 1000000).ToArray();
long total = 0;
Parallel.ForEach(nums,()=>0,(member,loopState,subTotal)=>
{
subTotal += member;
return subTotal;
},
(perLocal)=> Interlocked.Add(ref total,perLocal)
);
Console.WriteLine("The total is {0}", total);
} 要注意的是,我们必须要使用ForEach
Break、Stop
首先我们可以看到在Parallel.For的一个重载方法中:
public static ParallelLoopResult For(int fromInclusive, int toExclusive, Action body); 在委托的最后一个参数类型为ParallelLoopState,而ParallelLoopState里面提供给我们两个方法:Break、Stop来终止迭代,而Break跟Stop的区别是什么呢?我们来看两段代码:
private void StopLoop()
{
var Stack = new ConcurrentStack();
Parallel.For(0, 10000, (i, loopState) =>
{
if (i < 1000)
Stack.Push(i.ToString());
else
{
loopState.Stop();
return;
}
});
Console.WriteLine("Stop Loop Info:\n elements count:{0}", Stack.Count);
}
private void BreakLoop()
{
var Stack = new ConcurrentStack();
var stringList = this.ConstructString(10000);
Parallel.For(0, stringList.Count, (i, loopState) =>
{
Stack.Push(stringList[i]);
if (stringList[i].Contains("999"))
{
loopState.Break();
}
});
Console.WriteLine("Stop Loop Info:\n elements count:{0}", Stack.Count);
}
private List ConstructString(int number)
{
var stringList = new List();
Parallel.For(0, number - 1, i =>
{
stringList.Add(i.ToString());
});
return stringList;
} 测试方法:
[TestMethod()]
public void LoopTest()
{
StopLoop();
BreakLoop();
}来看看运行结果吧:
其实这个例子只是想告诉大家,为什么第一个用Stop,第二个用Break。原因是:第一个例子中我只关心的是循环的迭代变量i的值,我只要1000个字符串,而不去管这1000个字符串是什么东西。所以当达到1000时,我们就立刻停止所有的迭代包括其他线程上的。而第二个方法中我们是判断的源中的某个索引值,这个时候有可能较早的元素还未处理。
其实在我们调用过Stop或者Break方法后,循环上的其他的线程可能还会运行一段时间,其实我们可以通过IsStopped属性来判断循环是在其他线程上停止。Foreach中的使用就不再看了,跟For是一样的。
总结
在本文中,主要介绍了如何停止循环、使用线程局部变量。在里面我们看到了我们在使用并行开发时,有很多东西是需要我们去注意的。在下文中将介绍下异常处理、取消循环等话题。
出处: http://henllyee.cnblogs.com/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明。