145. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal(二叉树的后序遍历)两种解法(C++ & 注释)
145. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal(二叉树的后序遍历)
- 1. 题目描述
- 2. 递归(Recursion)
- 2.1 解题思路
- 2.2 实例代码
- 3. 迭代(Iteration)
- 3.1 解题思路
- 3.2 实例代码
1. 题目描述
给定一个二叉树,返回它的 后序 遍历。
题目链接:中文题目;英文题目
2. 递归(Recursion)
2.1 解题思路
我推荐大家把二叉树的三种遍历方式一起看了,对比理解,加深记忆(链接更新中,可先到个人主页查看):
- 二叉树三种遍历实现串讲(前中后序遍历) - 推荐;
- Binary Tree Preorder Traversal(二叉树的前序遍历);
- Binary Tree Inorder Traversal(二叉树的中序遍历);
递归方法非常的简单,首先我们先来看看后序遍历的顺序:

后序遍历和中序遍历比较相似,不同的是后序遍历走完左边,再走右边,最后才打印当前节点,所以整个递归访问顺序为:
postorderRecursion(root->left); // 往左走
postorderRecursion(root->right); // 往右走
ans.push_back(root->val); // 添加当前节点
2.2 实例代码
class Solution {
vector<int> ans;
void postorderRecursion(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return;
postorderRecursion(root->left);
postorderRecursion(root->right);
ans.push_back(root->val);
}
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
postorderRecursion(root);
return ans;
}
};
3. 迭代(Iteration)
3.1 解题思路
使用列队(Queue)实现迭代的方法和中序遍历是一样的,只是添加节点的顺序稍微有点区别(和递归保持一致),这里就不再赘述了,大家可以参考这里哒:Binary Tree Inorder Traversal(二叉树的中序遍历);
其实后序遍历的迭代使用stack会更加简单,这是因为后序遍历遵循“先进后得”的特点(先右后左添加节点),和stack“先进后出”的特点相匹配,使用stack的思路流程图如下,大家看一下就明白了啦,不难哒:
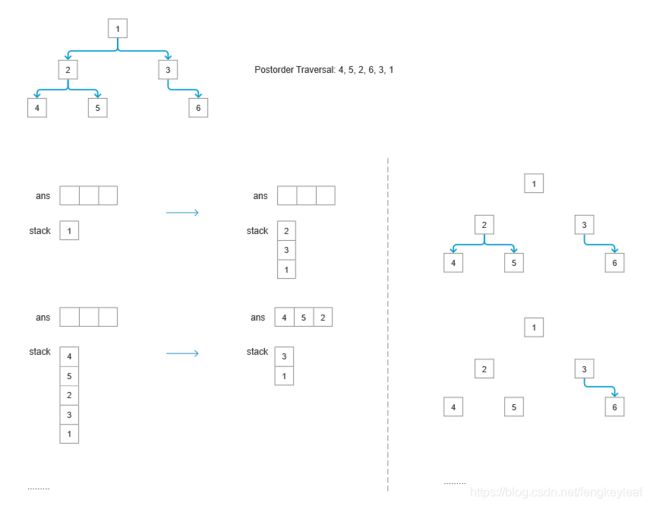
3.2 实例代码
class Solution {
vector<int> ans;
// 1. 使用queue的迭代
void iterationUsingQueue(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (q.size()) {
TreeNode* temp = q.front();
q.pop();
int len = q.size();
if (!temp->left && !temp->right) { ans.push_back(temp->val); continue; }
// 后序遍历顺序重组
if (temp->left) { q.push(temp->left); temp->left = nullptr; }
if (temp->right) { q.push(temp->right); temp->right = nullptr; }
q.push(temp);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { q.push(q.front()); q.pop(); }
}
}
// 2. 使用stack的迭代
void iterationUsingStack(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> s;
s.push(root);
while (s.size()) {
TreeNode* temp = s.top();
if (!temp->left && !temp->right) { ans.push_back(temp->val); s.pop(); continue; }
if (temp->right) { s.push(temp->right); temp->right = nullptr; }
if (temp->left) { s.push(temp->left); temp->left = nullptr; }
}
}
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return ans;
//iterationUsingQueue(root);
iterationUsingStack(root);
return ans;
}
};
