希望解决的问题
1. 在一些高流量、高IO的WAF中,是如何对规则库(POST、GET)中的字符串进行多正则匹配的,是单条轮询执行,还是多模式并发执行 2. Snort是怎么组织、匹配高达上千条的正则规则库的,怎样保证效率和准确性的平衡 3. 状态机、Aho-Corasick算法的核心思想 4. 怎么进行多模正则匹配的编程实现
相关学习资料
http://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E7%A1%AE%E5%AE%9A%E6%9C%89%E9%99%90%E7%8A%B6%E6%80%81%E8%87%AA%E5%8A%A8%E6%9C%BA http://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E9%9D%9E%E7%A1%AE%E5%AE%9A%E6%9C%89%E9%99%90%E7%8A%B6%E6%80%81%E8%87%AA%E5%8A%A8%E6%9C%BA http://stblog.baidu-tech.com/?p=418 http://blog.csdn.net/beta2/article/details/5698171 http://www.cnblogs.com/xudong-bupt/p/3433506.html http://blog.csdn.net/sealyao/article/details/4560427 http://www.cppblog.com/yefeng/archive/2009/12/06/102671.html http://www.wanghd.com/blog/2012/09/27/aho-corasicksuan-fa/ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aho-Corasick http://yzmduncan.iteye.com/blog/1217014 http://www.openfoundry.org/tw/tech-column/8265--snort-
http://www.freebuf.com/articles/system/37507.htm
目录
1. 状态机简介 2. 多模匹配算法简介 3. Aho-Corasick算法学习 4. 多模正则匹配的编程学习 5. Snort高速规则匹配原理学习
1. 状态机简介
状态机的概念非常复杂,我们着重理解其中的一些核心知识概念
0x1: 确定有限状态自动机
在计算理论中,"确定有限状态自动机"或"确定有限自动机"(deterministic finite automaton, DFA)是一个能实现状态转移的自动机。 对于一个给定的属于该自动机的状态(往往是初始状态)和一个属于该自动机字母表的字符(输入参数),它都能根据事先给定的转移函数转移到下一个状态(这个状态可以是先前那个状态,即状态自循
环)
"确定有限状态自动机"的数学定义:
组成 1. 非空有限的"状态集合": Q 2. 输入字母表: A(非空有限的字符集合) 3. 转移函数: F 它接收两个参数: 1) 当前状态: q 2) 输入字母: a 返回一个结果: 一个新的状态: p 4. 一个开始状态(初始状态): i 5. 一个接收状态的集合: S 这个所谓的"接收状态的集合"可以这么理解,当所有的输入字母表都输入完毕后,状态机停留在最后一个状态的位置,这个状态位置是否达到了我们的要求(即是否接收) (结合一下正则匹配的过程来理解,正则匹配最后输出的匹配位置其实就是一种状态机的"终点转移位置") 它们一起组成状态机的5元组 {Q、A、F、i、S}
"确定有限状态自动机"的工作方式
确定有限状态自动机从起始状态开始,一个字符接一个字符地读入一个字符串string,并根据给定的转移函数一步一步地转移至下一个状态。在读完该字符串后,如果该自动机停在一个属于S的接受
状态,那么它就接受该字符串,反之则拒绝该字符串 看到这里,我们可以很自然地想到这个理论的利用场景: 1) 正则的匹配(思考状态机的逐字符读取、以及最终状态的判定) 2) 目标字符串的搜索
0x2: 非确定有限状态自动机
在计算理论中,非确定有限状态自动机或非确定有限自动机(NFA)是对每个状态和输入符号对可以有多个可能的下一个状态的有限状态自动机。这区别于确定有限状态自动机(DFA),它的下一个可能
状态是唯一确定的。
非确定有限自动机有时被称为有限类型的子移位(subshift)。非确定有限状态自动机可推广为概率自动机,它为每个状态转移指派概率。
"非确定有限状态自动机"的性质
机器开始于任意初始状态并"逐个读取"来自它的符号表的符号的字符串。 自动机使用状态转移函数:F来使用当前状态: q,和刚读入的符号:a或空串: null来确定下一个状态: p 如果在自动机完成读取的时候,它处于接受状态,则称 NFA 接受了这个字符串,否则称为它拒绝了这个字符串
0x3: 有限状态自动机的原理性伪码表示
关于确定有限状态自动机、非确定有限状态自动机,除了数学上的定义理解,我们还可以从伪代码的角度去理解
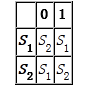
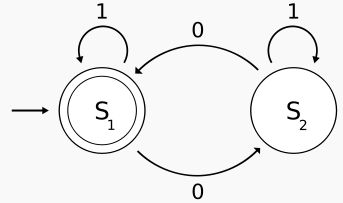
while(读取输入字母表的下一个字符: a) { curState: q = 状态转移函数F(p, a); lastState: p = curState: q; } function 状态转移函数F(p, a) { if(condition_1) {} else if(condition_2) {} else if ... else {} //condition_x: 状态和字符的笛卡儿积关系,以矩阵的形式表示了映射关系 }
这两张状态转移图很形象地说明了状态机的逻辑意义,我们可以很容易地将这个概念思想应用到编程实践中
2. 多模匹配算法简介
了解了状态机的基本概念之后,我们可以继续学习多模匹配算法的基本概念了
多模式匹配在这里指的是在"一个字符串"中寻找"多个模式字符字串"的问题。 一般来说,给出一个长字串和很多短模式字符串,如何最快最省的求出哪些模式字符串出现在长字串中是我们需要思考的(因为基本上大多数情况下是在给定的长字串中出现我们给的模式字串的其中
几个) 该算法的应用领域有很多,例如: 1) 关键字过滤 2) 入侵检测 3) 病毒检测 4) 分词等 多模匹配算法是一个概念性的称呼,它的具体实现有很多,例如: 1) Trie树 2) AC算法 3) WM算法
简单来说,多模匹配就是要我们实现下面的功能,用demo代码进行演示
php
public function CheckSql($db_string)
{
$express_1 = "/([A-Za-z])?(where)(.)*?(concat|char|(chr.*){4,}|case|floor|#.*|--)/i";
$express_2 = "/([A-Za-z])?(where).*(union)(\s)*(all)?(\s)*select(\s)*((\d|null),(\s)*){2,}/i";
$express_3 = "/[^0-9a-z@\._-]{1,}(sleep|benchmark|load_file|outfile|(user\(\).*){1,})[^0-9a-z@\.-]{1,}/i";
$express_4 = "/([A-Za-z])?(where)(.|\s)*?(or|and|like)('\d'(=|>|<|like)'\d')/i";
if (preg_match($express_1, $db_string) || preg_match($express_2, $db_string) || preg_match($express_3, $db_string) ||
preg_match($express_4, $db_string))
{
//die("detected!!!");
return 1;
}
else
{
//die("good");
return 0;
}
}
?>
文章 介绍了多模算法的基本原理,以及一种算法的实现: dictmatch
3. Aho-Corasick算法学习
0x1: Aho-Corasick(AC)算法的总体流程
1. 建立树过程 1) 根据关键字(即待搜索模式集合)建立起一颗Tire树 2) 设置第一层的不匹配的转移节点 3) 设置其余的不匹配转移节点 4) 设置Tire树的各个节点的输出字符(即当到达某个状态时表明某个模式匹配成功,需要输出对应的字符串) 5) 初始化状态到根节点 2. 查找过程 1) 逐个输入待搜索字符串 2) 根据状态机的转移结果判断是否有模式匹配成功
关于算法的原理、流程可以参阅文章头部给出的链接,我就不做重复的引用了。在这里,我想依托一个PHP的AC算法的DEMO,一边分析源代码,一边解析AC算法的流程
将下列文件放置在web目录下,即可运行
0x2: Aho-Corasick(AC)代码分析
demo.php
php /* 这个AC算法小程序的架构如下: 1) demo.php: UI显示层 2) php.ac.app.php: 业务实现层,封装了实现逻辑 3) php.ac.search.php: AC多模式匹配的搜索查找算法的实现逻辑 4) php.ac.pretreatment.php: AC算法的预处理(生成树)的实现逻辑 */ //引入文件 include("php.ac.app.php"); $obj = new ACAppClass(); echo "
=================
"; $words2 = array("microsome", "cytochrome", "cytochrome P450 activity", "gibberellic acid biosynthesis", "GA3", "cytochrome P450", "oxygen binding",
"AT5G25900.1", "protein", "RNA", "gibberellin", "Arabidopsis", "ent-kaurene oxidase activity", "inflorescence", "tissue"); $text2 = "The ga3 mutant of Arabidopsis is a gibberellin-responsive dwarf. We present data showing that the ga3-1 mutant is deficient in ent-kaurene
oxidase activity, the first cytochrome P450-mediated step in the gibberellin biosynthetic pathway. By using a combination of conventional map-based
cloning and random sequencing we identified a putative cytochrome P450 gene mapping to the same location as GA3. Relative to the progenitor line,
two ga3 mutant alleles contained single base changes generating in-frame stop codons in the predicted amino acid sequence of the P450. A genomic
clone spanning the P450 locus complemented the ga3-2 mutant. The deduced GA3 protein defines an additional class of cytochrome P450 enzymes. The
GA3 gene was expressed in all tissues examined, RNA abundance being highest in inflorescence tissue."; $res2 = $obj->findWordsInArray($words2, $text2); var_dump($res2); ?>
php.ac.app.php
php // 引入文件 include("php.ac.search.php"); class ACAppClass { private $showtimeFlag; // 是否显示运行时间,false:不显示;true:显示,默认为false /** * @function 构造函数 * @param * @return */ public function ACAppClass() { $this->showtimeFlag = false; } /** * @function 从字符串中查找单个关键词 * @param string word 关键词 * @param string text 被查找的字符串 * @return Array */ public function findSingleWord($word, $text) { try { if(strlen(trim($word))==0) { throw new Exception("Key word's content is empty."); } } catch(Exception $e) { echo $e->getMessage(); return; } //复用了从字符串中查找多个字符串的代码逻辑(单个是多个的一种特殊情况) $arr = array(trim($word)); return $this->findWordsInArray($arr, $text); } /** * @function 从字符串中查找多个关键词 * @param Array words 关键词数组 * @param string text 被查找的字符串 * @return Array */ public function findWordsInArray($words, $text) { $len = count($words); try { if($len==0) { throw new Exception("Array of keywords is empty."); } } catch(Exception $e) { echo $e->getMessage(); return; } if($this->showtimeFlag) { $starttime = $this->getmicrotime(); } /* 构造AC算法"搜索关键词字典树",主要有两个主要步骤 1) 状态转移树的建立(将需要查找的关键字模式转换为一个树的形式) 2) 失效转移树的建立(在状态转移树的基础上进行完善添加当出现转移失败时,状态应该跳转到的下一个状态) 3) 状态输出的建立(在到达某个状态的时候,可以表明某个模式匹配成功,可以输出某个字符串) */ $tree = new AhoCorasick(); try { for ($i=0; $i<$len; $i++) { if(trim($words[$i])=="") { throw new Exception("Key word's content is empty."); } /* 添加搜索词 将搜索词(待匹配的模式)转化到状态转移树的形式中 */ $tree->add(trim($words[$i])); } } catch(Exception $e) { echo $e->getMessage(); return; } //向状态转移Tire树中添加"失效转移"部分 $tree->prepare(); //状态转移Tire树准备完毕 $res = array(); /* 开始在目标字符串中进行多模式搜索 本质上来说: 搜索的过程是以目标字符串为输入参数,逐个输入来使状态在Tire树中进行状态转移,最终得到输出字符串 */ $obj = $tree->search($text); while($obj->hasNext()) { $result = $obj->next(); $res = array_unique(array_merge($res, $result->getOutputs())); } if($this->showtimeFlag) { $endtime = $this->getmicrotime(); echo "
run time is: ".($endtime-$starttime)."ms
"; } return $res; } /** * @function 从文件中查找关键词 * @param string $keyfile 关键词所在的文件名称及路径 * @param string $textfile 被查找的内容所在的文件名称及路径 * @return Array */ public function findWordsInFile($keyfile, $textfile){ try{ if(!is_file($keyfile) || !is_file($textfile)){ throw new Exception("Can not find the file."); } }catch(Exception $e){ echo $e->getMessage(); return; } // 搜索词所在的文件内容为空时,抛出异常 try{ if(strlen(trim(file_get_contents($keyfile)))==0){ throw new Exception("File's content is empty."); } }catch(Exception $e){ echo $e->getMessage(); return; } // 打开文件 $handle1 = fopen($keyfile, "r"); $handle2 = fopen($textfile, "r"); $arr = array(); $contents = ""; try{ while (!feof($handle1)) { $line = trim(fgets($handle1)); if(strlen($line)!=0){ $arr[] = $line; } } while (!feof($handle2)) { $line = trim(fgets($handle2)); if(strlen($line)!=0){ $contents .= $line; } } }catch(Excption $e){ echo $e->getMessage(); return; } // 关闭文件 fclose($handle1); fclose($handle2); return $this->findWordsInArray($arr, $contents); } /** * @function 获取时间戳,单位为毫秒 * @param * @return float */ function getmicrotime(){ list($usec, $sec) = explode(" ",microtime()); $value = (float)$usec*1000+(float)$sec; return round($value, 3); } } ?>
php.ac.search.php
php /** * @author: jessica.yang * @date: 2011-10-24 * @filename: php.ac.search.php * @description: Aho Corasick多模式匹配算法,简称AC算法,包含两个阶段,第一个是预处理阶段,即字典树的生成;第二个是搜索查找阶段,该文件完成第二阶段的搜索查找功能 */ // 引入文件 include("php.ac.pretreatment.php"); /** * @classname: AhoCorasick * @description: 用于实现AC多模式匹配的搜索查找算法 */ class AhoCorasick { private $root; // State对象,表示根节点 private $prepared; // boolean类型,表示搜索词是否装载完成。如果为true,则表示加载完成,并且不能再加载搜索词 private $arr_keys; // Array对象,存放第一级的搜索词 /** * @function 构造函数 * @param * @return */ public function AhoCorasick() { $this->root = new State(0); //构造字典树的单个状态节点 $this->root->setFail($this->root); //设置根节点的失效值,对于根节点来说,它的失效转移节点就是它自己本身 $this->prepared = false; //搜索词还未装载完成 $this->arr_keys = array(); //存放第一级搜索词 } /** * @function 获取根节点对象 * @param * @return State */ public function getRoot() { return $this->root; } /** *@function 添加搜索词 *@param string $keywords 要查找的搜索词 *@return **/ public function add($keywords="") { // 如果装载标志为true,则禁止再加载搜索词 try { if ($this->prepared) { throw new Exception("can't add keywords after prepare() is called."); } } catch(Exception $e) { echo $e->getMessage(); return; } // 如果搜索词不是字符串类型,或者内容为空,则返回 try { if(!is_string($keywords) || strlen(trim($keywords)) == 0) { throw new Exception("Added keywords is not string type, or content is empty."); } } catch(Exception $e) { echo $e->getMessage(); return; } $keywords = trim($keywords); $words = $this->str_split_utf8($keywords); // 把搜索词按字符为单位转换成单字符数组(因为Tire树的每个节点必须是单字符) $this->arr_keys = array_unique(array_merge($this->arr_keys, $words)); // 设置第一层级的搜索字符 /* 将搜索词的单字符数组逐个"压入"状态转移Tire树中 同时接收函数返回的: 添加完搜索词之后的最后一个State值(这个State代表某个模式匹配成功,可以输出对应的字符串) */ $lastState = $this->root->extendAll($words); /* 向最后一个State值中添加输出内容 这里要着重理解: lastState代表某个匹配模式匹配成功到了最后,即表示匹配成功,则对应的这个状态即为状态机中的"可接受状态",这时可输出对应的搜索字符串 */ $lastState->addOutput($keywords); } /** *@function 加载搜索词add()完成之后调用 *@param *@return **/ public function prepare() { $this->prepareFailTransitions(); //进行失效转移处理之后就不允许继续增加节点了,如果需要再次增加节点,则需要重头构建这个Tire树 $this->prepared = true; } /** *@function 设置字典树中每个State节点的失效值 *@param *@return **/ private function prepareFailTransitions() { $q = array(); //存放第一层级的所有搜索词 foreach($this->arr_keys as $value) { if(is_null($this->root->get($value))) { // 如果搜索词不存在于第一层级,则添加,并且设置失效值为根节点State对象 $this->root->put($value, $this->root); } else { // 设置第一层级的失效值为根节点State对象,并且把搜索词对应的State值添加到$q数组中 $this->root->get($value)->setFail($this->root); array_push($q, $this->root->get($value)); } } die(var_dump($q)); // 设置所有State节点的失效值 while(!is_null($q)) { $state = array_shift($q); // 将数组$q第一个State值移出该数组,并返回移出的State值 if(is_null($state)) // 如果取出的$state内容为空,则结束循环 { break; } $keys = $state->keys(); // 获取$state值对应的下一级所有搜索词 $cnt_keys = count($keys); for($i=0; $i<$cnt_keys; $i++) { $r = $state; $a = $keys[$i]; $s = $r->get($a); array_push($q, $s); $r = $r->getFail(); /* 递归查找失效值,直到根节点为止 这里要重点理解一下: 类似KMP算法,同样采用实效实效函数推进的方法,假设当前状态为s,s的一个孩子结点的根结点根节点 t状态,如果当前的失效函数已知为f(s),则显然地,f(t)必定是f(s)的孩子结点状态,所要做的就是在状态f(s)处寻找接受字 符同s->t下一个状态,如果能找到,那就是f(t),否则说明到s处匹配串的前缀长度太长,需缩减,所以需要找到更短的后缀, 于是就到f(s)处继续,如果仍然找不到,则转到f(f(s))处,形成状态的递归转移 */ while(is_null($r->get($a))) { //这是一个递归的过程,从根节点到当前节点,逐个向下,减少字符长度,并同时回溯查中啊是否有能够包含这个字符串的子节点 $r = $r->getFail(); } $s->setFail($r->get($a)); $s->setOutputs(array_unique(array_merge($s->getOutputs(), $r->get($a)->getOutputs()))); } } } /** *@function 查找函数 *@param string words 被查找的字符串 *@return Searcher **/ public function search($words) { return new Searcher($this, $this->startSearch($words)); } /** *@function 查找函数 *@param string words 被查找的字符串 *@return SearchResult **/ public function startSearch($words) { // 加载未完成时,不允许进行搜索查找 try { if (!$this->prepared) { throw new Exception("Can't start search until prepare()."); } } catch(Exception $e) { echo $e->getMessage(); return; } // 转换被查找的"字符串"为"单字符数组"。因为我们知道,AC搜索算法的过程是将被查找的字符串逐个的输入状态转换树,并根据转移状态结果进行判断 $arr_words = $this->str_split_utf8($words); // 搜索查找后结果集 $res = $this->continueSearch(new SearchResult($this->root, $arr_words, 0)); return $res; } /** *@function 真正的查找函数 *@param SearchResult lastResult SearchResult对象 *@return SearchResult or NULL **/ public function continueSearch($lastResult) { // 如果lastResult搜索结果对象为null,则返回 if(is_null($lastResult)) { return NULL; } $words = $lastResult->words; // 被查找的字符数组 $state = $lastResult->lastMatchedState; // 开始查找的State值 $start = $lastResult->lastIndex; // 开始查找的位置 $len = count($words); for($i=$start; $i<$len; $i++) { $word = $words[$i]; // 获取单个字符 // 如果获取的搜索词不存在,则递归转向失效值进行搜索,直到根节点为止 while (is_null($state->get($word))) { $state = $state->getFail(); if($state===$this->root) { break; } } if(!is_null($state->get($word))) { // 获取搜索词对应的State值,如果有输出内容,则输出 $state = $state->get($word); if (count($state->getOutputs())>0) { return new SearchResult($state, $words, $i+1); } } } return NULL; } /** *@function 字符串转换成字符数组,单位是字符 *@param string str 转换的字符串内容 *@return Array **/ function str_split_utf8($str) { $split=1; $array = array(); for($i=0; $i < strlen($str); ) { $value = ord($str[$i]); /* 处理宽字节的情况 http://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/UTF-8 1) 对于UTF-8编码中的任意字节B,如果B的第一位为0,则B为ASCII码,并且B独立的表示一个字符; 2) 如果B的第一位为1,第二位为0,则B为一个非ASCII字符(该字符由多个字节表示)中的一个字节,并且不为字符的第一个字节编码; 3) 如果B的前两位为1,第三位为0,则B为一个非ASCII字符(该字符由多个字节表示)中的第一个字节,并且该字符由两个字节表示; 4) 如果B的前三位为1,第四位为0,则B为一个非ASCII字符(该字符由多个字节表示)中的第一个字节,并且该字符由三个字节表示; 5) 如果B的前四位为1,第五位为0,则B为一个非ASCII字符(该字符由多个字节表示)中的第一个字节,并且该字符由四个字节表示; */ if($value > 127) { if($value >= 192 && $value <= 223) {//双字节 $split=2; } else if($value >= 224 && $value <= 239) {//三字节 $split=3; } else if($value >= 240 && $value <= 247) {//四字节 $split=4; } } else {//单字节 $split=1; } $key = NULL; //根据当前字节长度来生成相应的单字符 for($j = 0; $j < $split; $j++, $i++ ) { $key .= $str[$i]; } //http://www.w3school.com.cn/php/func_array_push.asp array_push( $array, $key ); } return $array; } } /// /** * @classname: SearchResult * @description: 搜索结果类,用于存储搜索查找后的结果集 */ class SearchResult { var $lastMatchedState;// State对象,最后匹配的State值 var $words;// Array对象,被搜索的内容 var $lastIndex;// int类型,最后出现的位置 /** * @function 构造函数 * @param State state State对象 * @param Array words 被查找的字符串 * @param int index 查找位置 * @return */ public function SearchResult($state, $words=array(), $index=0) { $this->lastMatchedState = $state; $this->words = $words; $this->lastIndex = $index; } /** * @function 获取输出的内容 * @param * @return Array */ public function getOutputs() { return $this->lastMatchedState->getOutputs(); } /** * @function 获取查找的位置 * @param * @return int */ public function getLastIndex() { return $this->lastIndex; } } //// /** * @classname: Searcher * @description: 搜索类 */ class Searcher { private $tree;// AhoCorasick对象 private $currentResult;// SearchResult对象 /** * @function 构造函数 * @param AhoCorasick tree AhoCorasick对象 * @param SearchResult result SearchResult对象 */ public function Searcher($tree, $result) { $this->tree = $tree; $this->currentResult = $result; } /** * @function hasNext 用于判断是否还有值存在 * @param * @param boolean true表示有值 false表示无值 */ public function hasNext() { return !is_null($this->currentResult); } /** * @function next 获取下一个值 * @param * @param 如果有值则返回SearchResult对象,否则返回NULL */ public function next() { if (!$this->hasNext()){ return NULL; } $result = $this->currentResult; $this->currentResult = $this->tree->continueSearch($this->currentResult); return $result; } } ?>
php.ac.pretreatment.php
php /** * @author: jessica.yang * @date: 2011-10-24 * @filename: php.ac.pretreatment.php * @description: Aho Corasick多模式匹配算法,简称AC算法,包含两个阶段,第一个是预处理阶段,即字典树的生成;第二个是搜索查找阶段,该文件完成第一阶段的预处理功能 */ /** * @classname: State * @description: 状态类,用于表示字典树中的每一个状态节点 */ class State { private $depth; // int类型,表示每一个状态对象的深度,从0开始表示 private $edgeList; // 类似于列表,用于包含该状态下所包含的下一级所有State对象 private $fail; // State对象,表示状态对象失效之后要跳转的地方 private $outputs; // array对象,存放某一状态下可以输出的内容 /** * @function State 构造函数 * @param int depth 状态所处的深度 * @return */ public function State($depth) { $this->depth = $depth; //初始化状态当前状态节点的深度 /* 存储State对象下一级对应的所有State内容,以数组形式存储 这里要着重理解的是: 树是在数据结构是以一种链表的形式存储的,链表中的每个节点都要存储指向它的所有子节点的指针,或者以一种数组的形式存储(只要能达到可寻址的目的即可) */ $this->edgeList = new DenseEdgeList(); $this->fail = NULL; //初始化当前状态节点发生失效时需要转移到的下一个节点(即失效转移指针) $this->outputs = array(); //初始化当前状态节点的输出字符串 } /** *@function extend 添加单个搜索词 *@param char character 单个搜索词,或者一个字母、数字、或者一个汉字等 *@return State **/ public function extend($character) { if (!is_null($this->edgeList->get($character))) { return $this->edgeList->get($character); } /* 新建一个新的State节点,作为当前节点的下级State节点 */ $nextState = new State($this->depth+1); $this->edgeList->put($character, $nextState); return $nextState; } /** *@function extendAll 添加搜索词 *@param array contents 搜索词数组 *@return State **/ public function extendAll($contents) { $state = $this; $cnt = count($contents); /* 循环遍历搜索词单字符数组,逐个压入Tire树 */ for($i=0; $i < $cnt; $i++) { // 如果搜索的关键词存在,则直接返回该关键词所处的State对象,否则添加该关键词 if(!is_null($state->edgeList->get($contents[$i]))) { //如果搜索词在当前节点中,则返回当前State节点 $state = $state->edgeList->get($contents[$i]); } else { //如果搜索词不在当前节点中,则新建一个新的State节点作为当前节点的下级节点,并返回新的State节点,接下来就继续在新的State节点中插入搜索词 $state = $state->extend($contents[$i]); } } //完成状态转移树的填充,最终的效果就是所有的搜索词都被填充到了一个层级的树状转移图中 return $state; } /** * @function 计算搜索词的总长度 * @param * @return int */ public function size() { $keys = $this->edgeList->keys(); $result = 1; $length = count($keys); for ($i=0; $i<$length; $i++){ $result += $this->edgeList->get($keys[$i])->size(); } return $result; } /** * @function 获取单个关键词所处的State对象 * @param char character * @return State */ public function get($character) { $res = $this->edgeList->get($character); return $res; } /** * @function 向State对象中添加下一级的搜索词及对应的State值 * @param char character * @param State state * @return */ public function put($character, $state) { $this->edgeList->put($character, $state); } /** * @function 获取State对象下一级的所有关键词 * @param * @return Array */ public function keys() { return $this->edgeList->keys(); } /** * @function 获取State对象失效时对应的失效值 * @param * @return State */ public function getFail() { return $this->fail; } /** * @function 设置State对象失效时对应的失效值(即失效时需要转移到的下一个状态) * @param * @return */ public function setFail($state) { $this->fail = $state; } /** * @function 向State对象的outputs中添加输出内容 * @param * @return */ public function addOutput($str) { array_push($this->outputs, $str); } /** * @function 获取State对象的输出内容 * @param * @return Array */ public function getOutputs() { return $this->outputs; } /** * @function 设置State对象的输出内容 * @param * @return */ public function setOutputs($arr=array()){ $this->outputs = $arr; } } //// /** * @classname: DenseEdgeList * @description: 存储State对象下一级对应的所有State内容,以数组形式存储 */ class DenseEdgeList { private $array; // State对象,包含对应的搜索词及State值 /** * 构造函数 */ public function DenseEdgeList() { $this->array = array(); } /** * @function 从链表存储形式的内容转为数组存储形式的内容 * @param SparseEdgeList list * @return DenseEdgeList */ public function fromSparse($list) { $keys = $list->keys(); $newInstance = new DenseEdgeList(); for($i=0; $i < count($keys); $i++) { $newInstance->put($keys[$i], $list->get($keys[$i])); } return $newInstance; } /** * @function 获取搜索词对应的State值 * @param char word * @return 如果存在则返回对应的State对象,否则返回NULL */ public function get($word) { if(array_key_exists($word, $this->array)) { return $this->array["$word"]; } else { return NULL; } } /** * @function 添加搜索词及对应的State值到数组中 * @param char word 单个搜索词 * @param State state 搜索词对应的State对象 * @return */ public function put($word, $state) { $this->array["$word"] = $state; } /** * @function 获取所有的搜索词 * @param * @return Array */ public function keys() { return array_keys($this->array); } } /// /** * @classname: SparseEdgeList * @description: 存储State对象下一级对应的所有State内容,以链表形式存储 */ class SparseEdgeList{ private $head;// Cons对象 /** * 构造函数 */ public function SparseEdgeList() { $this->head = NULL; } /** * @function 获取搜索词对应的State值 * @param char word * @return 如果存在则返回对应的State对象,否则返回NULL */ public function get($word) { $cons = $this->head; while(!is_null($cons)){ if ($cons->word === $word){ return $cons->state; } $cons = $cons->next; } return NULL; } /** * @function 添加搜索词及对应的State值到链接中 * @param char word 单个搜索词 * @param State state 搜索词对应的State对象 * @return */ public function put($word, $state){ $this->head = new Cons($word, $state, $this->head); } /** * @function 获取所有的搜索词 * @param * @return Array */ public function keys() { $result = array(); $c = $this->head; while(!is_null($c)){ array_push($result, $c->word); $c = $c->next; } return $result; } } /** * @classname: Cons * @description: 用于SparseEdgeList生成链表时表示的节点对象 */ class Cons { var $word;// 单个搜索词 var $state;// State对象 var $next;// Cons对象 /** * 构造函数 */ public function Cons($word, $state, $next){ $this->word = $word; $this->state = $state; $this->next = $next; } } ?>
上面是一个AC算法的PHP实现,为了更加清晰的说明这个算法的思想,我们接下来看几张图来进一步理解一下
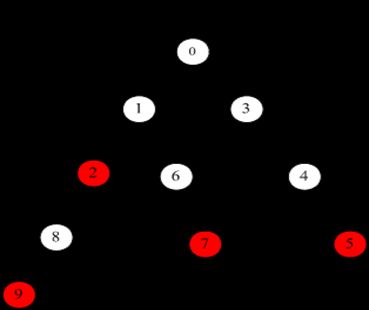
下图是多模式he/ she/ his /hers构成的一个确定性有限状态机,做几点说明:
1. 该状态机优先按照实线标注的状态转换路径进行转换,当所有实线标注的状态转换路径条件不能满足时,按照虚线的状态转换路径进行状态转换。如:状态0时,当输入h,则转换到状态1;输入s,则转换到状态3;否则转换到状态0。
2. 匹配过程如下:从状态0开始进行状态转换,主串作为输入。如主串为:ushers,状态转换的过程是这样的:
3. 当状态转移到2,5,7,9等红色状态点时,说明发生了模式匹配。
如主串为:ushers,则在状态5、2、9等状态时发生模式匹配,匹配的模 式串有she、he、hers
0x3: 关于AC算法的注意点
1. AC算法是一款非常优秀的算法,在Unix的fgrep中使用的就是这个算法 2. 要理解AC算法,我们的重点应该放到它的Tire树的建立上,将搜索词转换为一棵以字母顺序为索引关系的层次树(这里所谓的字母顺序就是转移方向) 3. 失效转换的思想和KMP算法的思想很类似,核心的思想是避免不必要的回溯,让搜索始终沿着向前的方向,尽最大可能减小时间复杂度 4. 输出字符串的个数和搜索词的数量是一致的,每个搜索词都会对应一条状态转移路径,这条路径的最后一个State状态会包含一个输出字符串 5. AC算法的时间复杂度为: O(m+n+z),是线性的,所以非常高效
4. 多模正则匹配的编程学习
这里还有一些关于多模匹配算法的代码学习资料
http://sourceforge.net/projects/multifast/ http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/12383/Aho-Corasick-string-matching-in-C http://search.cpan.org/~dankogai/Regexp-Trie-0.02/lib/Regexp/Trie.pm
5. Snort入门学习
我们之前说过,AC算法是一种多模匹配算法,它适用于一次匹配需要同时匹配多个模式的应用场景。我们在有了AC算法的原理基础之后,接下来可以继续深入学习一下Snort高速多规则匹配的原理了
0x1: Snort简介
Snort是一款开源的NIPS(Network Intrusion Prevention System)、NIDS(Network Intrusion Detection System) http://www.snort.org/ NIDS(Network Intrusion Detection System)的功能点: 1) 实时流量分析 2) IP数据包Log记录 3) 协议分析 4) 内容搜索 4.1) 单模式搜索 4.2) 多模式搜索 5) 对攻击行为的检测 1) 扫描器探针 2) 操作系统指纹探测 3) CGI(common gateway interface)探测 4) 缓冲区溢出 5) SMB探测 6) 端口遍历扫描 Snort的工作模式 1) 嗅探模式(Sniffer): 对网络数据进行实时嗅探并显示 2) 数据包记录(packet logger): 对捕获到的数据包记录都磁盘上 3) 网络入侵检测(Network Intrusion Detection): 对流量进行监控,并应用用户定义的规则进行模式匹配,Snort会根据用户的定义采取相应的相应动作action
0x2: Snort的相关架构
Snort是一种以攻击特征为基础的的入侵检测系统,利用事先建立好的的已知的攻击资料特征码,来比对接收到的封包内容是否含有攻击行为。若符合特征码则触发相对应的动作
Snort是一种以攻击特征为基础的的入侵检测系统,利用事先建立好的的已知的攻击资料特征码,来比对接收到的封包内容是否含有攻击行为。若符合特征码则触发相对应的动作
1. Packet Decoder(封包解码器) 当Snort取得原始的网络封包后,第一件事即将封包置入"封包解码器"模组中进行封包解码 2. Preprocessors(预处理器) Snort的预处理器为外挂式程序(plusin)的架构,主要功能在于重新标准化网络流量,如 1) 重组封包 2) 分段、重组TCP Stream 3) 编码的规范化、转换等 以使得网络流量能精确的被侦测引擎(Detection Engine)解析以及匹配特征码 3. Detection Engine(侦测模组) Detection Engine(侦测模组)主要功能在于"规则分析"与"特征侦测",Detection Engine将Snort的规则文件引入,并按照规则文件中的规则进行比对(单模比对、或者多模比对)。一旦发现
有符合规则文件定义的行为,即触发该规则文件中所定义的处理方式,当所有的规则都不符合时,即会丢弃该封包。 Snort的规则文件分为两个部分: 1) 规则表头(Rule-Header) 1.1) 决定封包比对来源范围(例如限定比对哪些范围的IP) 1.2) 比对成功时的动作(log或者直接丢弃) 2) 规则选项(Rule-Options) 利用一至多个关键字设定欲侦测的流量特征,规则选项按照功能可以分为下列4个部分 2.1) Meta-data: 设定欲显示的相关讯息,如当规则触发时所要产生的讯息 2.2) Payload: 用来比对封包内容的规则 2.3) Non-Payload: 用来比对各种协定的栏位值 2.4) Post-Detection: 当封包内容与规则匹配时,除了在规则表头(Rule-Header)所定义的动作外,另外会触发的动作
Example:
alert tcp any any → any 5432 (msg:"someone access PSQL command:SELECT"; content:"select";) alert(处理方式): 产生警示的 log tcp(来源通讯协定): 侦测 TCP 的封包 any(来源 IP): 侦测任何的来源 IP any(来源 port): 侦测任何的来源端口 any(目的 IP): 侦测任何的目的 IP 5432(目的 port): 侦测 5432 端口的封包 ...(规则匹配內容): 若符合内容含有"select"的字串,则将 msg 后的字串记录起来
0x3: Snort安装、配置
http://linuxmantra.com/2010/10/install-snort-2-9-on-rhel-5.html http://www.boyunjian.com/do/article/snapshot.do?uid=net.chinaunix.blog%2Fuid-522598-id-1764389.html 1. 下载准备环境 yum -y install mysql-bench mysql-devel php-mysql gcc pcre-devel php-gd gd glib2-devel gcc-c++ libpcap-devel cd /root mkdir snort cd snort wget http://www.snort.org/downloads/867 wget http://www.snort.org/downloads/860 2. 安装Snort(在安装过程中需要解决依赖库的问题方可正常安装) tar -zvxf snort-2.9.0.5.tar.gz cd snort-2.9.0.5 ./configure --with-mysql --enable-dynamicplugin make && make install 遇到报错: "ERROR! dnet header not found, go get it from http://code.google.com/p/libdnet/ or use the --with-dnet-* options, if you have it installed in an
unusual place" tar -xzvf libdnet-1.12.tgz cd libdnet-1.12.tgz ./configure make && make install 如果遇到报错 "ERROR! daq_static library not found, go get it from http://www.snort.org/" cd /root/snort/ tar -xzvf daq-0.5.tar.gz cd daq-0.5 ./configure make && make install 如果遇到报错: "ERROR! Libpcap library version >= 1.0.0 not found. Get it from http://www.tcpdump.org" cd /root/snort/ wget http://www.tcpdump.org/release/libpcap-1.1.1.tar.gz tar -zvxf libpcap-1.1.1.tar.gz cd libpcap-1.1.1 ./configure -prefix=/usr make && make install 3. 配置Snort groupadd snort useradd -g snort snort -s /sbin/nologin (添加一个不允许登录的虚拟账户) mkdir /etc/snort mkdir /etc/snort/rules mkdir /etc/snort/so_rules mkdir /var/log/snort chown snort:snort /var/log/snort cd /root/snort/snort-2.9.0.5/etc cp * /etc/snort cd /root/snort/ tar -xzvf snortrules-snapshot-2.8.tar.gz cd ./rules cp * /etc/snort/rules cp ../so_rules/precompiled/CentOS-5.0/i386/2.6.1.5/* /etc/snort/so_rules wget https://www.snort.org/downloads/893 --no-check-certificate vim /etc/snort/snort.conf 修改如下 将 RULE_PATH 和 SO_RULE_PATH 改为绝对路径 var RULE_PATH /etc/snort/rules var SO_RULE_PATH /etc/snort/so_rule 配置数据库(在同一个文件中) 在配置数据库信息之前先生成相应的数据库 mysql -uroot -p111 create database snort; use snort; source /root/snort/snort-2.9.0.5/schemas/create_mysql; grant all privileges on snort.* to snort@'localhost' identified by 'snort'; flush privileges; (在.conf中添加信息) vim /etc/snort/snort.conf output database: log, mysql, user=snort password=snort dbname=snort host=localhost 4. 启动Snort
1) 监听模式(Sniffer)
监听所有来往的封包,但不做攻击模式的比对
snort -v
2) NIDS(网络型入侵检测系统)
让Snort不仅监听所有来往的封包,并会对封包中是否包含攻击模式进行比较
snort -u snort -g snort -c /etc/snort/snort.conf
0x3: Snort捕获数据的可视化显示
和我们之前学习Kippo蜜罐的学习中,将捕获到的数据进行可视化展示很重要,对于Snort来说,可以使用BASE(Basic Analysis and Security Engine)进行数据可视化展示
http://freecode.com/projects/base-php
要使用BASE,需要准备一些环境:
1) ADOdb(PHP连接数据库的通用接口) 2) BASE需要绘图和Email的相关功能 2.1) Mail 2.2) Image_Color 2.3) Image_Canvas 2.4) Image_Graph
pear list
BASE本质上就是一些PHP文件组成的脚本
http://sourceforge.net/projects/secureideas/
启动Snort的检测模式
snort -u snort -g snort -c /etc/snort/snort.conf
用WVS进行模拟攻击
后记
1. 本篇文章完成了对AC算法、Snort的入门学习 2. 我们现在已经知道,Snort、WAF高速正则规则匹配使用的是AC算法 3. 下一步准备研究一下Snort的开源源代码,从源代码的角度来深入学习一下Snort的检测原理、入侵检测相关模块,AC算法在产品中的应用
Copyright (c) 2014 LittleHann All rights reserved