Google Colab 免费GPU服务器使用教程
本文来源:https://blog.csdn.net/cocoaqin/article/details/79184540
一、前言
不知道大家是否为了寻找免费GPU服务器而焦头烂额。 近些天,谷歌推出了Google Colab(Colaboratory)
链接:https://colab.research.google.com/
官方对其的说明是:
Colaboratory 是一个研究项目,可免费使用。
划重点,最重要的特点是 免费GPU!免费GPU!免费GPU!
虽然不确定这个项目是不是永久的
但这无疑给纠结在是否花大量钱租用GPU服务器进行研究的个人研究者带去了重磅福利!
经过查阅资料与亲自实践,特把相关教程写成博文分享给大家。
由于博主水平能力有限,难免有错误,欢迎指正哈!
二、Google Colab特征
Colaboratory 是一个 Google 研究项目,旨在帮助传播机器学习培训和研究成果。它是一个 Jupyter 笔记本环境,不需要进行任何设置就可以使用,并且完全在云端运行。
Colaboratory 笔记本存储在 Google 云端硬盘中,并且可以共享,就如同您使用
Google 文档或表格一样。Colaboratory 可免费使用。
利用Colaboratory ,可以方便的使用Keras,TensorFlow,PyTorch等框架进行深度学习应用的开发。
三、开始使用
注意:使用google服务可能需要梯子
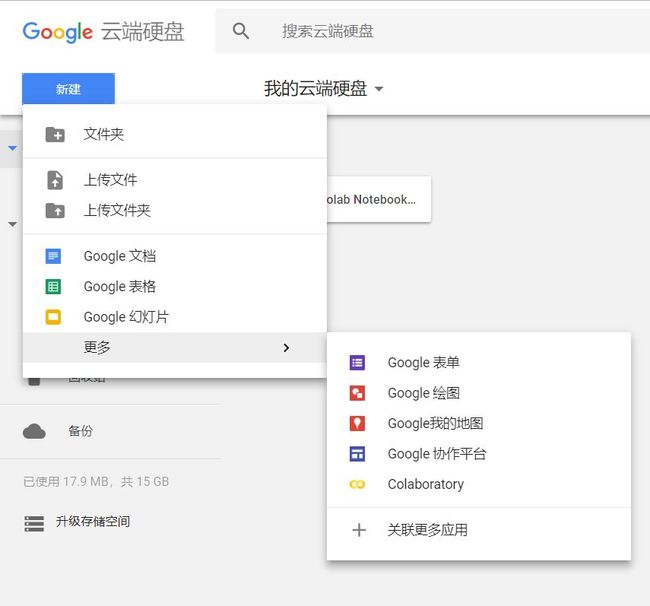
3.1在谷歌云盘上创建文件夹
当登录账号进入谷歌云盘时,系统会给予15G免费空间大小。由于Colab需要依靠谷歌云盘,故需要在云盘上新建一个文件夹。
选择新建文件夹,文件夹名称可自定义。
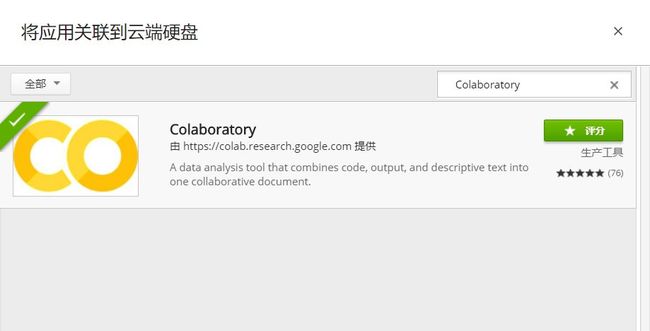
3.2创建Colaboratory
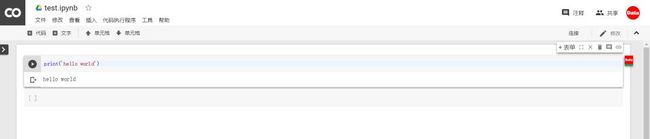
3.3创建完成
创建完成后,会自动生成一个jupyter笔记本,是不是很熟悉~
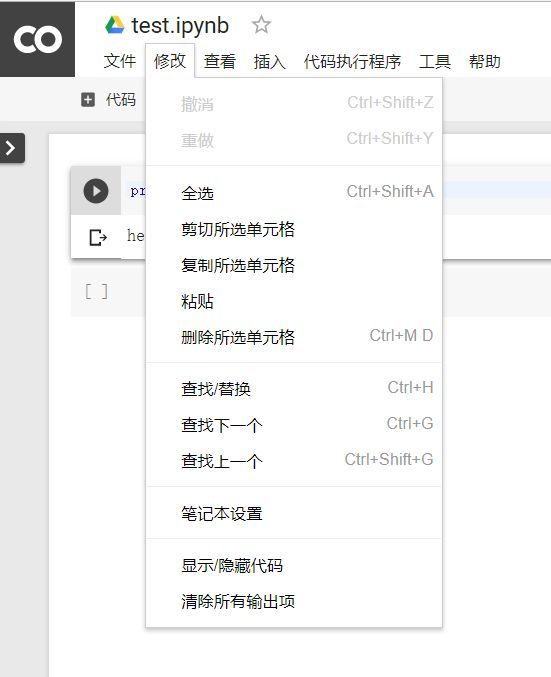
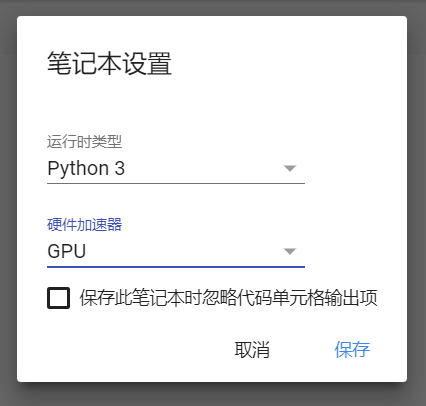
四、设置GPU运行
选择 修改-笔记本设置
将硬件加速器设置为GPU即可
五、运行.py文件
5.1安装必要库
输入相应代码,并执行(crtl+F9)
!apt-get install -y -qq software-properties-common python-software-properties module-init-tools
!add-apt-repository -y ppa:alessandro-strada/ppa 2>&1 > /dev/null
!apt-get update -qq 2>&1 > /dev/null
!apt-get -y install -qq google-drive-ocamlfuse fuse
from google.colab import auth
auth.authenticate_user()
from oauth2client.client import GoogleCredentials
creds = GoogleCredentials.get_application_default()
import getpass
!google-drive-ocamlfuse -headless -id={creds.client_id} -secret={creds.client_secret} < /dev/null 2>&1 | grep URL
vcode = getpass.getpass()
!echo {vcode} | google-drive-ocamlfuse -headless -id={creds.client_id} -secret={creds.client_secret}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
运行后,会出现以下提示
5.2 挂载云端硬盘
同上,输入下面命令,执行即可
!mkdir -p drive!google-drive-ocamlfuse drive -o nonempty1
2
5.3 安装Keras
同理,输入命令
!pip install -q keras1
5.4 Hello Mnist!
将代码粘入jupyter笔记本中,运行,即可开始奇妙的Google Colab之旅
https://github.com/keras-team/keras/blob/master/examples/mnist_cnn.py
'''Trains a simple convnet on the MNIST dataset.
Gets to 99.25% test accuracy after 12 epochs
(there is still a lot of margin for parameter tuning).
16 seconds per epoch on a GRID K520 GPU.
'''
from __future__ import print_function
import keras
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Flatten
from keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D
from keras import backend as K
batch_size = 128
num_classes = 10
epochs = 12
# input image dimensions
img_rows, img_cols = 28, 28
# the data, shuffled and split between train and test sets
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
if K.image_data_format() == 'channels_first':
x_train = x_train.reshape(x_train.shape[0], 1, img_rows, img_cols)
x_test = x_test.reshape(x_test.shape[0], 1, img_rows, img_cols)
input_shape = (1, img_rows, img_cols)
else:
x_train = x_train.reshape(x_train.shape[0], img_rows, img_cols, 1)
x_test = x_test.reshape(x_test.shape[0], img_rows, img_cols, 1)
input_shape = (img_rows, img_cols, 1)
x_train = x_train.astype('float32')
x_test = x_test.astype('float32')
x_train /= 255
x_test /= 255
print('x_train shape:', x_train.shape)
print(x_train.shape[0], 'train samples')
print(x_test.shape[0], 'test samples')
# convert class vectors to binary class matrices
y_train = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train, num_classes)
y_test = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test, num_classes)
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(32, kernel_size=(3, 3),
activation='relu',
input_shape=input_shape))
model.add(Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(128, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
model.add(Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax'))
model.compile(loss=keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy,
optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adadelta(),
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(x_train, y_train,
batch_size=batch_size,
epochs=epochs,
verbose=1,
validation_data=(x_test, y_test))
score = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, verbose=0)
print('Test loss:', score[0])
print('Test accuracy:', score[1])
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
是不是很有意思呢!
References: